
History of English Language
Modern English
Industrial Revolution (1760-1830)

This process made a change from an agrarian and handicraft economy to one dominated by industry and machine manufacturing.
Thirteen Colonies (1607-1776)

The colonies were divided into three regions: New England, Middle, and Southern colonies.
On September 9, 1776, the Continental Congress officially changed the name of the 13 colonies from the “United Colonies” to the “United States of America.”
American Revolution (1775-1783)
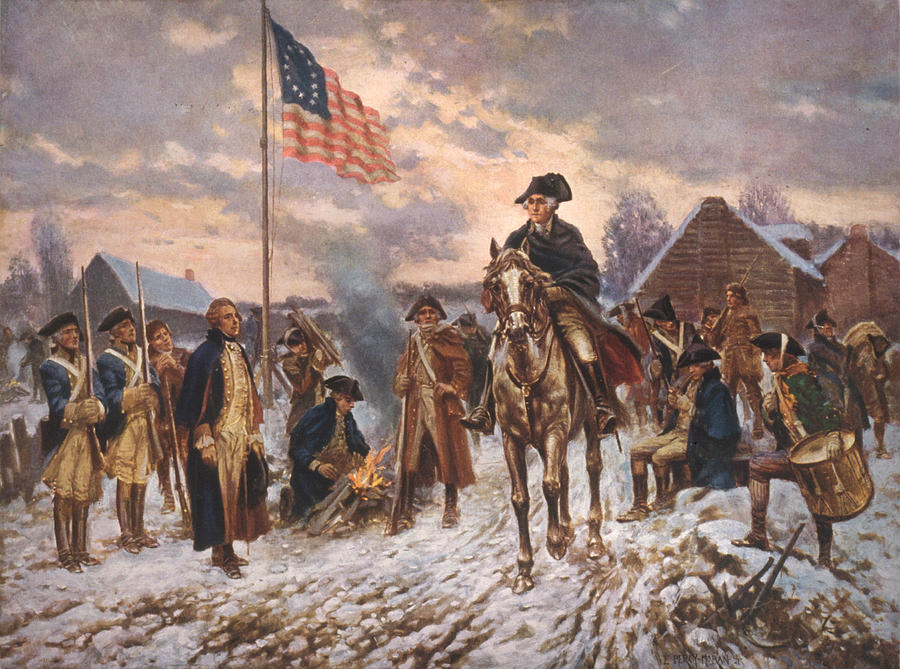

It was an insurrection
by American Patriots in the 13 colonies
to British rule, resulting in American
independence.
By 1776 Americans developed a new idiom with its own accent and vocabulary, but people still looked to England for proper linguistic guidance.

Ouisconsin with Wisconsin colour with color and musick with music.
French Revolution (1789)

It was a period of far-reaching social and political upheaval in France and its colonies beginning in 1789.
The English words from French were associated with goverment, law, art, literature, food and many other aspects of life.

Allée - Alley
Bon voyage - Good trip
En garde - On guard
British Empire (late 16th - early 18th centuries)

This period was made up of the colonies, protectorates, mandates and other territories which were controlled by the United Kingdom.

The main legacy of the british empire in the world is the English languagea
English
Varieties of English
Indian
New Zealand

Australian

Canadian

Caribbean
Old English
Indo European
Derived from a hypothetical language called Proto-Indo-European.

Eg. "dens" - tooth "duo" - two
Romans (750 BC-500 AD)

Roman Army invaded Britain in 43 A.D.
Romans official language was the Latin.
The romantization was the influence of Romans in other civilizations.
Normans (1066 AD)

The Normans colonized the southern Italy, Sicily, England, Wales, Scotland and Ireland.

The dialects spoken

Mercia

Kentish
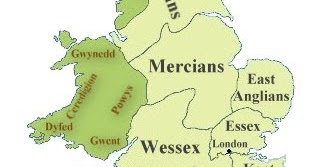
England: East Anglia and Wessex

Northumbian
Jutes (5th century)

A Germanic tribe with the Anglo and Saxon invaded Britain.
Old English (450-110 AD)
The earliest form of the English language spoken and written in Anglo-Saxon Britain.

Example
Middle English
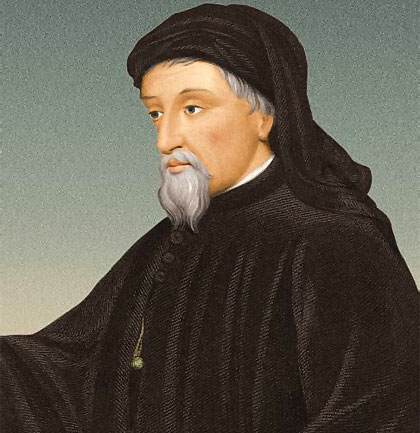

Geoffrey Chauser (1343-1400)
Known as the father of literature. He decide to write in English instead of French.

Canterbury Tales

Considered the 1st great work of English literature.

William Shakespeare
He is considered as one of the greatest writers.

He wrote: Romeo and Juliet, Hamlet, Macbeth, and over 150 sonnets.

Pentameter

Printing Press (1450)
Johannes Gutenberg is usually cited as the inventor
of the printing press.
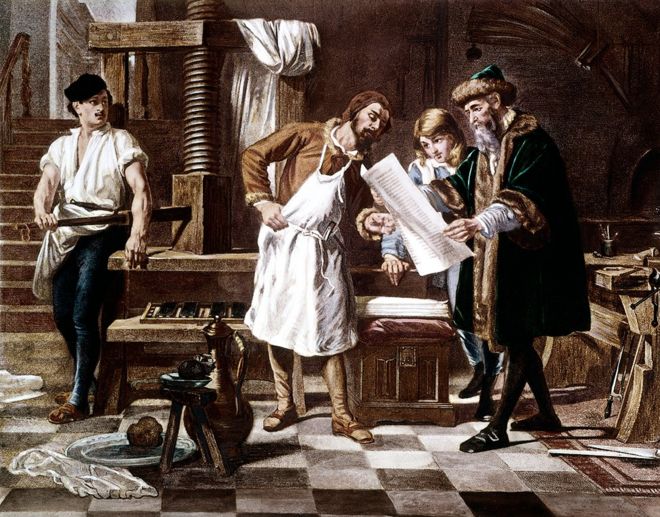

This technology
enabled the mass production
of books and the rapid dissemination of knowledge.

More people were able to access books, that's why the rules about the look of letters and spelling of words became more concrete.

Inquisition
It started in 12th-century with a group of institutions within the government system of the Catholic Church whose aim was to combat heresy.
