“Basic concepts and curricular Theory”
Education is an action that implies the intention of progressive social improvement that allows human beings to develop their full potential.

Plato
goal of clarifying the nature of justice
features
guardians who ruled it
philosophers-rules
study of mathematics and philosophy
nature of absolute reality

"form of the good"
practical experience
members of society
intellectual qualities or interests
not allowed
Level high
theory of shapes or ideas
idea of knowledge
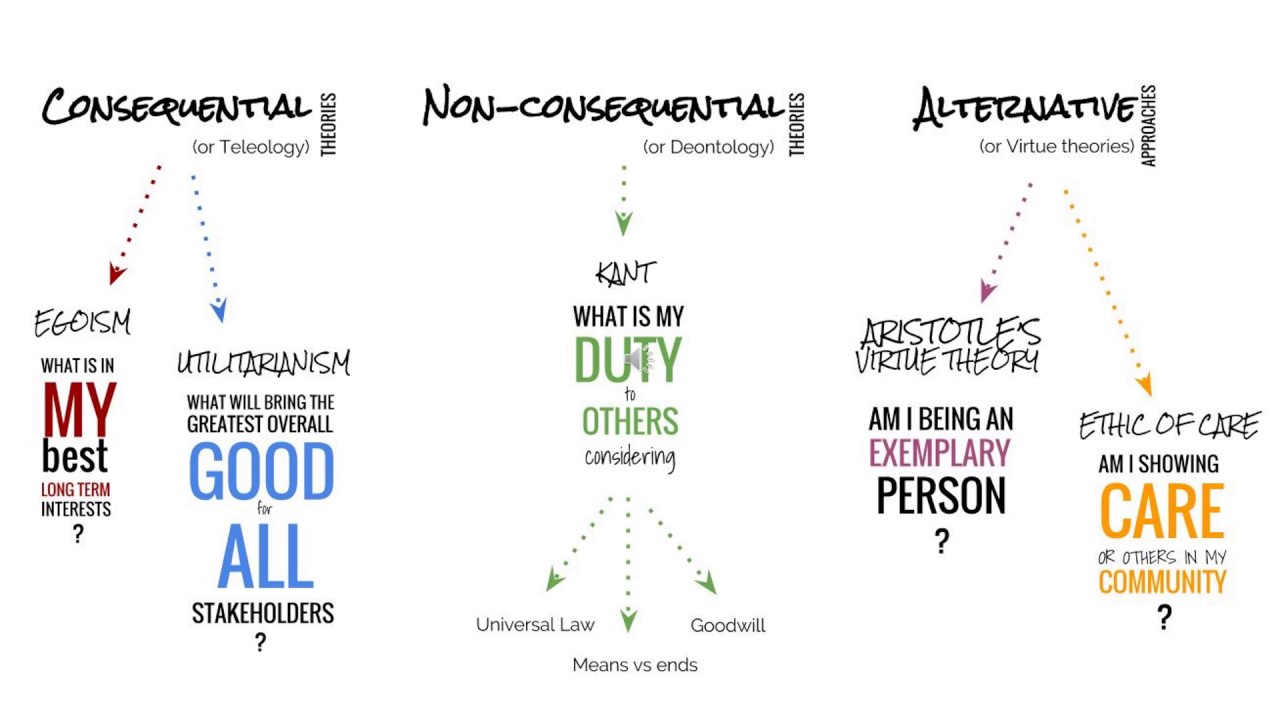
ethical theory
psychology
concept of the State

conception of art

Aristotle
fuller and deeper philosophical systems of ancient thought
reflection on main areas of philosophy

metaphysics
nature philosophy

knowledge theory
logic
anthropology

ethics

politics
aesthetics
dominates western thought
new systems in the Renaissance (Galileo)
Modern Age (rationalism, empiricism, Kant)
disappearance of the idea of the world

Kant
pedagogy seeks to transform the spontaneous process of education into systematic knowledge
physical education or practical education
student must show passive submission and obedience

governs a mechanical force
rest on exercise

discipline
student is allowed to make use of their capacity for reflection
freedom that is determined or guided by the laws that govern society

fuerza moral

Montessori
study of children with mental disorders
observation

the child in school
loving environment
materiales manipulables
maestros como guías
respect the child's sensitivity
1907
the first Children's House
practical living room
house made to the scale of the little ones
practiced hygiene and manners
"the child, guided by an inner teacher works tirelessly with joy to build man."
the child developed with dignity, freedom and independence.

Jean-Jacques Rousseau
"liberator of the child and as the father of modern progressive education”
natural processes are better
advises
"fix your eyes on nature, follow the path traced by it"

Rising children

naturalistic education
learning was postponed through books
the child should not be arbitrarily punished
suffer the natural consequences of their actions
manners should be avoided
artificial behaviors
interests and peculiarities
interaction with the physical world

games