World War One
Main causes of ww1
1: Militarism: Belief in the power of armies and navies
to decide issues.
Example- Britain had the largest navy and
controlled the seas, but Germany
resented this and also wanted to
control the seas. They competed in
an arms race.
2: Alliances: Agreement between countries to
provide military services/assistance to each other
if one's attacked.
Triple Alliance: Alliance between
Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy.
Triple Entente: Made up of Great Britain,
France, and Russia.
3: Imperialism: Policy of obtaining political, economic
and social control over other countries and building an
empire.
Example- Both Germany and Britain were
fighting for more colonies and ended up bringing
all their colonies into war with them.
4: Nationalism: When people see their country
as being the best and put its interests/regards
ahead of other countries.
5: National Rivalries: European leaders used
their citizens feelins towards other nations to
stir up patriotism and nationalism. This created tension.
Immediate Cause
"The Spark that set off
the explosion"
The Spark: Archduke Franz Ferdinand,
heir to the throne of Austria, was assassinated
on June 28, 1914 in Sarajevo, Bosnia by Gavrillo
Princip, a member of the Serbian terrorist group
the Black Hand.
July 28th: Austria-Hungary declares War
on Serbia.
July 31st: Germany sends an ultimatum
to Russia to backdown and to France to
stay neutral; Russia does not reply and
France says "No" on August 1st.
August 2nd: Germany invades Luxembourg
and sends an ultimatum to Belgium to let
them in or face the consequences.
August 4th: Britain sends an ultimatum to
Germany to leave Belgium or else; Germany
does not answer. Britain declares war. WW1
officially begins.

Canada enters the war!
The Schlieffen Plan
Devised in 1981, by German General
Alfred Von Schlieffen. His strategy for
a 2 front war (France and Russia) was
still in place, with modification in 1914.
It's purpose was to put a quick end to
the war between France and Russia.
How the plan would have worked...
Germany would attack through the flatlands
of Holland and Belgium allowing for a rapid
advance and deployment of mass armies.
This plan had two major flaws...
- Rigid ideas for movement and timing
- Violating political treaties.
War Measures Act
Was a federal law adopted after the outbreak
of WW1.
This new law allowed the government to...
Control communication
systems.
Censor the media.
Organize the militia.
Control all transportation routes.
Control trade and production.
Arrest, detain, execute and
deport people.
Pass laws without the approval
of parliament.
No. 2 Construction Battalion
Was a segregated black battalion
led by mostly white leaders excpet for
chaplain Dr. William A. White. Their role
was to support front line by building roads,
bridges, digging trenches, repaired barbed wires.
War at Sea
Canada's navy increased in size. Convoys were
merchantt ships which were encircled by navy ships
to protect food and supplies.
Germans wanted to control the waters
so they could stop boats from getting to Britain
so they could starve them, and that was their key
to defeating Britain.
Sinking of Lusitania: Germans warned they would
sink passenger ships. At 2:15 pm Germans fired 2
torpedoes which hit the ocean liner. 18 min later
the ship sank to the bottom of the ocean. 1198
passengers sunk, 128 of them were Americans.
Propaganda
Type of messaging to recruit men aged 18-45
years old, "able bodied men". To raise money/
resources to sustain military campaign. To urge
conservation/ration. To encourage people to purchase
patriotic funds.
7 Tricks of Propaganda
Name Calling: Links person/
idea to a negative symbol.
Card Stacking: Technique that seeks
to manipulate audience by showing 1 side of story.
Testimonial: Public figure promotes something.
Plain folks: To convince audience spokesperson
is from humble origins, has their interests at heart.
Transfer: Links authority of something respected.
Glittering Generality: Vague statements using virtue
words opposite of name calling, links a person/
idea to symbolize.
Conscription
Forced military service.
French Canadians were against this.
British Canadians were for this.
Robert Borden was the PM of Canada
from 1911-1920.
Conscription was a big deal because
after the battle of Somme people did not
want to sign up.
Military Service Act: Conscription.
All men aged 18-45 able bodied men had
to go to war.
Military Voters Act: Gave the right to vote
to all Canadian soldiers.
Wartime Elections Act: Gave women the right
to vote on a mans behalf if he was at war.
How WW1 Ended
Germany's big move: Once the US entered the
war in 1917, Germany quickly moved all of its
troops towards the western front to defeat France.
Germany needed to end the war before the US fully
mobilized.
The Last Hundred Days: Germans were stopped
in France by the now experienced Canadian and
Allied troops. Aug 18th 1918 Canada began the
Allied Attack.
Armistice: On Nov 11, 1918, both sides ended
the battle in Armistice (they put down their weapons
at 11 am).
Treaty of Versailles
Wilson developed a plan called
"The Fourteen Points". Some terms
of the treaty were...
War guilt clause; Germany had to admit she
was responsible for starting the war.
Reparations: Germany had to pay for damages
caused to Belgium and France.
German army was restricted to 100,000 men.
New countries created were Yugoslavia, Poland,
Lituania, Estonia, Latvia, and Czechoslovakia.
This treaty sparked WW2

Trench Warfare
Type of fighting during WW1 in which
both sides dug trenches protected by
mines and barbed wire.
Trench: A long narrow ditch in ground that's
deeper than wind.
No man's land: Area between 2 lines
of attackers.
The Trench Cycle: Soldiers would rotate
between the 3 lines; front, support,
reserve line, and then a short period in
rest before beginning cycle again. Daily
life was spent with inspections, chores,
supplies and endless waiting.
Conditions in the trenches:
Unsanitary, smell was putrid, dead
bodies laying around. Lot's of critters
like rats who fed off decomposing bodies
and carried diseases. There was lice too.
Trench foot was a fungal infection of feet
caused by prolonged exposure to damp
and cold conditions, could lead to death.
Shell shock was a name given to soldiers
expierencing mental trauma/PTSD.

