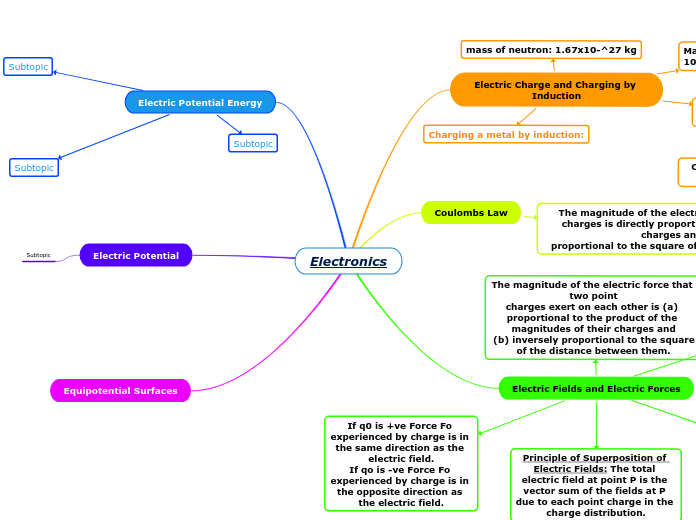
Electronics
Electric Charge and Charging by Induction
mass of neutron: 1.67x10-^27 kg
Mass of proton = 1.67x10-27
kg
Charge of proton and electron: 1.602 × 10^-19 C
Mass of electron = 9.109x 10^-31 kg
Charging a metal by induction:
Coulombs Law
The magnitude of the electric force between two point
charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely
proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Electric Fields and Electric Forces
The electric force on a charged object is exerted by the electric field created by other charged objects.
The magnitude of the electric force that two point
charges exert on each other is (a) proportional to the product of the magnitudes of their charges and
(b) inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Principle of Superposition of Electric Fields: The total electric field at point P is the vector sum of the fields at P due to each point charge in the charge distribution.
Electric Field Points towards -ve charge.
Electric Field points away from +ve charge.
If q0 is +ve Force Fo experienced by charge is in the same direction as the electric field.
If qo is -ve Force Fo experienced by charge is in the opposite direction as the electric field.
Electric Potential Energy
Subtopic
Subtopic
Subtopic
Electric Potential
Subtopic