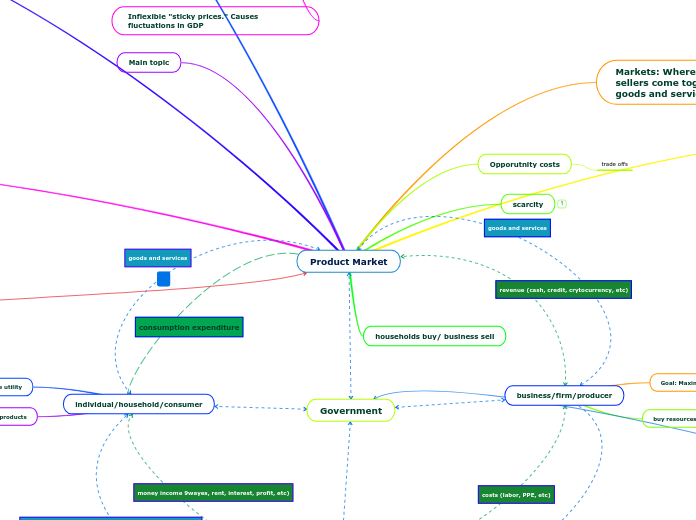
Product Market
Markets: Where buyers and sellers come together to exchange goods and services
Supply and Demand
Opporutnity costs
trade offs
scarcity
households buy/ business sell
The Business Cycle
Aggregate Demand
Main topic
Aggregate Supply
individual/household/consumer
Goal: Maximize utility
sell resources, buy products
business/firm/producer
Goal: Maximize profit
buy resources, sell products
Resource Market
Unemployment
consumption expenditure
revenue (cash, credit, crytocurrency, etc)
goods and services
resources
costs (labor, PPE, etc)
resources- factors of production (land, labor, capital, entrepreneurial)
money income 9wayes, rent, interest, profit, etc)
goods and services
Supply: amount producers are able/willing to sell at given price
Demand: amount consumers are able/willing to buy at given price
Law of Demand
as price rises, quantity demanded falls
As price falls, quantity demanded rises
Determinates
change in consumer expectations
change in income
change in price of related goods
change in consumer tastes
change in # of consumers
Consumer surplus
what consumers are willing to pay vs what they actually pay
Demand Failure
Law of Supply
As price rises, quantity supplied rises
As price falls, quantity supplied falls
Producer Surplus
what producers are willing to get paid vs what they actually get paid
Supply failures
Determinates
change in producer expectations
Change in number of sellers
change in taxes
change in price of other goods
change in resource costs
change in technology
Equilibrium- Where supply and demand intersect. Where the price is right
Types of Markets
Command: Government determines how things are made/sold
Mixed: Mix of Command and Market
Market: Consumers choose what they buy (invisible hand)
Traditional: Relies on customs, religion, etc.
Real GDP
GDP (Gross Domestic Product)
Adjusts for inflation
Nominal GDP/ price index
Inflexible "sticky prices." Causes fluctuations in GDP
Nominal GDP
In Current U.S. $'s
Calculating GDP
Income Approach
Expenditures approach. COGS
Economic Growth
determinates of growth
efficiency factors
demand factors
supply factors
economic scale
increasing returns
increase GDP over time
modern economic growth
approx # of years to double real GDP
GDP per capita= GDP/population
Multiplier effect= change in GDP/ initial change in spending
Phillip's Curve
inverse relationship between unemployment and inflation
Types of Unemployment
Structural: difficult to find new jobs without retrain, relocate, etc
Frictional: Those looking for a new job
Cyclical: Unemployed because of less spending
=Unemployed/Work Force
Work Force= 16+, not in jail, not in active service, not retired, actively searching for a job
Phases
peak
Recession
Trough
Expansion
Demand- side shocks (taxes, unemployment, financial instability)
Supply- side shocks (changes in resource prices, political events, natural disasters, new technology)
Downward sloping because:
real balance effect
interest rate effect
foreign purchases effect
Factors that shift the AD curve
government spending
consumer spending
investment spending
net export spending
expected returns
borrowing
expectations
consumer wealth
personal taxes
Factors that shift the AS curve
input prices
productivity
Legal- Institutional environment
price of imported goods
time horizons
immediate short run
input and output prices are fixed
long run
input and output are variable
short run
input is fixed and output may vary
Government
Government
Public Goods
externality
"Free Rider Problem"
nonexcludability
nonrivalry
Quasai- Public Goods
Fiscal Policy
tax systems
progressive: avg rate= tax revenue/ GDP
Proportional: rate stays the same as GDP rises
Regressive: rate falls as GDP falls
built in stabilizers
Budget Deficit
increased government spedning
less taxes
Budget Surplus
less government spending
increased taxes
Expansionary FP
when recession occurs
raise real gdp
+ gov't spending, - taxes
Contractionary FP
when demand-pull inflation occurs
decrease aggregate demand
- gov't spending, + taxes
Problems with Fiscal Policy
Future policies/ reversals
Timing
recognition lag 9seeing what's happening)
administrative lag (getting policy)
operational lag (seeing effects)
offsetting local/state finances
political consideration (using policies to boost votes)
Money
Money M1
currency + all checkable deposits
Financial Services industry
commercial banks
insurance companies
thrifts
security funds
mutual fund companies
investment banks
Fed Functions
issuing currency
setting reserve requirements
proving for check collections
lending to financial solutions
supervising banks
acting as a fiscal agent
controlling the money supply
Federal Reserve Banks
Assets
securities
loans to commercial banks
Liabilities
reserves to commercial banks
treasury deposits
federal reserve notes outstanding
Money M2
M1 + savings deposits, including MMDA + small denominated time deposits +MMF held by individuals
Purchasing power
$V- 1/P
interest
interest yield
bond/interest rate
Money Creation
Monetary multiplier
tools of monetary supply
open market operations
Selling securities
bank transactions to create money
1. create a bank
2. acquiring property and equipment
3. accepting deoposits
4. depositing reserves in a Fed Reserve bank
5. clearing a check drawn against the bank
6. granting a loan
7. buying government security
monetary policy
Asset Demand for Money
transactions demand for money
fractional reserve system
required reserve
reserve ratio (>20%)
excess reserve 9actual reserve - required reserve)