por Anne Marie Hillewaere hace 5 años
297
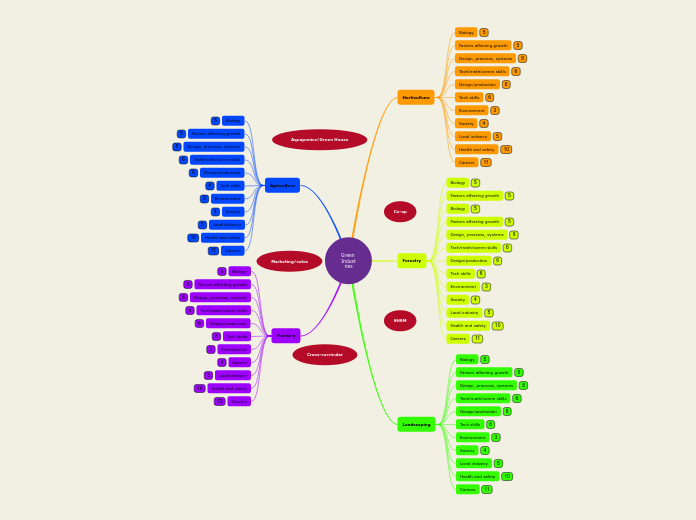
Green Industries Shared
por Anne Marie Hillewaere hace 5 años
297

Ver más
ways of acquiring knowledge and experience in green industry occupations (through part-time work experience, cooperative education, guest speakers, field trips, job shadowing
ability to demonstrate and identify the importance of MSDS, proper use of shears, use of protective gloves for own safety
the personal protective clothing andequipment needed to perform various green industry tasks safely, and use as required to ensure their own and others’ safety in the work environment
legislation, regulations, and guidelines pertaining to the healthand safety of workers in the green industries (Occupational Health and Safety Act [OHSA], Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System [WHMIS]).
ethical issues related to the green industries (e.g., animal welfare, breeding of animals for fur, animal cloning, migrant labour, monopoly control of food production as a possible consequence of the use of genetically modified crops)
the societal and economic implications of recent innovations and trends in the green industries mechanization and its effects on productivity and employment, expanded distribution systems and their consequences for consumer choice and local production, transgenic plants and their effects on food cost and availabilit
interpret simple working drawings garden sketches, plans for a forest, field plot designs, greenhouse drawings)
competence in the application of fundamental construction skills (selecting materials, measuring, cutting, joining) to a variety of construction projects (hard construction, laying pavers and flagstones, constructing a garden, building storage bins, creating a display booth, raised garden beds, compost bins);
complete a variety of green industry projects and tasks using appropriate tools, equipment, and materials (e.g., make a hand-tied bridal bouquet, prune a tree, scale a log, transplant a shrub, create a walkway, design a butterfly garden)
competence in applying techniques related to the propagation and growth of plants and/or the breeding and growth of animals (seeding, hatching eggs, making cuttings)
the ability to use skills required in green industry design and planning processes ( prepare a site inventory, create a base plan for a layout, complete a twodimensional survey, create a floral design, use plan symbols, interpret a plan)
sources of information about techniques and best practices in the green industries (government reports and fact sheets; news articles; manufacturers’ catalogues, manuals, and fact sheets; industry newsletters; industry events; Internet information)
understaning and proper terminology used in the green industries and use it correctly in oral and written communication (hardwood, propagation, line flower, vine, topsoil);
correctly using imperial and metric measurement (land area, volume, distance, scaling, weight, unit conversions)
a variety of design concepts and production processes and systems used in the green industries (simple garden designs, floral designs, greenhouse production layouts, barn layouts, lumber grading systems, sow operations)
steps in problem-solving process to green industry tasks
biological factors that affect growth and post-harvest quality (plant type, photosynthesis, genetics);
environmental factors that affect growth and post-harvest quality (light, temperature, soils, nutrients, water, wind)
physiological processes in plants and/or animals (germination, photosynthesis, reproduction, digestion)
characteristics of different plant and/or animal groups (shrubs, trees, annuals, flowers, animal breeds)
ways of acquiring knowledge and experience in green industry occupations (through part-time work experience, cooperative education, guest speakers, field trips, job shadowing)
an understanding of the Essential Skills that are important for success in the green industries, as identified in the Ontario Skills Passport (reading text, writing, document use, computer use, oral communication, numeracy, thinking skills)
identify MSDS, identify and demonstrate proper lifting technique, identify and demonstrate the importance of wearing proper footware to ensure their own safety
potential hazards (trip hazards, environmental conditions, danger zones) related to the materials, site conditions, and equipment used in the work environment
the societal and economic implications of recent innovations and trends in the green industries (mechanization and its effects on productivity and employment, expanded distribution systems and their consequences for consumer choice and local production, transgenic plants and their effects on food cost and availability
ways in which green industry activities affect the environment (contamination of water by fertilizers, pesticides, and manure; emission of greenhouse gases from animals, tilled soils, and equipment; emission of air pollutants from gasoline- and diesel-powered machinery; noise pollution; high energy demand)
competence in the application of construction skills (selecting materials, measuring, cutting, joining) to a variety of construction projects (hard construction, laying pavers and flagstones, constructing a garden, building storage bins, creating a display booth)
complete a variety of green industry projects and tasks using appropriate tools, equipment, and materials (make a hand-tied bridal bouquet, prune a tree, scale a log, transplant a shrub, create a walkway, design a butterfly garden, raised garden bed, compost bin)
the ability to use skills required in green industry design and planning processes (prepare a site inventory, create a base plan for a layout, complete a twod imensional survey, create a floral design, use plan symbols, interpret a plan)
