neurology
Biochem
Na (135-145mmol/L)
Urea (3.0-8.5mmol/L)
K (3.5-5.0mmol/L)
PO4 (0.75-1.5mmol/L)
CRP, Alb
Cholesterol
Triglycerides
clinical presentation
Paralysis
Immobility
Abnormal motor dysfunction
Neuropsychological disorders (depression)
Oropharyngeal dysphagia
Dysphasia (speech comprehension/generation impairment)
Disordered swalloing
Oral phase usually 1-2 sec, pharyngeal <1s, Oesophageal 8-10s
Aphasia- speech impairment
Impact- impaired ability to obtain, prepare and consume food safely
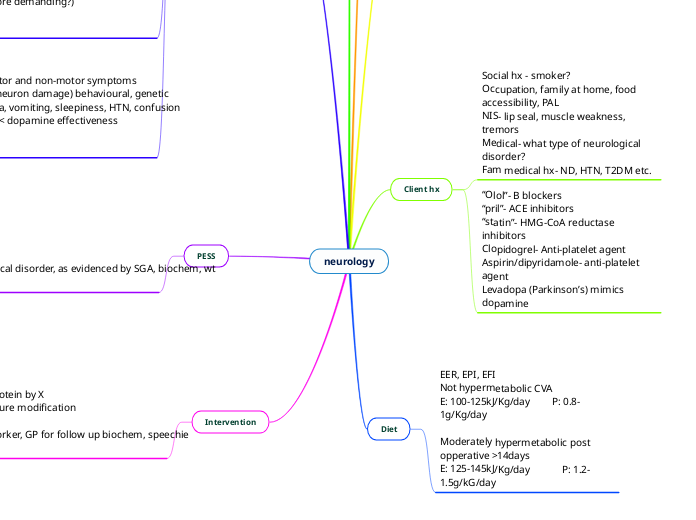
Client hx
Social hx - smoker?
Occupation, family at home, food accessibility, PAL
NIS- lip seal, muscle weakness, tremors
Medical- what type of neurological disorder?
Fam medical hx- ND, HTN, T2DM etc.
“Olol”- B blockers
“pril”- ACE inhibitors
“statin”- HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors
Clopidogrel- Anti-platelet agent
Aspirin/dipyridamole- anti-platelet agent
Levadopa (Parkinson’s) mimics dopamine
Diet
EER, EPI, EFI
Not hypermetabolic CVA
E: 100-125kJ/Kg/day P: 0.8-1g/Kg/day
Moderately hypermetabolic post opperative >14days
E: 125-145kJ/Kg/day P: 1.2-1.5g/kG/day
Anthro
Wt decrease
wt % decrease
Check SGA
BMI- CVA could be as same as CVD
Neurological conditions
Stroke/CVA
- Ischaemic (70% of cases)= obstruction of cerebral blood flow= heart attack
- Haemorrhagic: rupture of weakened blood vessels
- Weakness, paralysis, speech difficulties, dysphagia, impaired cognition
MS- multiple sclerosis
MOST common in young adults
- Disease of white matter on CNS affecting brain and SC
- Immune system attacks myelin sheath; impaired nerve translation
Symptoms: fatigue, bladder & bowl issues, muscle weakness, spasticity, ataxia, tremor, neuropathic pain, mood swings. Intervention: Vit D can help in severe cases
MND- Motor neuron disease AKA amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Degeneration of motor neurons in the brain stem and SC
- Weakness and wasting of muscles
- 20% of MND develop malnutrition
- 70-80% develop dysphagiaundefined
Huntington's disease
- 20-40 years of age
- Faulty chromosome of 4
- Speech difficulties, mental deterioration, cognitive decline associated w/ dementia
- Impaired ability to self-feed, depression, aggression, antisocial behaviour
- EE raise (mitochondria less efficient/more demanding?)
Parkinsons
- 18% affected are of working age
- Progressive neurological condition. Motor and non-motor symptoms
- Factors: environmental (toxin induced neuron damage) behavioural, genetic
- Dopamine agonists side effects: Nausea, vomiting, sleepiness, HTN, confusion
- Anticholinergic agents: Block acetyl Ch < dopamine effectiveness
PESS
- Inadequate energy and protein
- Malnutrition
- Inadequate oral intake
As related to NIS on the BG of nuerological disorder, as evidenced by SGA, biochem, wt loss, EEI, EPI
Intervention
Goal: increase energy by X increase protein by X
HEHP, nutrition oral supplements, texture modification
motivational interviewing
Coord: psych, EP for CVA, OT, social worker, GP for follow up biochem, speechie for follow up