The Origins of Theatre

Aristotle's 3 Unities
Unity of Action: one single plot with no loose threads

Unity of Time: action takes place within a single day

Unity of Place: action takes place in a single location
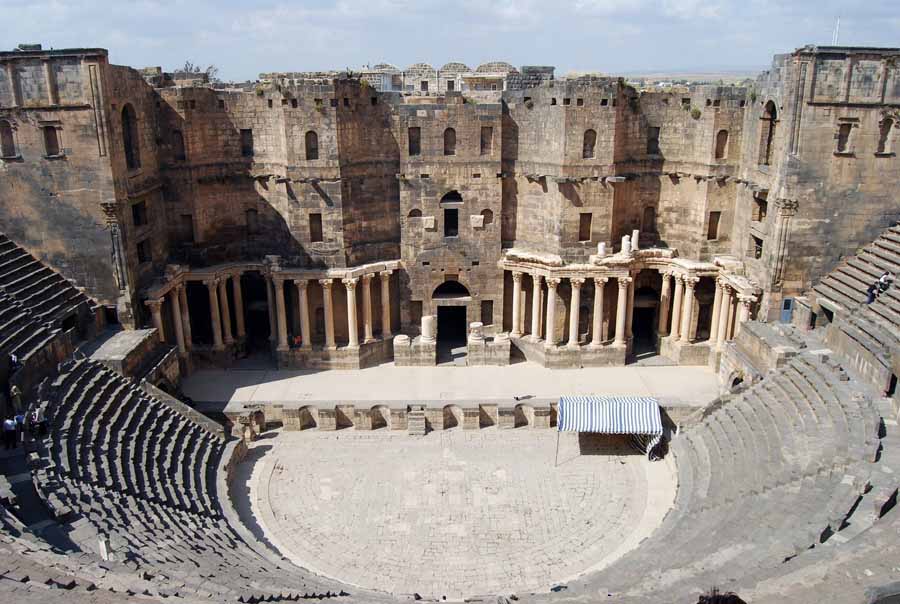

Living in Ancient Rome
The Theater and Domestic Games
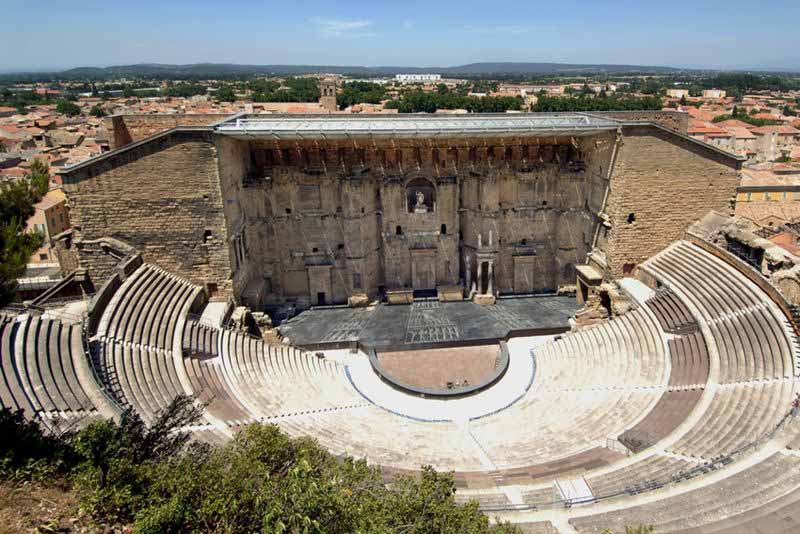

Theaters are similar to Greek's except they are made of concrete and stone, and are more elaborate and larger in size
The first theater was built by Pompey the Great and it can seat 27 00 people
Before the Greeks' influence, theaters were flimsy and only created for a particular God

Actors, Masks, and Plays
Actors wear masks and women are allowed to perform too

The masks enhance expression and amplify voices
The most popular plays are mime, pantomime and bandy farces. They are violent, but sophisticated.
Pantomimus: one who imitates all things and mime the story's actions using masks, musicians and dancers

Scaenae Forms: a backdrop that is threes stories tall and has a hundred columns

Pulpitum: a stage where the actors perform

Ritual
A ritual is the observance or enactment or dramatization of a set form of rites (ceremonies).