an understanding of terminology used in the green industries and use it correctly in oral and written communication (hardwood, propagation, line flower, vine, topsoil);
accurately use imperial and metric measurements and measurements for various applications in the green industries (land area, volume, distance, scaling, pacing, weight, unit conversions, tree height)
a variety of structural or mechanical systems used within the green industries (systems for heating, cooling, storage, irrigation, fertilizing, feeding, harvesting, cleaning, milling).
a variety of design concepts and production processes and systems used in the green industries (simple garden designs, floral designs, greenhouse production layouts, barn layouts, lumber grading systems, sow operations, grape production)
a variety of structural or mechanical systems used within the green industries (systems for heating, cooling, storage, irrigation, fertilizing, feeding, harvesting, cleaning, milling).
an understanding of a variety of processes used in plant and/or animal care (plant growth experiments, propagation, pruning, sheep shearing)
a variety of pests and diseases (Asian long-horned beetle, thrips, grubs, moles, Dutch elm disease, mastitis, hoof-and-mouth disease) and describe their effects on plants and/or animals.
key distinguishing characteristics of different plant and/or animal groups (shrubs, trees, annuals, flowers, animal breeds)
pieces of work and other materials that provide evidence of their skills and achievements in areas related to the green industries, for inclusion in a portfolio (work logs, skills checklist, résumé, references, safety certificates)
groups and programs that are available to support students who are interested in pursuing non-traditional career choices in the green industries mentoring programs, virtual networking/support groups, specialized postsecondary programs, relevant trade/industry associations)
ways of acquiring knowledge and experience in green industry occupations (through part-time work experience, cooperative education, guest speakers, field trips, job shadowing
legislation, regulations, and guidelines pertaining to the health and safety of workers in the green industries (Occupational Health and Safety Act [OHSA], Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System [WHMIS]).
an understanding of the work habits that are important for success in the green industries, as identified in the Ontario Skills Passport (working safely, teamwork, reliability, organization, working independently, initiative, self-advocacy, customer service)
identify tics, demonstrate how to properly remove a tics, demonsrate the importance of wearing long pants
the personal protective clothing and equipment needed to perform various green industry tasks safely, and use as required to ensure their own and others’ safety in the work environment
an understanding of appropriate uses, safe operating practices, and correct maintenance procedures for materials, tools, and equipment that are commonly used in the green industries (lawn maintenance equipment, garden tools, mechanical harvesting equipment, feeding systems)
local green industries (largescale farms, greenhouse operations, florists, community gardens, golf courses) and describe their activities or products within a specific region
ethical issues related to the green industries (animal welfare, breeding of animals for fur, animal cloning, migrant labour, monopoly control of food production as a possible consequence of the use of genetically modified crops)
the societal and economic implications of recent innovations and trends in the green industries (mechanization and its effects on productivity and employment, expanded distribution systems and their consequences for consumer choice and local production, transgenic plants and their effects on food cost and availability)
interpret simple working drawings (garden sketches, plans for a forest, field plot designs, greenhouse drawings)
competence in the application of construction skills (selecting materials, measuring, cutting, joining) to a variety of construction projects (hard construction, laying pavers and flagstones, constructing a garden, building storage bins, creating a display booth, raised garden beds, comost bins)
complete a variety of green industry projects and tasks using appropriate tools, equipment, and materials (make a hand-tied bridal bouquet, prune a tree, scale a log, transplant a shrub, create a walkway, design a butterfly garden)
e competence in the application of a production process used in the green industries (foundation planting, pasteurization, inspection, electronic sorting, transplanting)
competence in applying techniques related to the propagation and growth of plants and/or the breeding and growth of animals (seeding, hatching eggs, making cuttings)
the ability to use skills required in green industry design and planning processes (prepare a site inventory, create a base plan for a layout, complete a twodimensional survey, create a floral design, use plan symbols, interpret a plan)
techniques relating to the maintenance, care, and handling of plants and/or animals, using environmental best practices (mulching gardens, feeding and watering, product processing, visual inspection)
imperial and metric units of measurement correctly and make accurate calculations and measurements for various applications in the green industries (land area, volume, distance, scaling, pacing, weight, unit conversions, tree height)
a variety of design concepts and production processes and systems used in the green industries (simple garden designs, floral designs, greenhouse production layouts, barn layouts, lumber grading systems, sow operations, grape production)
a variety of structural or mechanical systems used within the green industries (systems for heating, cooling, storage, irrigation, fertilizing, feeding, harvesting, cleaning, milling).
