Finish
Congratulations Guest! You are done.
You could do the following steps:
- Print this map out, take it with you and quickly rehearse before you begin your interview at Kinematics and Dynamics
- Save this map and come back later to refine it
Good luck with your interview!
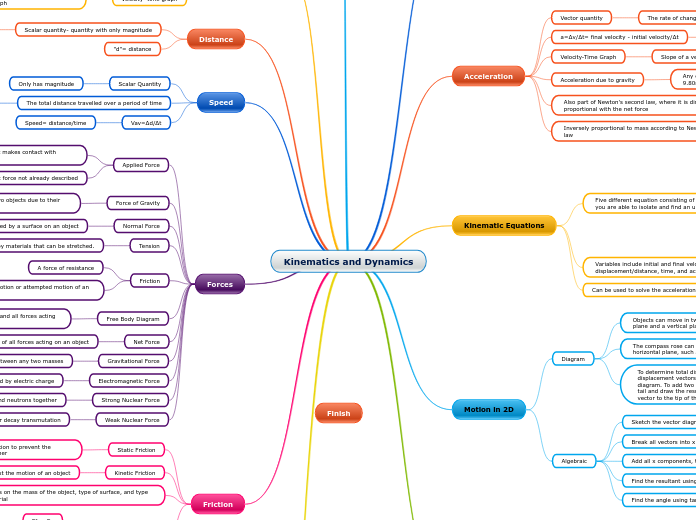
Kinematics and Dynamics
Type in the name of the company you are going to have an interview with.
Free Fall
Gravitational Field Strength
Weightlessness
Force of gravity is still acting but both the object and frame of reference are in free fall
Weight
Measure of the force of gravity on the object (N)
Mass
The amount of matter in an object (kg)
The force per unit mass acting on an object when placed in a gravitational field
9.80 N/kg [down]
Force field
A region of space around an object that exerts a force on the other object within that region
The motion of a falling object where only the force of gravity is acting on it
Air Resistance
Increases when speed increases
Increases as cross-sectional area increases
Type of friction
Terminal Speed
The maximum constant speed of a falling object
Uniform velocity as it has constant speed and will be falling in the same direction; downwards
How ambitious are you?
Coefficient of friction
Uk= Fk/Fn
Us= Fs/Fn
Ff= uFn
Depends on the mass of the object, type of surface, and type of material
Where and how do you see yourself in 5 years time?
Type in the answers.
Kinetic Friction
What are your long-term goals ?
Type them in.
Force that acts against the motion of an object
Static Friction
What are your short-term goals ?
Type them in.
Force that acts against attempted motion to prevent the sliding of one surface relative to another
Forces
Weak Nuclear Force
Involves nuclear decay transmutation
Strong Nuclear Force
Keeps protons and neutrons together
Electromagnetic Force
Caused by electric charge
Gravitational Force
Exists between any two masses
Net Force
The sum of all forces acting on an object
Must add the x and y forces seperately
Free Body Diagram
A simple drawing representing the object and all forces acting on it
Friction
Always acts opposite to the motion or attempted motion of an object
A force of resistance
Tension
The force exerted by materials that can be stretched.
Ex: ropes, strings, cables, etc
Normal Force
What experience have you got from your previous jobs? Make sure you specify all your previous work experience, part-time jobs, vacation jobs, voluntary work, and unpaid work experience that are relevant for the position you are applying for.
A pushing force exerted by a surface on an object
Always acts away from and perpendicular to the surface
Force of Gravity
Describe a typical work day in your previous/current position.
The force of attraction between any two objects due to their mass.
Fg= mg
g= 9.80 m/s^2
Acceleration due to gravity (kinematics)
Applied Force
Why will/did you leave your existing/last job?
Any contact force not already described
A force that results when one object makes contact with another and pushed or pulls it
Speed
Do you fully understand what this position implies?
After you've made some research on the company, read the job description thoroughly, and try to fully understand what your responsibilities will be.
Vav=Δd/Δt
What would you do on the first day?
What about the first week(s)? Fill in some of the actions that you are planning to take.
Speed= distance/time
The total distance travelled over a period of time
What do you think the main challenges will be?
Type them in.
Represented in meters per second, m/s
Scalar Quantity
What will be your main tasks?
Type them in.
