por Mia Mahima hace 1 año
280
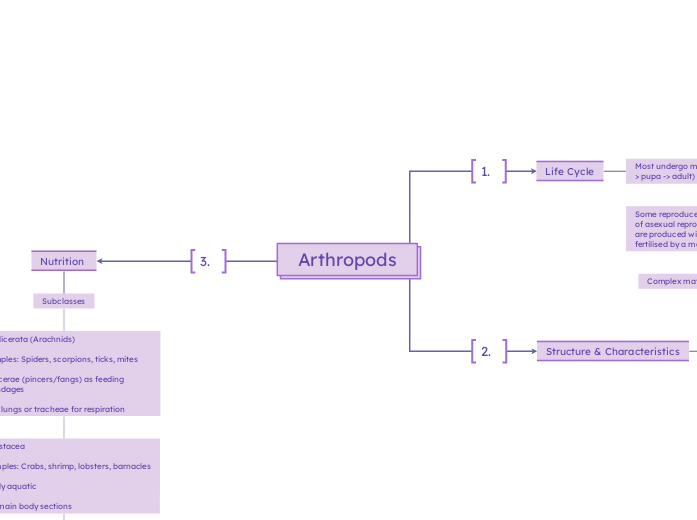
Arthropods
por Mia Mahima hace 1 año
280

Ver más
1. Chelicerata (Arachnids) -Examples: Spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites -Chelicerae (pincers/fangs) as feeding appendages -Book lungs or tracheae for respiration
2. Crustacea -Examples: Crabs, shrimp, lobsters, barnacles -Mostly aquatic -Two main body sections
3. Hexapoda (Insects) -Examples: Ants, butterflies, beetles -Three body parts: head, thorax, abdomen -Six legs, often winged -Most successful and widespread group
Bilateral symmetry
Compound eyes and other sensory organs
Exoskeleton made out of chitin
Some reproduce parthenogenetically (a form of asexual reproduction whereby offspring are produced without the embryo being fertilised by a male).
Complex mating rituals in some groups