Chemical Reactions
Physical and Chemical Properties
and Changes
Physical Property
A description of a substance that does not involve
forming a new substance.
Types
Color, texture, density, smell, solubility,
taste, melting point, physical state.
Chemical Property
A description of what a substance does
as it changes into one or more new substances
Physical Change
A change that does not produce a new substance
Example
Dissolve, cutting, melting, breaking.
Chemical Change
A change that produces a new substance
Example
Mixing baking soda with vinegar, forest fire
Patterns and the Periodic Table
Chemical Periods and Groups
Period
A row of elements in the periodic table
The column number indicates the amount of valence
electrons present in a given column
Group
A column of elements in the periodic table
with similar properties
Alkali Metals
The elements in the first column of the periodic table
(except hydrogen)
Alkaline Earth Metals
The elements in the second column
Halogens
The elements in the seventeenth column
Noble Gases
The elements in the eighteenth column
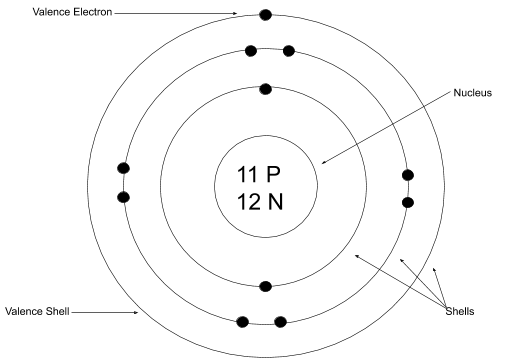
Bohr-Rutherford Diagram
A model representing the arrangement of
electrons in orbits around the nucleus of an atom
Electron Arrangements and Reactivity
Compounds
A pure substance composed of two or more
elements in a fixed ratio
Reactivity
The closer an atom is to a full electron orbit, the more stable
Atoms and Ions
Ion
Definition
A charged particle that results when an atom
gains or loses one or more electrons
Naming Ions
Ions
A positively charged ion
Cations
A negatively charged ion
Polyatomic Ions
An ion made up of more than one
atom that acts as a single particle
Bonds
Ionic Bond
Definition
The simultaneous strong attraction of positive and
negative ions in an ionic compound
Ionic Compounds
Definition
A compound made up of one or more positive
metal ions and one or more negative non-metal ions
Ionic Bond
The simultaneous strong attraction of positive
and negative ions in an ionic compound
Properties of Ionic Compounds
Hard, brittle, solid. Often electrolytes.
Electrolytes
A compound that separates into ions when it
dissolves in water, producing a solution that
conducts electricity
Names and Formulas of Ionic Compounds
Naming Ionic Compounds
Metal + Non-Metal
The first part of a name refers to the metal ion
in the compound and the second part to the non-metal.
The non-metal also has its ending changed to "ide"
Example
Magnesium + Chlorine
Magnesium chloride
Compounds formed from charged ions are electrically neutral. Therefore, equations must be balanced so that the total charges of the formula are neutral.
Covalent Bond
Definition
A bond that results from the sharing of outer
electrons between non-metal atoms
Molecule
A particle in which atoms are
joined by covalent bonds
Diatomic Molecule
A molecule consisting of only two atoms of
either the same or different elements
HOFBrINCl
Common diatomic molecules
Acids and Bases
Acids
Definition
An aqueous solution that conducts electricity,
tastes sour, turns blue litmus red, and neutralizes bases
Types
Binary Acids
Acids that contain two elements, Hydrogen and one other
Always have the "Hydro" prefix and "ic acid" suffix.
Oxyacids
Acids that contain three elements,
Hydrogen, Oxygen and one other
Acid-base Indicator
A substance that changes color depending on
whether it is in an acid or a base
Bases
Definition
An aqueous solution that conducts electricity
and turns red litmus paper blue
pH Scale
pH
A measure of how acidic a basic or solution is
pH Scale
Neutral
Neither acidic or basic; pH of 7
Physical and Chemical Reactions
Describing Chemical Reactions
Terms
Chemical Reaction
A process in which substances interact,
causing the formation of new substances
with new properties
Word Equation
A way of describing a chemical reaction using
the names of the reactants and products
Chemical Equation
A way of describing the chemical reaction using the
chemical formulas of the reactants and products
Reactant
A chemical, present at the start of a reaction, that
is used up during the reaction
Product
A chemical that is produced during a chemical reaction
State Symbols
A symbol indicating the physical state of the
chemical at room temperature
Types of Reaction
Reactants are Atoms/Molecules
Synthesis
Decomposition
Reactants are Compounds/Elements
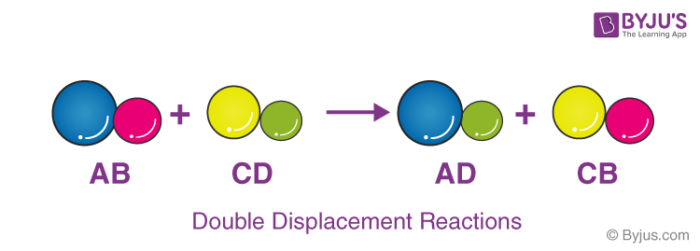
Single Displacement
Double Displacement
Conserving Mass in Chemical Reactions
Law of Conservation of Mass
The statement that, in any given chemical
reaction, the total mass of the reactant
equals the total mass of the products
Equations
The same amount of numbers, or atoms, are present
on both sides of a chemical equation
Hazardous Products and Workplace Safety
WHMIS
Product Labels
Materials Safety Data Sheet