a variety of pests and diseases (Asian long-horned beetle, thrips, grubs, moles, Dutch elm disease, mastitis, hoof-and-mouth disease) and describe their effects on plants and/or animals.
biological factors that affect growth and post-harvest quality (plant type, photosynthesis, genetics)
e environmental factors that affect growth and post-harvest quality (light, temperature, soils, nutrients, water, wind)
basic components of common plants and/or animals and describe their functions (leaves, flowers, bark, internal organs)
physiological processes in plants and/or animals (germination, photosynthesis, reproduction, digestion)
pieces of work and other materials that provide evidence of their skills and achievements in areas related to the green industries, for inclusion in a portfolio (work logs, skills checklist, résumé, references, safety certificates)
ways of acquiring knowledge and experience in green industry occupations through part-time work experience, cooperative education, guest speakers, field trips, job shadowing
legislation, regulations, and guidelines pertaining to the health and safety of workers in the green industries (Occupational Health and Safety Act [OHSA], Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System [WHMIS]).
an understanding of the work habits that are important for success in the green industries, as identified in the Ontario Skills Passport (working safely, teamwork, reliability, organization, working independently, initiative, self-advocacy, customer service)
identify MSDS, identify wild parsnip and understand how to properly handle it, demonstrate ability to wear protective gloves
legislation, regulations, and guidelines pertaining to the health and safety of workers in the green industries (e.g., Occupational Health and Safety Act [OHSA], Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System [WHMIS]).
potential hazards (trip hazards, environmental conditions, danger zones) related to the materials, site conditions, and equipment used in the work environment
the personal protective clothing and equipment needed to perform various green industry tasks safely, and use as required to ensure their own and others’ safety in the work environment
legislation, regulations, and guidelines pertaining to the health and safety of workers in the green industries (Occupational Health and Safety Act [OHSA], Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System [WHMIS]).
