key terms of term # 3
A3: 20p. handwritten mindmap, covering the term contents, showing links between key terms/processes/structures.
Assessment criteria: 10 p. If main terms, concepts (structures, processes, theories) are there.
+10p if the terms and concepts are clearly organized in a meaningful way. No long explanations are needed.
CELL

Robert hook
CELL THEORY
all living organisms are made up of cells
cell theory has 3 basic principles,
1. all organisms are composed of cells.
2. all cells come from pre-existing cells.
3. cells are smallest unit of life.
Characteristics of life
5. GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
6. NUTRITION
1. MADE UP OF CELLS
2. RESPOND TO ENVIRONMENT
7. METABOLISM
3. HEMOSTASIS
4. REPRODUCTION
8. EXCRETION
pond organisms
Chlamydomonas is green algae. Chlamydomonas is a common component of plankton and are often used by biologists to study pollution and photosynthesis.
made up of cells: single-celled organisms with nuclei and many other organelles.
Responds to Environment: A light-sensitive “eye spot” allows Chlamydomonas to sense light and swim to it using its flagella. eyespot area name is PYRENOID.
Homeostasis: contractile vacuoles fill up with water and expel it to regulate cell’s water content
Reproduction: Nucleus of cell divides via mitosis to make extra nuclei needed for cell to reproduce (usually asexual)
Growth and Development: Photosynthesis happens inside the cytoplasm (carbon dioxide is converted to compounds needed for growth)
Nutrition: Chlamydomonas absorb CO2 into the chloroplasts found in its cytoplasm. “Food” is synthesized via photosynthesis.
Metabolism: Cytoplasm contains enzymes that break down substances to release energy
Excretion: Oxygen, a by-product of photosynthesis, freely diffuses out through the cell membrane
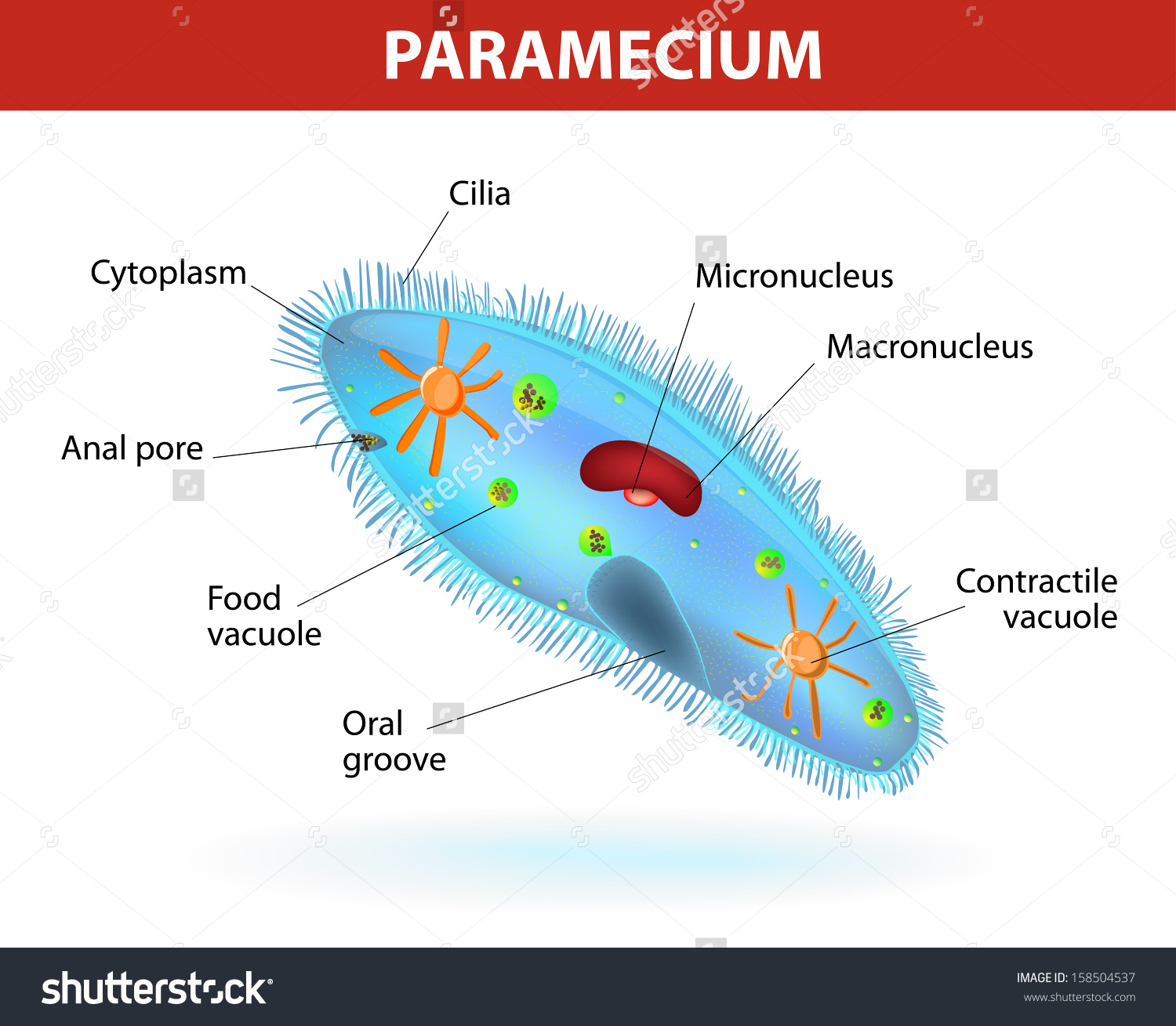
Paramecium is a unicellular organism that lives in freshwater. It feeds by ingesting small items of food through its oral groove. Food is digested inside the animal’s body, inside a food vacuole. Paramecium is one of a group of organisms known as ciliates because they move in water using rows of tiny cilia, which beat to propel them along.
made up of cells: single-celled organisms with nuclei and many other organelles.
Responds to Environment: Paramecium control beating of cilia to move in different directions in response to changes in environment
Homeostasis:
contractile vacuoles fill up with water and expel it to regulate cell’s water content
Reproduction: Nucleus of cell divides via mitosis to make extra nuclei needed for cell to reproduce
Growth and Development: The cell will enlarge until a maximum size, at which point it will divide
Nutrition: Paramecium consumes smaller organisms that are packaged into food vacuoles. “Food” is gradually digested and absorbed into the cytoplasm.
Metabolism: Cytoplasm contains enzymes that break down substances to release energy
Excretion: Waste products are excreted through anal pore.