Only has magnitude
Distance
"d"= distance
Scalar quantity- quantity with only magnitude
The total length of the path travelled by an object in motion
Represented in meters, m
Displacement
Velocity- time graph
Displacement can be found by calculating the area under the curve or line of the velocity-time graph
Refers to the change in an object's position
∆d=Final displacement-intial displacement
Displacement is a vector quantity- has both magnitude and direction
Direction is represented in terms of direction in square brackets, [N], [S], [W], [E].
Represented in meters along with direction, m [direction]
Newton's Laws
Basic kinematic problems are approached using Newton's laws of motion
Newton's Third Law
For every action force there is a simultaneous reaction force that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction
Newton's Second Law
Fnet= ma
Acceleration can also be found using the kinematic equations, when given other variables
The magnitude of the acceleration is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass
An object will accelerate in the direction of the net force
Newton's First Law
All objects will remain in a state of rest or continue to move with a constant velocity unless acted upon by an unbalanced force
Velocity would be linear on a velocity-time graph, indicating it is constant
Net Force= 0
Projectiles
The five kinematic equations of motion can be used to solve projectile motion problems
Projectile motion can begin and end at the same or at different heights
Objects can be projected horizontally or at an angle to the horizontal.
Projectiles undergo uniform acceleration in the vertical direction, due to gravity
Projectiles move horizontally at a constant velocity
The horizontal and vertical motions of a projectile take the same amount of time
Projectile motion consists of independent horizontal and vertical motions
Motion in 2D
Algebraic
Find the angle using tan
Find the resultant using the Pythagorean theorem
Add all x components, then add all y components
Break all vectors into x and y components
Sketch the vector diagram and label it
Diagram
To determine total displacement in two dimensions, displacement vectors can be added together using a scale diagram. To add two or more vectors together, join them tip to tail and draw the resultant vector from the tail of the first vector to the tip of the last vector
The compass rose can be used to express directions in a horizontal plane, such as [N 40° W]
Objects can move in two dimensions, such as in horizontal plane and a vertical plane
Kinematic Equations
Can be used to solve the acceleration for Newton's second law
Variables include initial and final velocity, displacement/distance, time, and acceleration
Five different equation consisting of different variables, where you are able to isolate and find an unknown variable
How would you describe yourself?
Type in a short description.
∆d=v2∆t-1/2a∆t^2
v2^2= v1^2+2a∆d
∆d=v1∆t+1/2a∆t^2
∆d=1/2(v1+v2 )∆t
v2=v1+a∆t
Acceleration
Are you qualified for this position?
Interviewers will want to know whether or not you are able to do the job.
Answer the questions from this section and see if you are the right person for this position.
Inversely proportional to mass according to Newton's second law
Also part of Newton's second law, where it is directly proportional with the net force
Acceleration due to gravity
Any object falling freely near Earth will accelerate at 9.80m/s^2 [down]
Velocity-Time Graph
Which qualities were easily observed by your colleagues and/or your former/existing boss?
Type them in.
Slope of a velocity-time graph will give you the acceleration
a=∆v/∆t= final velocity - initial velocity/∆t
What are your weaknesses?
Examples:
stubbornoverly critical, can't accept authoritytoo demandingtoo talkativetoo quiettoo sensitivelacking assertivenesslacking social tact
Acceleration= velocity/time
Vector quantity
What strengths qualify you for this job?
Example:
ambitiousgood communicatorfocuseddeterminedadaptablecuriousoptimisthard workerhonestpoliteco-operativeself motivatedenthusiasticgood leaderstrategic thinkerquick learnerflexiblegood problem solver
The rate of change of velocity with respect to time
Represented in meters per second squared, m/s^2 [direction]
Why do you think you have this strength?
Give an example.
Velocity
Research the company
You should find and learn as much as you can about the company where you are having an interview.
The interviewer will want to see what you know about them and why you chose the company.
Doing your homework will show that you are really interested.
Acceleration-Time Graph
The area under the line or curve in an acceleration-time graph will give you the velocity
Position-Time Graph
When the data is not linear, draw a tangent line at a given time
Slope of the tangent line will give you the instantaneous velocity at the specific time
Slope of a position-time graph will give you the velocity
Vav= Δd/Δt= d2-d1/Δt
Velocity= displacement/time
What is the company's turnover for last year?
Vector Quantity
What can you do for this company that someone else can't?
Type in several unique traits that will turn you into the perfect candidate for the position.
The total displacement travelled over a period of time
Represented in meters per second with direction, m/s [direction]
Uniform Velocity
What do you know about the company?
Type a short description of the company's background.
Constant velocity means a net force of zero, according to Newton's first law of motion
Motion with a constant speed and constant direction