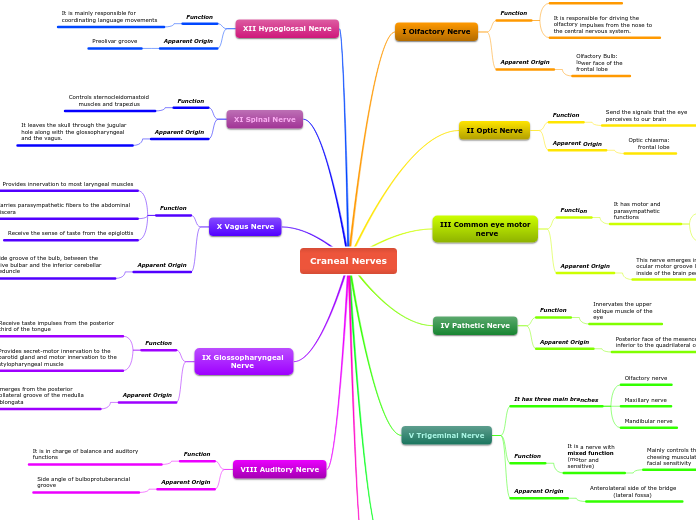
Craneal Nerves
VII Facial Nerve
Bulboprotuberancial groove at olive level
It is a mixed nerve, with mainly motor function and with a sensitive portion
Collect taste impressions of the previous two thirds of the language
VIII Auditory Nerve
Side angle of bulboprotuberancial groove
It is in charge of balance and auditory functions
IX Glossopharyngeal
Nerve
Emerges from the posterior collateral groove of the medulla oblongata
Provides secret-motor innervation to the parotid gland and motor innervation to the stylopharyngeal muscle
Receive taste impulses from the posterior third of the tongue
X Vagus Nerve
Side groove of the bulb, between the olive bulbar and the inferior cerebellar peduncle
Receive the sense of taste from the epiglottis
Carries parasympathetic fibers to the abdominal viscera
Provides innervation to most laryngeal muscles
XI Spinal Nerve
It leaves the skull through the jugular
hole along with the glossopharyngeal
and the vagus.
Controls sternocleidomastoid
muscles and trapezius
XII Hypoglossal Nerve
Preolivar groove
It is mainly responsible for coordinating language movements
VI Abducens Nerve
Bulboprotuberancial groove at the level of the pyramids
It innervates the lateral rectus muscle of the eyeball, being responsible for turning the eye outward
V Trigeminal Nerve
Anterolateral side of the bridge
(lateral fossa)
It is a nerve with mixed function (motor and sensitive)
Mainly controls the chewing musculature and facial sensitivity
It has three main branches
Mandibular nerve
Maxillary nerve
Olfactory nerve
IV Pathetic Nerve
Posterior face of the mesencephalic
inferior to the quadrilateral colicules
Innervates the upper oblique muscle of the eye
III Common eye motor
nerve
This nerve emerges in the common ocular motor groove located on the inside of the brain peduncles.
It has motor and parasympathetic functions
Parasympathetic: Responsible for pupil size
Motor:It is one of the nerves that controls eye movement
II Optic Nerve
Optic chiasma:
frontal lobe
Send the signals that the eye perceives to our brain
I Olfactory Nerve
Apparent Origin
Olfactory Bulb:
lower face of the frontal lobe
Function
It is responsible for driving the olfactory impulses from the nose to the central nervous system.
Its function is sensitive