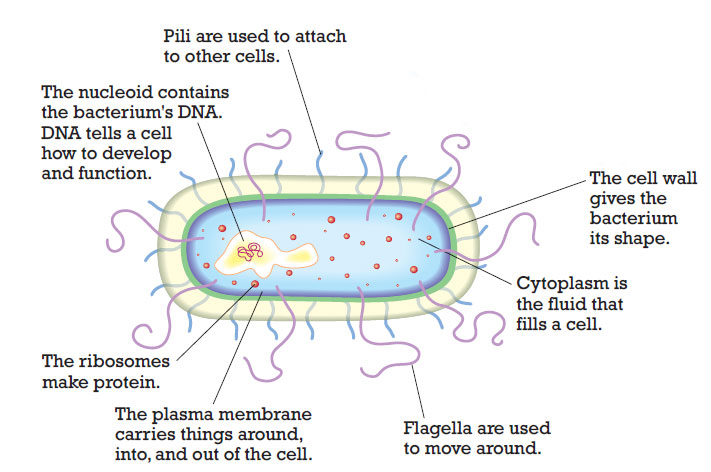
PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS
EUKARYOTIC CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS

PROKARYOTIC CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS

plasma membrane

Types of Transport
Tonicity is a term that describes
the ability of a solution to cause a
cell to gain or lose water
Active Transport
1. movement of materials from low concentration to high concentration).
2. it requires ATP.
Sodium-Potassium Pump

Passive Transport
1. movement of material from high concentration to low concentration)
2. It does not require ATP
There are three main types of passive transport:
1. Simple diffusion – movement of small molecules (e.g. O2, CO2, etc.) through plasma membrane.
2. Osmosis – movement of water molecules.
3. Facilitated diffusion – movement of large or charged molecules via membrane proteins (e.g. ions, sucrose, etc.)