Elements of Rituals:
1. Repetition and Stylization of verbal and non-verbal actions (chanting or gestures)
2. Symbolic Role
3. Sense of order
4. Collective Identification
Equivalent for Theater
A church, synagogue or temple is a theater
An alter or platform is a stage
A priest or an elder is an actor
Believer, followers or congregation is an audience
A torah, scripture, Qur'an or Bible is a script
Ritual is based on reality while theater is the imitation of reality
Ritualization is the creation and enactment of new rites
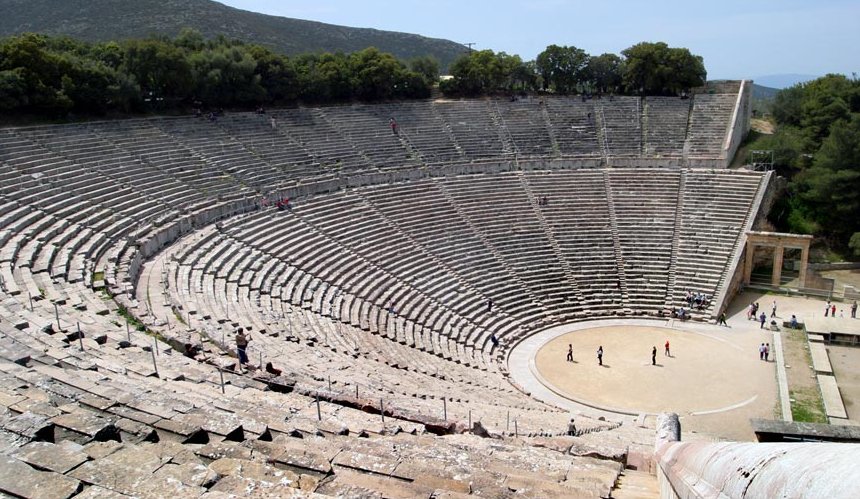

Living in Ancient Greece
A Day at the Theater

Dionysus Festival: Athens' most religious celebration that lasts five days, the first day devoted to processions and sacrifices, and the last 4 days are taken up with drama and competition.

Aeschylus: father of modern theater
Interesting Facts
Drama is a Greek word meaning action.

From the name of Thespis, who wrote the first play with dialog, we derive the word "thespian", meaning actor.
The Theater Festival of Athens
The three most popular play writers:

Euripides
Focuses on common emotion and weaknesses of mankind, making it relatable to the audience.
Play finales involve actors subjecting to the judgement of God.

Aristophanes
Plays contain attacks of Athenian officials, music, and a lot of action.
Very humerous

Sophocles
Plays fores the imagination of theatre-goers
He is the master of dramatic tension.
Plays contain amazing conclusion that thrill audiences
There were three types of plays:

Tragedies
Themes are about human passions and conflicts, the misuse of power, and whether or not to bow to the will of God.
Usually about heroes of the Mycenean past
Each year three tragedy play writers enter their plays into the contest

Comedies
Feature ordinary folk, with commentaries on the politics and personalities of the day
Humorous with rude jokes
Five authors enter one play each every year

Satyr
A play that makes fun of the tragic theme of another play, both written by the same author
When performing, people dress as satyrs (half-man, half-beast)
The Actors
All men
Have emphasis on speech, not action.

