arabera Aulakh Mehak 3 years ago
497
internal systems assignment
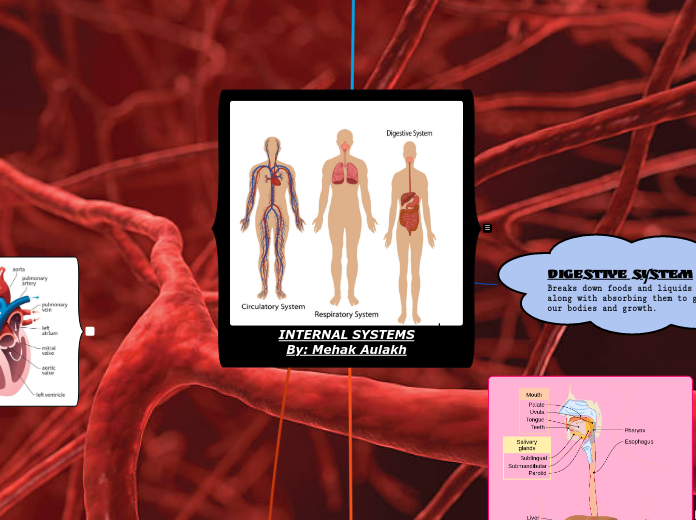
arabera Aulakh Mehak 3 years ago
497

Honelako gehiago
(Vitamins and Minerals, 2012)
(Lovering, 2021)
(Biofabricating the human circulatory system, 2020)
(Human Body- Organ Systems Test, 2021)
Ch. 1 Introduction - Biology 2e | OpenStax. (2018). Openstax.org. https://openstax.org/books/biology-2e/pages/1-introduction
Enzymes: What Are Enzymes, Pancreas, Digestion & Liver Function. (2022). Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/21532-enzymes
The Digestive Process: What Does the Small Intestine Do? | University Hospitals. (2021). Uhhospitals.org. https://www.uhhospitals.org/health-information/health-and-wellness-library/article/adult-diseases-and-conditions-v1/the-digestive-process-what-does-the-small-intestine-do
What are proteins and what do they do?: MedlinePlus Genetics. (2021). Medlineplus.gov. https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/understanding/howgeneswork/protein/
Pharynx: Anatomy, Function, Throat, Tonsils. (2022). Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/21869-pharynx
Coeliac disease and gluten sensitivity - Better Health Channel. (2017). Vic.gov.au. https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/coeliac-disease-and-gluten-sensitivity#:~:text=It%20affects%20the%20small%20intestine,other%20parts%20of%20your%20body.
Chronic Bronchitis. (2013). Physiopedia. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Chronic_Bronchitis
Health, A. (2020). How to use your peak flow meter. Healthing.ca; Healthing.ca. https://www.healthing.ca/other/how-to-use-your-peak-flow-meter/
Cafasso, J. (2019, April 8). 10 Symptoms of a Lung Infection. Healthline; Healthline Media. https://www.healthline.com/health/symptoms-of-lung-
infection#:~:text=A%20lung%20infection%20can%20be,be%20caused%20by%20a%20virus.
