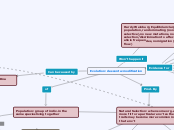
Evolution: descent w modification
of
Population: group of indiv. in the same species living together
Subtopic
Genotype frequency
Freq. of both in
Allele freq.
Prod. By
Natural Selection: when some org. are more fit for a particular env't so their traits may become more common in that env't
Effected by
Adaptation: inherited trait that makes an org. more fit for an env't
Modes of selection
Stabilizing selection: the average trait becomes/stays most common
Directional Selection: selection against the most common trait. Happens at one extreme or the other.
Disruptive Selection: occurs against the average -> extreme traits become more common than average trait
Natural Variation: the different members of a species due to inheritance
Things that may contribute
Sexual reproduction
Bacterial conjugation
Selective pressure: change in the env'tl characteristics that may lead to natural selection
Non-random Mating
vs
Artificial selection: when humans select trait they desire for breeding purposes in other organism
Evidence for
Fossils: parts of past organisms
DNA/RNA/Proteins: high gene similarity means they're evol. related, low gene similarity means they're evol. unrelated
Comparative embryology: comp. embryonic dev. of organisms in the same kingdom
Genetic code: almost ALL (few bacterial exceptions) use the same code to build proteins
Endosymbiosis: mitochondria & chloroplasts were likely some sort of prokaryotic organism that was engulfed by a larger cell
Homologies/Homologous structures: traits that are conserved in evolutionarily related organisms
Analogous structures: structures that are similar in shape/function in unrelated organisms that live in similar env'ts
Convergent evolution: process where unrelated org.in similar env'ts have similar adaptations
Divergent evolution: organisms are thought to have the same ancestor, but separated over time.