Aliaihe
Osmosis is the net movement of water molecules across a semi-permeable membrane from a region of low solute concentration to a region of high solute concentration (until equilibrium is reached).
Effects of Solute Concentrations on Cells

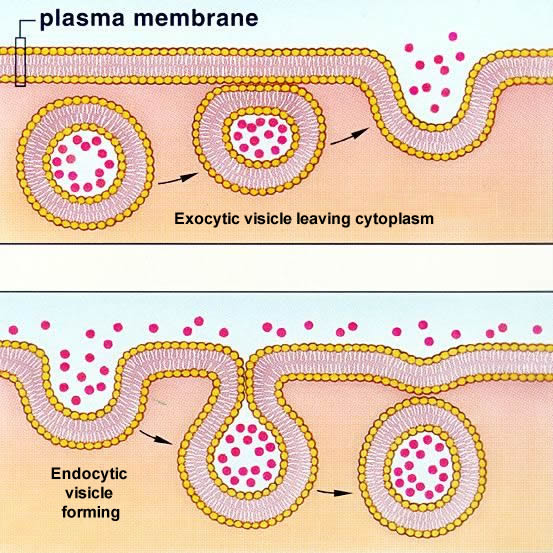
Vesicular Transport:
Materials destined for secretion are transported around the cell in membranous containers called vesicles
materials pass through two places and are then secreted:
1.Endoplasmic Reticulum
2.Golgi Apparatus
Endoplasmic Reticulum:
Materials are transported from the ER when the membrane bulges and then buds to create a vesicle surrounding the material
Golgi Apparatus:
The vesicle is then transported to the Golgi apparatus and fuses to the internal (cis) face of the complex
BULK TRANSPORT:
The spontaneous breaking and reforming of the bilayer, allowing larger materials to enter or leave the cell without having to cross the membrane (this is an active process and requires ATP hydrolysis)
Subtopic
Tumors:
Tumors are abnormal cell growths resulting from uncontrolled cell division and can occur in any tissue or organ.Diseases caused by the growth of tumors are collectively known as cancers.
A mutagen is an agent that changes the genetic material of an organism.

Oncogenes:
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer

positive correlation / negative correlation / no correlation
extra knowledge

Aliaihe
cell cycle

Mitosis: it is a process of nuclear division by which replicated copies of cells DNA are organized into chromosomes. the identical copies of the DNA are then divided equally between two daughter cells.
Mitosis is four steps process
1. prophase
2. metaphase
3. anaphase
4. telophase
A. PROPHASE:
1. nuclear membrane and nucleolus
begin's to fade.
2. dna condences to form chromosomes.
3. mitotic spindle begins to form and attach
to center of chromosomes
B. METAPHASE:
1. CHROMOSOMES MOVE TO CENTER OF CELL BY SPINDLE MICROTUBULUSES
D. TELOPHASE
1. the nuclear membrane begins to reform and chromosomes relax as DNA unwinds.
telophase is followed by cytokinesis(division of cytoplasm).
cytoplasm is divided into two equal parts means original cell is divided into two daughter cells.
C. ANAPHASE:
chromosomes is broken down into chromatids and taken to opposite directions.

meiosis

Stem cells = cells, that have
ability to differentiate
and divide

How/for what could one use stem cells?
A. Adult stem cells are transplanted for therapy
e.g. Bone marrow and variety of blood disorders (leukemia, lymphoma..)
B. Embryonic stem cells are transplanted in therapy
= culturing and differentiating embryonic stem cells to replace lost/damaged tissues, even grow new organs. treatments for
– Cardiac – following heart damage
– Nervous system – stroke/spinal cord, Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s
– Burns
– Diabetes
– Solid organ regeneration
Stargardt’s disease:
The progressive vision loss associated with Stargardt disease is caused by the death of photoreceptor cells in the central portion of the retina called the macula.
Cells capacity to divide and differentiate decreases during development
A. Totipotent: can become any type (cells from early embryos – 1-3 days)
B. Pluripotent: – cells can form any cell type except embryonic
membrane, placenta – from blastocyst inner cell mass (5 to 14 days)
C. Multipotent: – cells are to certain extent differentiated, but can still
become a number of different cell types – found in fetal tissue, cord
blood, adults in varying locations
D. Unipotent: can only become one cell type.
E. Nullipotent: cannot divide (red blood cells)

basic teechniques to know for exam
1. multiplying DNA (PCR)

3. DNA profiling

2. DNA fingerprinting


