por Patricia Brownell hace 3 años
326
Genitourinary System Imaging
por Patricia Brownell hace 3 años
326

Ver más
-any activity in the upper urinary tracts at any of the phases
-No reflux visualized -all or nearly all voided from bladder
-120 second immediate post void static image
-120 second immediate static of posterior and right/left posterior obliques
-Dynamic at 5 seconds for 1 minute
-Radionuclide cystography is preferred to iodinated contrast cystography -tracer is injected into tubing connected to bladder catheter
0.5-1mCi
Abnormal
-non uniform uptake/cold spots -no uptake in column of Bertin is indicative of tumor
Normal
-Smooth renal contour -uniform uptake of tracer concentration
-ID Patient, verify order, explain procedure -Patient should void before starting -Inject radiopharmaceutical via IV -Image patient in supine position at 2-4 hours
Static Images
-Image Posterior -Post/RAO/LAO/RPO/LPO -500k total counts per image -If pinhole is used 100k counts or 5 mins
- LFOV gamma camera - parallel hole collimator for differential calculation -Pinhole collimator for cortical images
99mTc-GH (Gluceptate)
-Secreted by glomerular filtration and tubular secretion -permits visuatization of renal blood flow and imaging of renal cortex -must be refrigerated -50% renal clearance in 3 hours
Subtopic
10-15 mCi
99mTc-DMSA (Dimercaptosuccinic Acid
-90% is bound to plasma protients which prevents most glomerular filtration -25-50% of the inject dose is in the kidney with an increase over time -DMSA is taken up in the renal cortex (proximal convoluted tubal -highest radiation dose of all renal due to much longer retention
5 mCi
-patient history (abdominal surgery) -advise patient of exam and timing -void just before exam
-pregancy -patient movement
-detects the amount of functioning renal cortical tissue -ex: detect small renal infarctions, scaring, acute pyelonephritis (typically caused by UTI) -differentiate a prominent column of Bertin from a true mass
-Dynamic acquisition -1-2 mins/frame for 20-30 mins
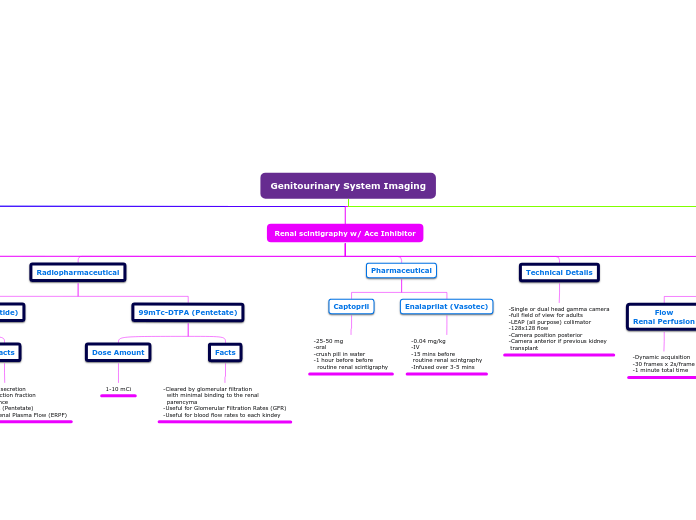
-0.04 mg/kg -IV -15 mins before routine renal scintgraphy -Infused over 3-5 mins
-25-50 mg -oral -crush pill in water -1 hour before before routine renal scintigraphy
1-10 mCi
-Patient is supine -one arm can be at patient's side and other is placed on side table for easy flow injection -bolus of rph inject via IV -IV at antecubital preferred -Sternal notch in top one third of image -Begin flow acquisition immediately after injection -IV inject 40mg of furosemide (lasix) when collecting systems are full, typically at 20 minutes post inject of rph -Continue imaging for ~20 minutes -Have patient void and take post void static
-Dynamic acquisition -20-40 minutes of 20 s/frame
-Single or dual head gamma camera -full field of view for adults -LEAP (all purpose) collimator -128x128 flow -Camera position posterior -Camera anterior if previous kidney transplant
-Furosemide (Lasix) -40mg Dose IV inj -Typically at 20 mins post rph inj
-Cleared by glomerular filtration with minimal binding to the renal parencyma -Useful for Glomerular Filtration Rates (GFR) -Useful for blood flow rates to each kindey -Not commonly used for diuretic renography
-recent iodine contrast study -pregancy -dehydrated patients
-to distinguish between obstructive hydronephrotic and non-obstructive collecting system dilation -caused by vesicoureteral reflux, urinary tract infections, congenital malformations, previous obstruction, or a noncompliant bladder -this test evaluates both renal function and urodynamics in in a single test
-posterior static acquisition for 2 minutes
-Dynamic acquisition -19 minutes of 20 s/frame
-Dynamic acquisition -30 frames x 2s/frame -1 minute total time
-Cleared by glomerular filtration with minimal binding to the renal parencyma -Useful for Glomerular Filtration Rates (GFR) -Useful for blood flow rates to each kindey
Facts
-Excreted by tubular secretion -high first pass extraction fraction -rapid plasma clearance -Preferred over DTPA (Pentetate) -Used for Effective Renal Plasma Flow (ERPF)
Dose Amount
10-20 mCi