physical Geography of
Canada
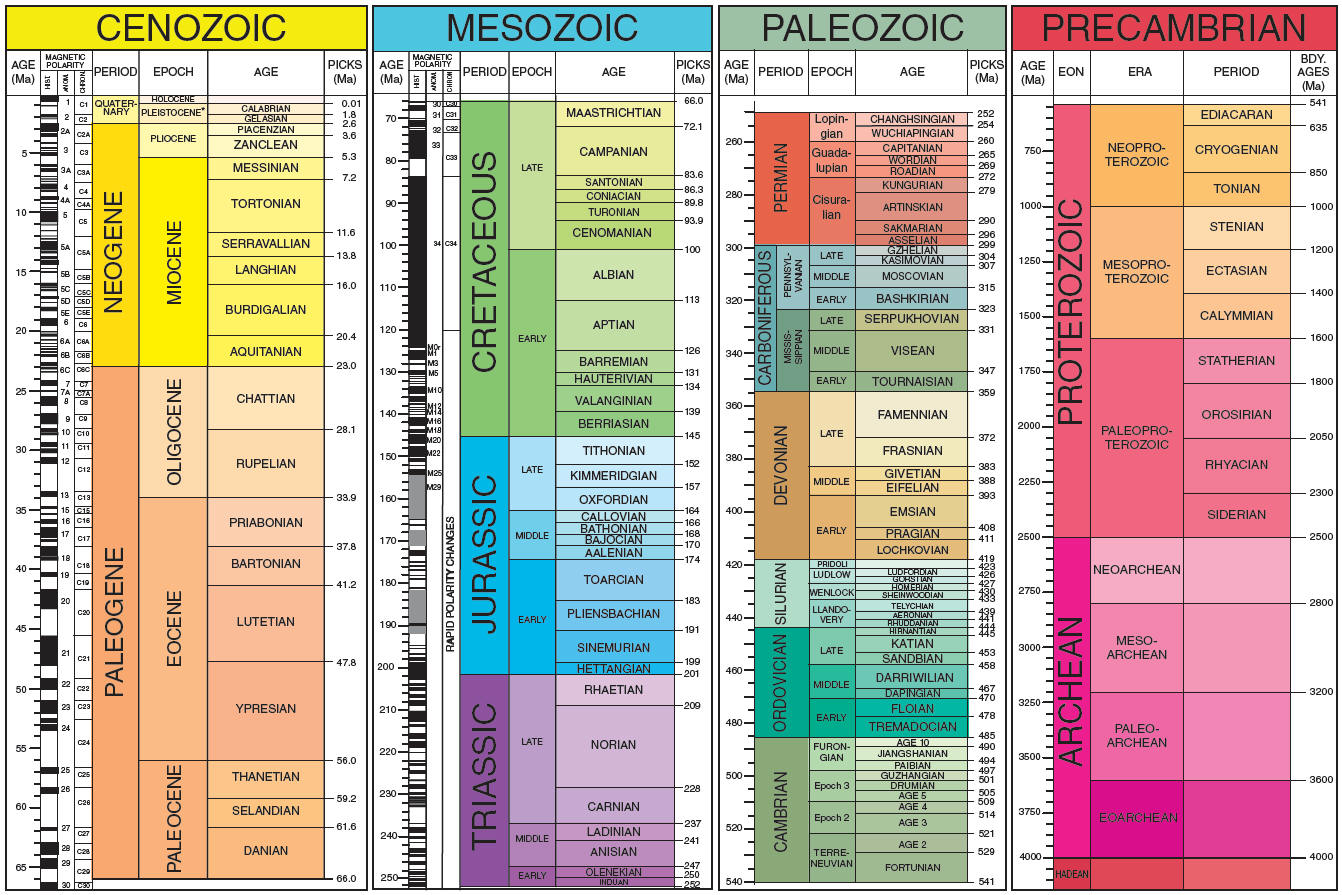
Geologic time
Human life
Earth life
Mesozoic
Cenozoic
Paleozoic
Precambrian
How it all began
Science
Big bang
Success universe theory
Religion
Religious creation

Turtle island

Earth layers
Crust
Lithosphere
Atmosphere
mantle
Outer core
inner core

Ice ages
Ended 100 years ago
Humans were alive living on ice
Earth had many heating + cooling ages
Glaciation
Earths Physical Features

Erosion
Wind
Water
Ice
Landslide
Earthquakes
Volcano's
Folding
Mountains
Soft rock
Faulting
Hard rock
diamonds

Types of precipitation

Relief precipitatipn
Cyclonic precipitation

Vegetation
Decidous
Convenctional preciptation
Hardwood
Broad leafed trees
Softwood
Coniferous
Needles
Prarie grasslands
Short or long grass
Tundra
Perma frost
Treeline
The more north you go smaller the trees get

Natural disasters
Ring of fire
Hurricanes
Tornados
Tsunamis
Earthquakes
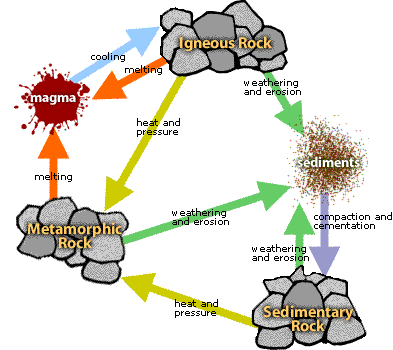
Rock cycle
Igeous rock
Magma rock
Metaphoric rock
Sedimentary rock
Sediment

Climate Systems
Latitude
Ocean currents
Wind
Elevation
Relief precipitation
Near water
Humans
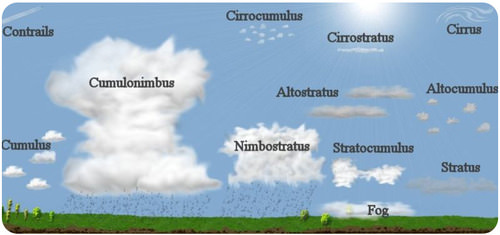
Classification Of Clouds
Cirrus
Cirrocumulus
Cirrostratus
Cumulonimbus
Altostratus
Altocumulus
Stratocumulus
Cumulus
Nimbostratus
Stratus
Soil
Ingredients
water
Minerals
Air
Decomposing organic matter

Types of soil
Humus
Soil
Sand
Clay
Gravel
Bed rock
Calcification
National parks
Banff national park
Jasper national park
Yoho national park

Algonquin national park
Waterton Lakes national park

Landform regions
Western cordillera
Interior plains
The canadian shield
Hudson bay lowlands
Great lakes- st lawerence lowlands
Appalachian
Artic lowlands

Climate Regions
Artic
Talga
Cordilleran
Pacific maritime
Boreal
Prarie
South eastern
Atlantic maritime
