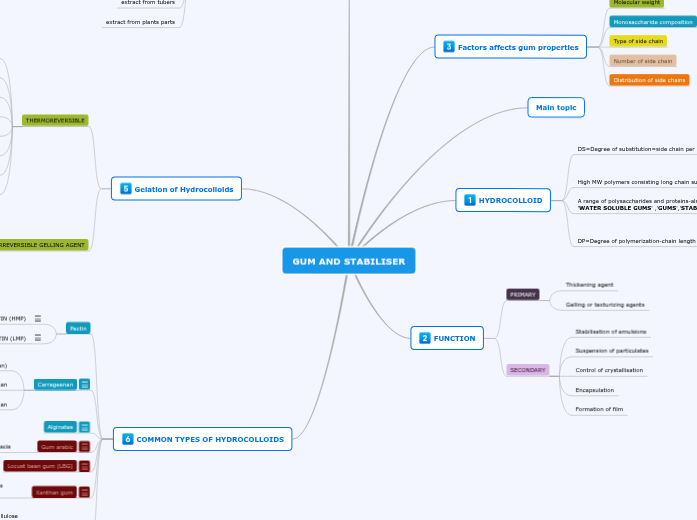
GUM AND STABILISER
Factors affects gum properties
Molecular weight
Monosaccharide composition
Type of side chain
Number of side chain
Distribution of side chains
Main topic
HYDROCOLLOID
DS=Degree of substitution=side chain per unit
Higher DS~faster to hydrate
Lower DS~slower to hydrate
High MW polymers consisting long chain sugar unit
A range of polysaccharides and proteins-also known as 'WATER SOLUBLE GUMS' ,'GUMS','STABILISERS'
DP=Degree of polymerization-chain length
Higher DP~Higher viscosity~slower to hydrate
Lower DP~Lower viscosity~faster to hydrate
FUNCTION
PRIMARY
Thickening agent
Gelling or texturizing agents
SECONDARY
Stabilisation of emulsions
Suspension of particulates
Control of crystallisation
Encapsulation
Formation of film
Main classes of Hydrocolloids
Exydation or sap of tree
extract from seed
extract from seaweeds
microbial gums
extract from tubers
extract from plants parts
Gelation of Hydrocolloids
THERMOREVERSIBLE
gelatin
agar
kappa carrageenan
iota-carrageenan
low methoxyl pectin (LMP)
Gellan gum
methyl cellulose
hydropropylmethylcellulose (HPMC)
THERMO-IRREVERSIBLE GELLING AGENT
Alginates
starch
konjac
High methyl pectin (HMP)
COMMON TYPES OF HYDROCOLLOIDS
Pectin
HIGH METHOXY PECTIN (HMP)
LOW METHOXY PECTIN (LMP)
Carrageenan
Kappa (k-carrageenan)
Lambda carrageenan
Iota carrageenan
Alginates
Gum arabic
Known as gum Acacia
Locust bean gum (LBG)
Xanthan gum
linear chain of mannose with single galactose unit attached as side chains
Cellulose
chemically modified cellulose
alkaline treatment converts cellulose into an ether
ex: carboxytmethylcellulose (CMC) , hydropropylmethylcellulose (HPMC)