an understanding of and apply safe shop and site practices (using correct lockout procedures, using equipment guards, holding shop orientation sessions, having sanitary wash stations available, cleaning up spills and leaks when they happen, keeping areas clean and clear of obstruction, storing materials and equipment neatly and safely)
an understanding of appropriate uses, safe operating practices, and correct maintenance procedures for materials, tools, and equipment that are commonly used in the green industries (lawn maintenance equipment, garden tools, mechanical harvesting equipment, feeding systems)
local green industries (largescale farms, greenhouse operations, florists, community gardens, golf courses) and describe their activities or products within a specific region;
the effects of local green industries on the community (effects on employment, water and air quality, leisure opportunities, aesthetics; availability of locally produced specialty products)
ethical issues related to the green industries (animal welfare, breeding of animals for fur, animal cloning, migrant labour, monopoly control of food production as a possible consequence of the use of genetically modified crops)
the societal and economic implications of recent innovations and trends in the green industries (mechanization and its effects on productivity and employment, expanded distribution systems and their consequences for consumer choice and local production, transgenic plants and their effects on food cost and availability)
best management practices, environmentally sustainable practices, and technologies that can be used to reduce the harmful effects of green industry operations (composting, recycling, use of renewable energy sources, land retirement, minimal use of fertilizers and pesticides)
ways in which green industry activities affect the environment (e.g., contamination of water by fertilizers, pesticides, and manure; emission of greenhouse gases from animals, tilled soils,and equipment; emission of air pollutants from gasoline- and diesel-powered machinery; noise pollution; high energy demand)
interpret simple working drawings (garden sketches, plans for a forest, field plot designs, greenhouse drawings)
competence in the application of fundamental construction skills (e.g., selecting materials, measuring, cutting, joining) to a variety of construction projects (hard construction, laying pavers and flagstones, constructing a garden, building storage bins, creating a display booth, raised garden beds, compost bins);
complete a variety of green industry projects and tasks using appropriate tools, equipment, and materials (make a hand-tied bridal bouquet, prune a tree, scale a log, transplant a shrub, create a walkway, design a butterfly garden)
competence in the application of a production process used in the green industries (foundation planting, pasteurization, inspection, electronic sorting, transplanting)
competence in applying techniques related to the propagation and growth of plants and/or the breeding and growth of animals (seeding, hatching eggs, making cuttings);
the ability to use skills required in green industry design and planning processes (prepare a site inventory, create a base plan for a layout, complete a twodimensional survey, create a floral design, use plan symbols, interpret a plan)
techniques relating to the maintenance, care, and handling of plants and/or animals, using environmental best practices (mulching gardens, feeding and watering, product processing, visual inspection)
an understanding of terminology used in the green industries and use it correctly in oral and written communication (e.g., hardwood, propagation, line flower, vine, topsoil)
imperial and metric units of measurement correctly and make accurate calculations and measurements for various applications in the green industries (land area, volume, distance, scaling, pacing, weight, unit conversions, tree height)
a variety of design concepts and production processes and systems used in the green industries (e.g., simple garden designs, floral designs, greenhouse production layouts, barn layouts, lumber grading systems, sow operations, grape production)
a variety of structural or mechanical systems used within the green industries (systems for heating, cooling, storage, irrigation, fertilizing, feeding, harvesting, cleaning, milling).
steps in applying a design or problem-solving process to green industry tasks
an understanding of a variety of processes used in plant and/or animal care (plant growth experiments, propagation, pruning, sheep shearing);
a variety of pests and diseases (Asian long-horned beetle, thrips, grubs, moles, Dutch elm disease, mastitis, hoof-and-mouth disease) and describe their effects on plants and/or animals.
biological factors that affect growth and post-harvest quality (plant type, photosynthesis, genetics);
basic components of common plants and/or animals and describe their functions (leaves, flowers, bark, internal organs)
key distinguishing characteristics of different plant and/or animal groups (shrubs, trees, annuals, flowers, animal breeds)
pieces of work and other materials that provide evidence of their skills and achievements in areas related to the green industries, for inclusion in a portfolio work logs, skills checklist, résumé, references, safety certificates)
groups and programs that are available to support students who are interested in pursuing non-traditional career choices in the green industries (mentoring programs, virtual networking/support groups, specialized postsecondary programs, relevant trade/industry associations)
networking in green industry occupations (e.g., through part-time work experience, cooperative education, guest speakers, field trips, job shadowing
an understanding of the work habits that are important for success in the green industries, as identified in the Ontario Skills Passport (working safely, teamwork, reliability, organization, working independently, initiative, self-advocacy, customer service)
an understanding of the Essential Skills that are important for success in the green industries, as identified in the Ontario Skills Passport (reading text, writing, document use, computer use, oral communication, numeracy, thinking skills)
pieces of work and other materials that provide evidence of their skills and achievements in areas related to the green industries, for inclusion in a portfolio (work logs, skills checklist, résumé, references, safety certificates)
ability to demonstrate and identify when and how to propelrly use a ladder to prevent falls, the importance of proper footware, identidy a list of safety rules for the industry
legislation, regulations, and guidelines pertaining to the health and safety of workers in the green industries (Occupational Health and Safety Act [OHSA], Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System [WHMIS]).
potential hazards (rip hazards, environmental conditions, danger zones) related to the materials, site conditions, and equipment used in the work environment
the personal protective clothing and equipment needed to perform various green industry tasks safely, and use as required to ensure their own and others’ safety in the work environment
legislation, regulations, and guidelines pertaining to the health and safety of workers in the green industries (e.g., Occupational Health and Safety Act [OHSA], Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System [WHMIS]).
