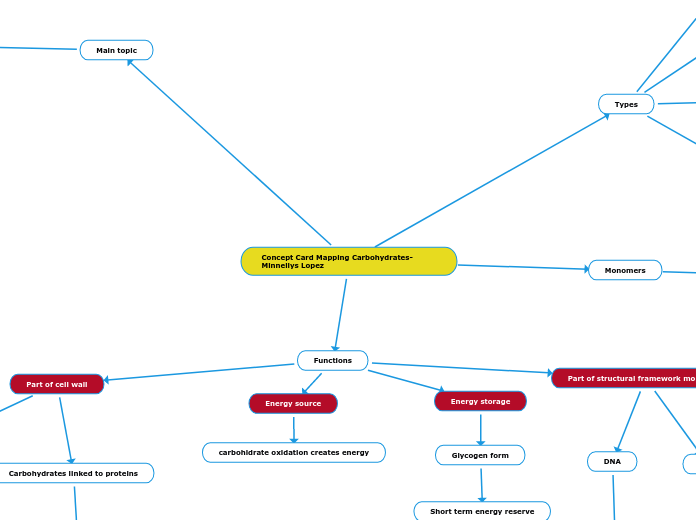
Concept Card Mapping Carbohydrates-Minnellys Lopez
Functions
Energy source
carbohidrate oxidation creates energy
Energy storage
Glycogen form
Short term energy reserve
Part of structural framework molecules
DNA
Deoxyribose
RNA
Ribose
Part of cell wall
Carbohydrates linked to lipids
Cell wall
Carbohydrates linked to proteins
Cell molecular recognition process
Main topic
Subtopic
Types
Monosaccharides
mono- = “one”; sacchar- = “sugar”
Disaccharides
di- = “two” sacchar
Linking Monosaccharides Process: Condensation- H2O released Covalent bond known as a glycosidic linkage Reversing process: Hydrolysis-add water
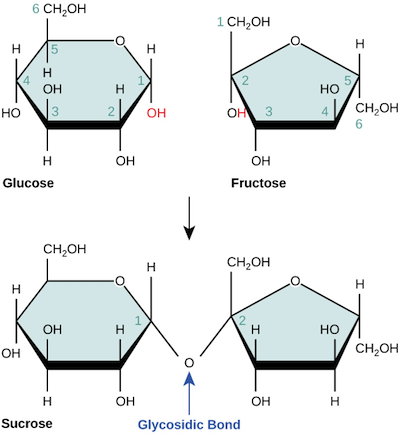
Oligosaccharides
Less than 20 monosaccharides
Polysaccharides
More than 20 monosaccharides
Fructose
Galactose
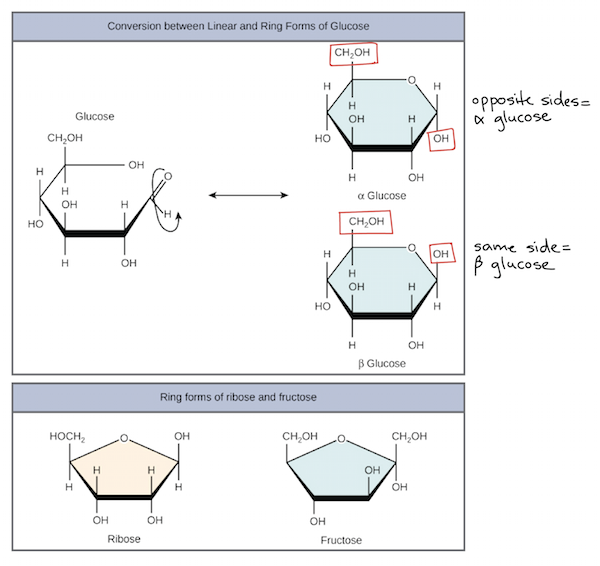
Glucose
A six-membered ring Two different forms with different properties 1) α glucose: Hydroxyl is down and CH 2OH opposite side 2) β glucose: Hydroxyl is up and CH 2OH same side
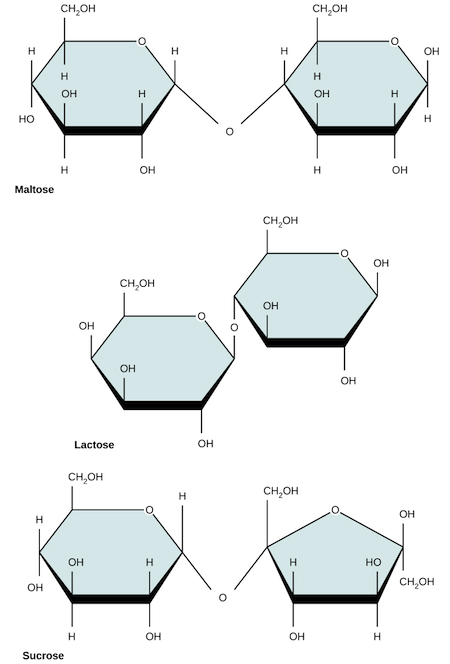
Maltose
Lactose
Sucrose
Maltotriose
Cellulose
Starch
Chitin
Amylose