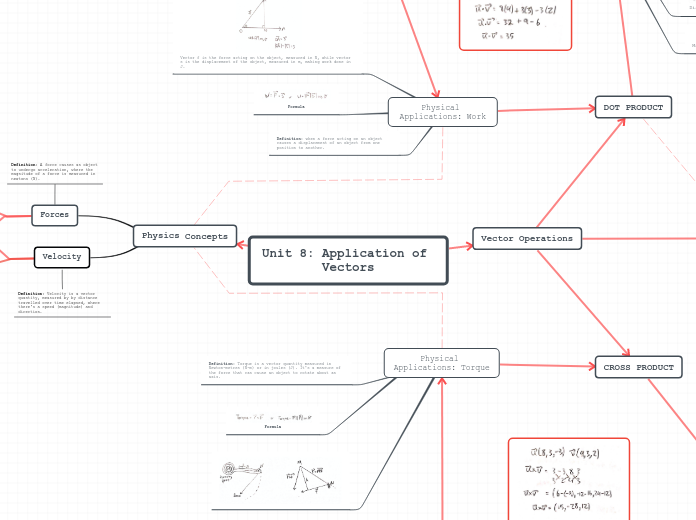
Unit 8: Application of Vectors
DOT PRODUCT
CROSS PRODUCT
Equilibrium
Definition: a state of rest or a state of uniform motion, meaning the net force is 0, velocity is unchanging (steady speed), meaning an acceleration of 0.
It is the counterbalance of the resultant force.
Resolve
Definition: Taking a single force and decomposing it into two components. A
vector can be resolved into its corresponding horizontal and vertical components by creating a right triangle with the given vector. The magnitudes of the vertical and horizontal components can be found using primary trigonometric ratios and a given angle.
PROJECTIONS
Physical Applications: Work
Vector f is the force acting on the object, measured in N, while vector s is the displacement of the object, measured in m, making work done in J.
Formula
Definition: when a force acting on an object causes a displacement of an object from one position to another.
Special Case
Perpendicular Vectors
Formulas
Properties
The dot product is a scalar product
Commutative Property
Associative Property With A Scalar
Distributive Property
Magnitudes Property
Physical Applications: Torque
Definition: Torque is a vector quantity measured in Newton-metres (N-m) or in joules (J). It's a measure of the force that can cause an object to rotate about an axis.
Formula
Properties
The cross product is a vector product
Not Commutative
Distributive Law
Scalar Law
Formulas
Special Cases
Parallel Vectors
Area of a Parallelogram/Triangle
Formula for area of a parallelogram. Area of a triangle is 1/2 of the area of a parallelogram.
Vector Operations
Physics Concepts
Forces
Definition: A force causes an object to undergo acceleration, where the magnitude of a force is measured in newtons (N).
Velocity
Definition: Velocity is a vector quantity, measured by by distance travelled over time elapsed, where there's a speed (magnitude) and direction.