an understanding of and apply safe shop and site practices (using correct lockout procedures, using equipment guards, holding shop orientation sessions, having sanitary wash stations available, cleaning up spills and leaks when they happen, keeping areas clean and clear of obstruction, storing materials and equipment neatly and safely)
appropriate uses, safe operating practices, and correct maintenance procedures for materials, tools, and equipment that are commonly used in the green industries (lawn maintenance equipment, garden tools, feeding systems)
local green industries (largescale farms, greenhouse operations, florists, community gardens, golf courses) and describe their activities or products within a specific region)
the effects of local green industries on the community (effects on employment, water and air quality, leisure opportunities, aesthetics; availability of locally produced specialty products)
the relationships between a variety of local green industries and their local outlets (garden centre and nursery, vegetable production and farmers’ market, maple syrup production and specialty food store, flower producer and florist)
ethical issues related to the green industries (animal welfare, breeding of animals for fur, animal cloning, migrant labour, monopoly control of food production as a possible consequence of the use of genetically modified crops)
the societal and economic implications of recent innovations and trends in the green industries (mechanization and its effects on productivity and employment, expanded distribution systems and their consequences for consumer choice and local production, transgenic plants and their effects on food cost and availabilit)
best management practices, environmentally sustainable practices, and technologies that can be used to reduce the harmful effects of green industry operations (composting, recycling, use of renewable energy sources, land retirement, minimal use of fertilizers and pesticides)
ways in which green industry activities affect the environment (contamination of water by fertilizers, pesticides, and manure; emission of greenhouse gases from animals, tilled soils, and equipment; emission of air pollutants from gasoline- and diesel-powered machinery; noise pollution; high energy demand)
interpret simple working drawings (garden sketches, plans for a forest, field plot designs, greenhouse drawings)
construction skills (selecting materials, measuring, cutting, joining) to a variety of construction projects (e.g., hard construction, laying pavers and flagstones, constructing a garden, building storage bins, creating a display booth, raised garden beds, compost bins)
complete a variety of green industry projects and tasks using appropriate tools, equipment,and materials (make a hand-tied bridal bouquet, prune a tree, scale a log, transplant a shrub, create a walkway, design a butterfly garden)
production process used in the green industries (foundation planting, pasteurization, inspection, electronic sorting, transplanting)
competence in applying techniques related to the propagation and growth of plants and/or the breeding and growth of animals (seeding, hatching eggs, making)
skills required in green industry design and planning processes (prepare a site inventory, create a base plan for a layout, complete a twodimensional survey, create a floral design, use plan symbols, interpret a plan)
techniques relating to the maintenance, care, and handling of plants and/or animals, using environmental best practices (mulching gardens, feeding and watering, product processing, visual inspection)
sources of information about techniques and best practices in the green industries (government reports and fact sheets; news articles; manufacturers’ catalogues, manuals, and fact sheets; industry newsletters; industry events; Internet information)
an understanding of terminology used in the green industries and use it correctly in oral and written communication (hardwood, propagation, line flower, vine, topsoil)
Accureatly uses imperial and metric units of measure and measurements for various applications in the green industries (land area, volume, distance, scaling, pacing, weight, unit conversions, tree height)
a variety of structural or mechanical systems used within the green industries (systems for heating, cooling,storage, irrigation, fertilizing, feeding, harvesting, cleaning, milling).
a variety of design concepts and production processes and systems used in the green industries (simple garden designs, floral designs, greenhouse production layouts, barn layouts, lumber grading systems, sow operations, grape production)
a variety of structural or mechanical systems used within the green industries (systems for heating, cooling, storage, irrigation, fertilizing, feeding, harvesting,cleaning, milling).
steps in applying a design or problem-solving process to green industry tasks
an understanding of a variety of processes used in plant and/or animal care (plant growth experiments, propagation, pruning, sheep shearing)
a variety of pests and diseases (Asian long-horned beetle, thrips, grubs, moles, Dutch elm disease, mastitis, hoof-and-mouth disease) and describe their effects on plants and/or animals.
biological factors that affect growth and post-harvest quality (plant type, photosynthesis, genetics)
environmental factors that affect growth and post-harvest quality (light, temperature, soils, nutrients, water, wind)
basic components of common plants and/or animals and describe their functions (e.g., leaves, flowers, bark, internal organs)
physiological processes in plants and/or animals (e.g., germination, photosynthesis, reproduction, digestion)
key distinguishing characteristics of different plant and/or animal groups (e.g., shrubs, trees, annuals, flowers, animal breeds)