Tragic figures wear dark costume, while comic figures wear bright colors
Padded clothes, large shoes and wigs are common
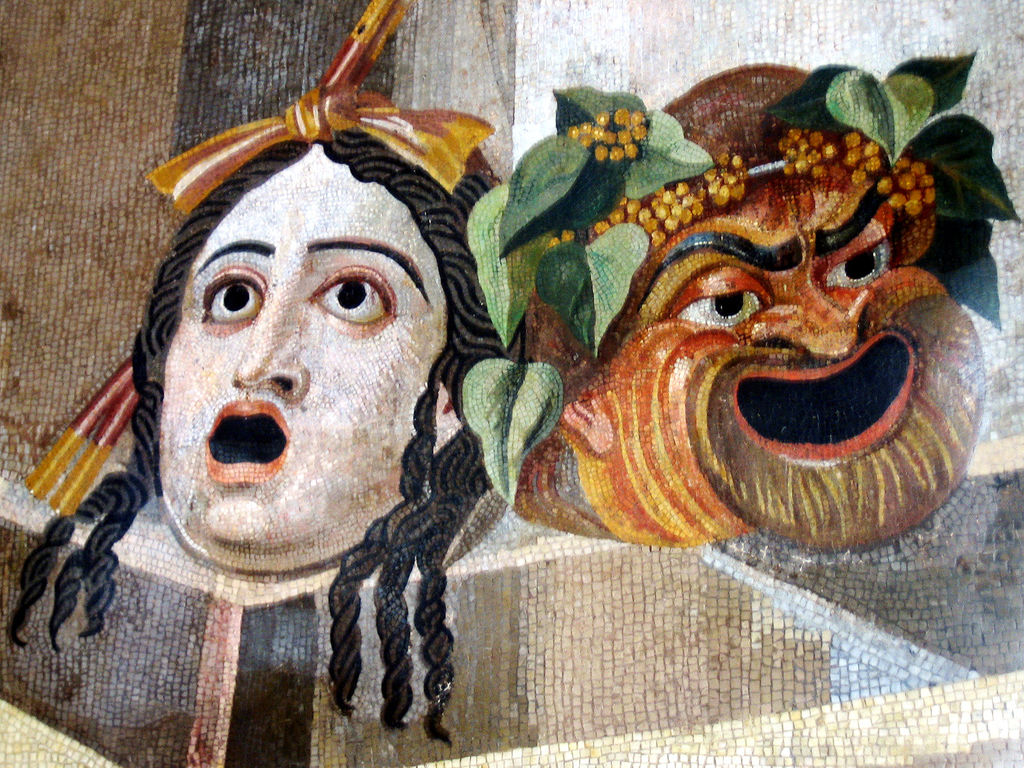

Masks
Painted masks of stiffened fabric
the expression show cahracters' gender, age, feeling, etc.
Actors can easily switch roles by changing there masks
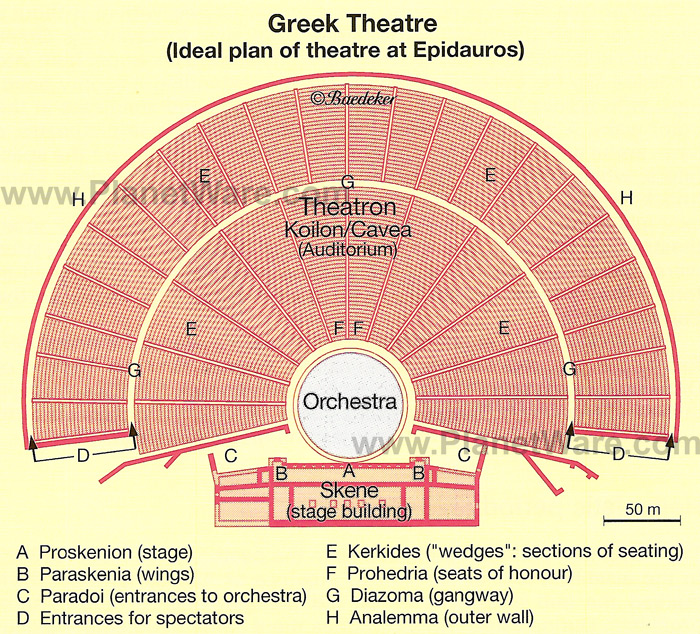
Inside the Theater
Cavea: blocks of seats inside an auditorium
Proedria: the first and lowest row of seats reserved for senior figures
Polis: a city state in Ancient Greece
Theologeion: flat roof covering the stage
Aeroema: a crane that allows actors to fly onto the skene
Ekeclema: wheeled platform for presenting or removing "dead" characters
Periaktoi: triangular pillars that are turned to present a new item of scenery or remove an old one

The Theater's Main Elements
Orchestra: circular, oval or rectangular chorus space located in front of the logeion
Koilon: a auditorium built in a semi-circle of rising stone seating
Skene: backdrop
Logeion: raised platform, main stage that allows actors to stand over proceedings
Koryphaios: director of the orchestra
Themili: a small Dionyslan altar of the threshing floor
Proskenion: acting areas, forward edge of the logeion
Paradoi: two walkways between the skene and the koilon
Parados: an ode sung at the orchestra in the beginning of the play