Sam Hughes
Minister of militia. He made decisions
about training/equipment. Two of his
choices; Ross Rifle, and McAdams Shovel,
were not succesful.
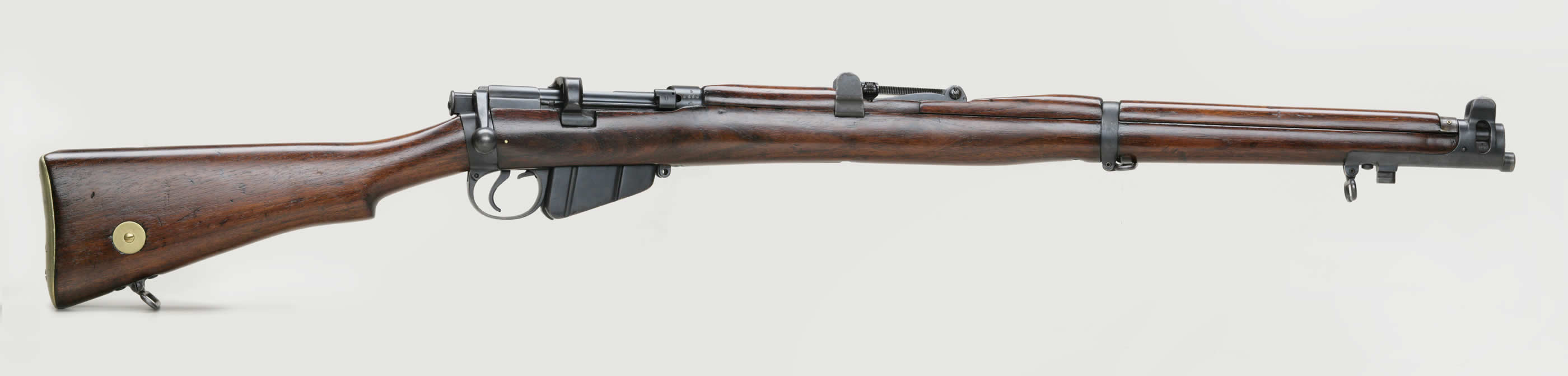

Ross Rifle- Did not work in muddy
conditions, and kept jamming.

McAdams Shield Spade
had a hole in the middle,
so did not shovel mud well.
WW1 Started on July
28th 1914. WW1 ended
at 11 am on Nov 11 1918.
The 4 Canadian Battles
Battle of Ypres
April 1915 in Ypres Belgium. First use of
of poison chlorine gas. Used over 5000
canisters of gas followed by 100,000
German soldiers. Canadians peed on
handkerchiefs and put them to their face
to neutralize the gas. 6000 Canadian
casualties in 48 hours. John McCrae served
as a doctor in Ypres.
Battle of the Somme
The battle with the most casualties. July
1916 in Beaumont Hamel, France along
the Somme River. It was meant to be the
big push to destroy the German lines.
Armoured tank was introduced and machine
guns. 24,000 Canadians died, 80,000
Canadians fought.
Battle of Vimy Ridge
Easter of April 1917, in Northern France.
General Arthur Currie led Canadians to
victory. Attacked using the "creeping barrage"
strategy. This battle brought out Canadian identity.
Was the first time Canada fought separate from
British units. 3600 Canadians dead. Canada won
the battle in 2 days.
Battle of Passchendale
Oct 1917 in Passchendale village. Soldiers
fought mud, mustard gas, and machine guns
as they seized the city. Heaviest rainfall in 30
years resulted in quicksan like mud. 16,000
Canadian casualties. 9 Canadians won the
Victoria Cross medal.
War in the Air
At the beginning of war ther was no
pilots/ planes. When planes were first introduced
they were used for scouting enemy territory.
Ace: A pilot who had five or more kills.
Dog Fights: A method of plane fighting pilots
used where they would chase enemy tails.
Pilots could not carry parachutes so they would be
encouraged to save the plane first not themselves.
Billy Bishop: The leading "Ace". He had 72 hits.
Red Baron: Counterpart. A German pilot named
Manfred Von Ritchthoften, he had 80 hits.
A lifespan of a pilot ws usually
arounf 3 weeks.
Canada's Homefront
Women took the roles of men.
Income tax was put on Canada to help
with war costs. This tax still remains today.
At home Canadians were encouraged to join
war, ration food, buy victory bonds, and patriotic funds.
Canadians joined war because of unemployment, and needed
money, forced to go due to peer pressure/propaganda.
Victory bonds were issued by the government
because they needed money during war.
Patriotic funds gave financial/social assitance to
soldiers' families.
Changing role of women
Women were unable to sign on as
soldiers, so they enlisted as nurses.
Women fought to change their right
to vote.
1916 Manitoba government gave certain
women the right to vote on their husbands
behalf.
The Famous Five pushed this act of suffrage.
Nellie McClung fought for women's right to vote.
The USA
The entered the war because of 3 reasons...
1: The sinking of the Lusitania in 1915 angered
many Americans.
2: The Zimmerman Telegram was sent from the
German ambassador to the US to Mexico, suggesting
Mexico to attack the US to regain some of their lost
land and that Germany would supoort them.
3: Germany declared "unrestricted" submarine
warfare on all ships/ trading with Triple Entente.
Effects of the War on Canada
Approximately 60,000 Canadian soldiers died.
Conscription deepened the resentment between
French and English in Canada.
Canada got her own seat at the Paris Peace
Conference and signed the treaty as a seperate nation.
Costed Canada $3 Billion dollars.
Increased sense of nationalism, and earned
respect from other nations in the world.
Economic growth/modernization.
More women gained rights and were now
seen as "workers".