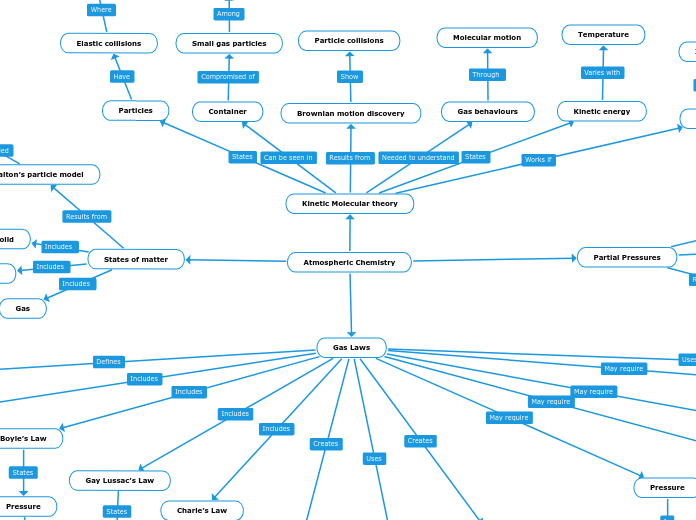
Atmospheric Chemistry
Gas Laws
Avogadro’s law
Volume
Number of particles
P1/n1=P2/n2
Boyle’s Law
Pressure
Volume
Inverse operation
P1xV1=P2xV2
Gay Lussac’s Law
Pressure
Temperature
P1/T1=P2/T2
Charle’s Law
Volume
Temperature
V1/T1=V2/T2
Ideal Gas Law
Hypothetical gas properties
PV=nRT
Quantitative relationships
Gas variables
Physical property
Gasses
Standard conditions
Fixed variables
Temperature and pressure
Compare different sets of experiments
Physical constant
Molar gas constant
Pressure
Force exerted
Gas particles
Surface
KiloPascals
Temperature
Speed of motion
Gas particles
Kelvin
Volume
Container
Litres
Number of moles
Gas particles
Large quantities
Atoms or molecules
Combined Gas Law
Hypothetical gas properties
P1 x V1 / T1 = P2 x V2 /T2
Number of moles
Constant
Kinetic Molecular theory
Brownian motion discovery
Particle collisions
Gas behaviours
Molecular motion
Kinetic energy
Temperature
Container
Small gas particles
Large number of particles
Particles
Elastic collisions
Kinetic energy
Conserved
All particles
Ideal gas behaviour
Not true
Partial Pressures
Specific pressure of gas
Ideal gas mixture
Atmosphere
Nitrogen, oxygen, argon
Dalton’s Law of partial pressures
Total pressure
Container
The sum of each individual gas pressures
Ptotal = P1 + P2 + P3….
Pgas = proportion x ptotal
States of matter
Dalton’s particle model
Idea of atoms
The properties
The states of matter
Solid
Fixed shape, volume, position
Strong attraction
Particles
Liquid
Fixed volume
Can flow to different places
Somewhat strong attraction
Particles
Gas
Shape of container
Lots of space
Little attraction
Particles