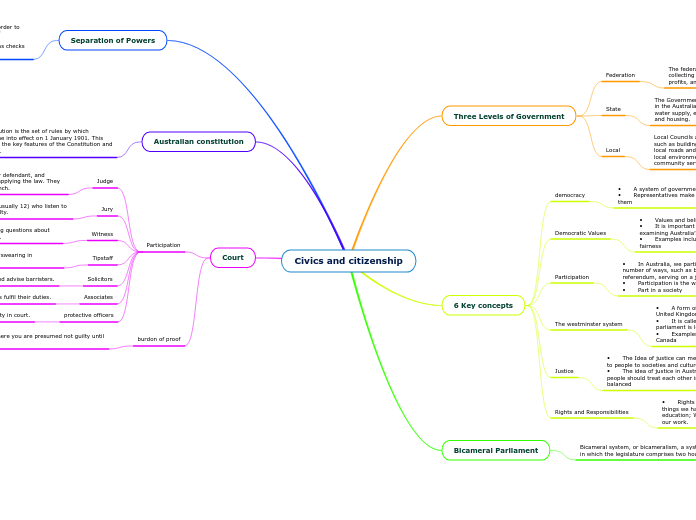
Civics and citizenship
Three Levels of Government
Federation
The federal government raises money to run the country by collecting taxes on incomes, goods and services, and company profits, and spends it on national matters.
State
The Government is responsible for all matters not mentioned in the Australian Constitution including police, education, water supply, electricity supply, health, agriculture, planning and housing.
Local
Local Councils are concerned with matters close to our homes, such as building regulations and development, public health, local roads and footpaths, parks and playing fields, libraries, local environmental issues, waste disposal, and many community services.
6 Key concepts
democracy
• A system of government run by the people for the people
• Representatives make laws for the people who elect them
Democratic Values
• Values and beliefs held by a democratic society
• It is important to understand democratic values when examining Australia’s political system
• Examples include: Freedom, respect, equality and fairness
Participation
• In Australia, we participate in the running of society in a number of ways, such as by voting in an election or referendum, serving on a jury or paying taxes
• Participation is the way good citizens contribute or take
• Part in a society
The westminster system
• A form of parliamentary government beginning in the United Kingdom
• It is called after the area of London where the British parliament is located.
• Examples include: Australia, Uk, New Zealand and Canada
Justice
• The Idea of justice can mean different thing to different to people to societies and culture
• The idea of justice in Australia ultimately means that people should treat each other in a manner that is fair and balanced
Rights and Responsibilities
• Rights are things we are able to do. Responsibilities are things we have to do. Example: We have the right to an education; We have the responsibility to attend school and do our work.
Bicameral Parliament
Bicameral system, or bicameralism, a system of government in which the legislature comprises two houses
Separation of Powers
The principle of the separation of powers is that, in order to prevent oppressive government, the three powers of government should be held by separate bodies—the Legislature, Executive and Judiciary—which can act as checks and balances on each other.
Australian constitution
The Australian Constitution is the set of rules by which Australia is run. It came into effect on 1 January 1901. This fact sheet summarizes the key features of the Constitution and how it can be changed.
Court
Participation
Judge
decide on what sentence to give a guilty defendant, and ensure proper procedure is followed in applying the law. They sit in an elevated area known as the bench.
Jury
consists of randomly chosen citizens (usually 12) who listen to a case and decide if a defendant is guilty.
Witness
present evidence to the court by answering questions about what they know about an event or person.
Tipstaff
complete many different tasks, including ‘swearing in witnesses’.
Solicitors
prepare cases and advise barristers.
Associates
help judges fulfil their duties.
protective officers
maintain order and safety in court.
burdon of proof
The burdon of proof is where you are presumed not guilty until proven guilty