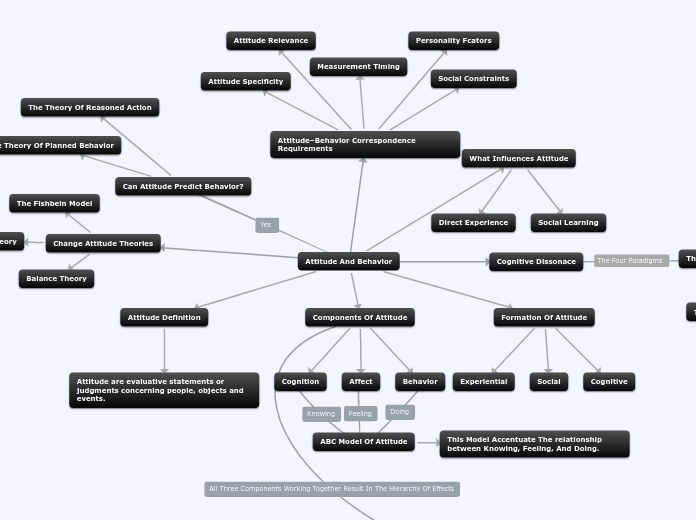
Attitude And Behavior
Attitude Definition
Attitude are evaluative statements or judgments concerning people, objects and events.
Components Of Attitude
Cognition
Affect
Behavior
Formation Of Attitude
Experiential
Social
Cognitive
What Influences Attitude
Direct Experience
Social Learning
ABC Model Of Attitude
This Model Accentuate The relationship between Knowing, Feeling, And Doing.
Hierarchy Of Effects
The Standard-Learning Hierarchy
Hierarchy Of Effects Is A Concept Used To Distinguish Between The Involvement Levels or Motivation An Individual Might Have Toward The Attitude Object.
Low-Involvement Hierarchy
Experimental Hierarchy
Attitude–Behavior Correspondence Requirements
Social Constraints
Attitude Relevance
Attitude Specificity
Measurement Timing
Personality Fcators
Can Attitude Predict Behavior?
The Theory Of Planned Behavior
The Theory Of Reasoned Action
Change Attitude Theories
Balance Theory
Multi-Attribution Theory
The Fishbein Model
Cognitive Dissonace
The Induced-Compliance Paradigm
The Free-Choice Paradigm
The Effort-Justification Paradigm
The Belief Disinformation Paradigm