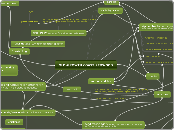
OLD-GROWTH COAST REDWOOD
carbon
carbohydrates
Mycorrhizal Network (connects fungus, bacteria, and roots from plants and trees. Keystone for redwood forest.)
mycorrhizal propagules
mammals
indirectly water transfer for photosynthesis
nutrient transfer (especailly phosphorus)
plant hormones
nitrification (nitrate) ammonia
roots/exudates
rizosphere (good in droughts): organic acids, enzymes, amino acids, proteins, simple sugars, carbon
hyphae from mycorrhizal fungus
tree crown (nutrients from air through epiphytes)
photosynthesis
Oxygen
coastal fog reduces transpiration, which keeps stomata open, allowing for more carbon dioxide intake.
Lichen (alga and fungus-rock weathering for soil) (endophytes inhibit plant pathogens)
Douglas fir
voles
marten
fisher
Coastal Fog
Decrease temperature, increase humidity, reduce solar radiation (prevents denitrification)
foliar uptake (80% redwood forest species)
regeneration
wood rats strip bark off new trees
nutrients, water, sunlight
plants
moisture
soil compostion (nutrients)
lower nutrient
Pigmy forest-provides a range of habitats through this ecotone
Diversity in plants (Keeps soil nutrient rich and promotes soil organisms)
pH
Disturbances
erosion/landslides
colluvial and alluvial sites
change aquatic sites, causes silt to alter fish habitats, loss of steep banks
floods
soil minerals
fires
Coast redwood has high resistance and fire thins understory allowing more nutrient availability for the old-growth trees (reduces competition and monitors invasive species).
minerals from leaching
controls pests
It can also cause loss of nutrients through heat and fly ash.
global warming
increase in temperature, less fog, moisture, and possible drought which leads to insufficient nutrients, and less primary productivity.
logging
compacting soil (which negeatively effects plants because less oxygen and water. With less vegetation there is more solar radiation and denitrifiers prosper, taking the nitrogen out of the soil), damage aquatic sites,
causes invasive species because of excess solar radiation
monoculture sites drains nutrients and soil organisms from soil
possible old-growth recovery over time
canopy drip
animals/insects (disperse fungi and seeds)
chickaree
cerambycid beetle
Endangered species
Marbled Murrelet
Spotted Owl
saprophages (bacteria, fungi, macroinvertebrates)
nitrogen-fixation
chelators (increase solubility of nutrients)
transfers nutrients from soil to litter through hyphae
immobilize, mineralize nutrients (nutrient conservation)
soil protozoa, invertebrates, fauna
reduce fungi favoring bacteria
NH3
dead trees/logs (auotgenic engineers) environment for nitrifixation, animals, and microbes.
allogenic engineers (possibly aid in regeneration of plants)
microlitter,CWD, litterfall
decomposition of organic material
saproxylic insects
makes cavaties for birds
insect infestations, herbivores
birds (Pileated Woodpecker)
control insect infestations
Sometimes causes decay on upper trunk