Body, V. (2021). Red blood cell. Visiblebody.com. https://www.visiblebody.com/learn/respiratory/5-functions-of-respiratory-system
Newman, T. (2021, December 21). What is the function and structure of the lungs, and how to do a lung function test. Medicalnewstoday.com; Medical News Today. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/305190
Irritable bowel syndrome - Symptoms and causes. (2021). Mayo Clinic; https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/irritable-bowel-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20360016
heart attacks can lead to irregular heart beats
a normal resting heart rate is 60-100 beats per minute
it can vary with a person having a heart attack
(Heart attack - Symptoms and causes, 2020)
treatment for a heart attack
take aspirin
begin cpr on the affected patient if they are unconscious
Call 911 right away
Symptoms
pressure or squeezing
chest pain or discomfort
diagram displaying how your heart looks when a heart attack is present
(Heart attack - Symptoms and causes, 2020)
to help prevent them
Be careful of your diet take care of your body
blood flow being blocked to the heart
with no blood flow the muscles in the heart begin to die
if not restored in time
it can lead to serious life threatening problems
death
heart failure
permanent heart damage
Pulmonary circulation allows the flow of the blood to go away from the heart where then oxygenation occurs and returns back to the heart again
Systemic and Pulmonary Circuit
(Circulatory Pathways | SEER Training, 2022)
Systemic circulation flow blood away from the heart to the brain, liver, kidneys, stomach, other organs, limbs, muscles of the body and then return this blood to the heart
3rd Type of blood vessel in your body that takes deoxygenated blood from your body back to your heart to be breathed out by your lungs
(Body, 2021)
Blood provides our body cells with oxygen and removes waste like carbon dioxide from cells
(Cade Hildreth (CEO, 2018)
2ed Type of blood vessel that are super tiny which pass oxygen and food nutrients each body cell as well as take away
(Capillary Fluid Exchange Video, 2021)
1st Type of blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood (except for the pulmonary artery) away from your heart to all body cells
(Rimas Gilvydis, 2019)
Alveoli is located where the lungs and blood exchange carbon dioxide during the process of breathing in and out
(L.W, 2020)
made up of 3 layers of tissues
made up of a overall tissue called- cardiac muscle
1- Endocardium --> thin layer of lining around the heart chambers which forms the surface of the valves
2 -Myocardium --> heart chambers to contract which then also relax your body to pump blood by the thick layer of muscle in your heart
3- Pericardium --> sac around the heart
(Seladi-Schulman, 2019)
The heart is a network of blood vessels that beats to pump blood through all the blood vessels to the rest of your body
(Anatomy of a Human Heart, 2020)
Subtopic
Coronary arteries supply blood to the heart muscle
Most common disease Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
(Coronary Artery Disease: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatments, 2022)
2 Medical Examples used to monitor CAD
Cardiac CT Scan
Imaging test using x-rays to take very close up and detailed images of your heart and blood vessels
(Cardiac Computed Tomography (CT) Scan - University of Ottawa Heart Institute, 2019)
EKG (Electrocardiogram, ECC)
Most effective and easy to use to check for any coronary artery disease signs/symptoms
ECG device shown on patient
(Esposito, 2016)
ECG Monitor
(Mitroff, 2019)
this device test is avoided for people who don't experience any of the following diseases for the disease or have not had previous heart attacks
displays the electrical signal from your heart
waves shown on a monitor
can detect your heartbeat and when it is abnormal which could by decreased waves
it can detect blocked arteries which is known as the Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
(Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) - Mayo Clinic, 2020)
this test lasts a couple minutes
avoid oily and greasy creams the day of the test
painless test which helps to decrect for any heart problems
How a coronary Artery Disease is treated
An inflated balloon is pushed through the catheter to improve the blood flow in your arteries
(Coronary artery disease - Diagnosis and treatment - Mayo Clinic, 2020)
to keep the dialed arteries open a tube (stent) is used
ways to prevent a CAD
(NHS Choices, 2022)
get your heart beat up
become more active
stop smoking
healthy diets
feeling week or light headed
shortness of breath
chest pains
Blockage of coronary arteries caused by plaque a fatty build-up material. Continuous plaque collected on artery walls will narrow your arteries. Plaque can also damage arteries which stops blood from flowing to your heart muscle which can add on to other many diseases and risks.
(The Heart, Part 7: Coronary Circulation, 2020)
Main purpose of this cycle is to pump blood to the heart
Cardic cycle
(Phases of the Cardiac Cycle, 2017)
key notes
blood is being flowed from higher to lower pressure
quick youtube video explaining in animations
i really liked this youtube video as it really helps explain the cardiac cycle is detail along with animations which help visuals learns like me!
start at one minute
(Alila Medical Media, 2017)
click the red youtube button on the right and start at 1 minute
phase one (diastole)
the heart chambers are fully relaxed and blood is starting to flow into the heart
phase two (Atrial systole; ventricular diastole)
the heart chambers are contracting and the blood is being pushed to the ventricles
phase three (Atrial Diastole; ventricular systole)
after the atrial is relaxed, the ventricles contract which pushes the blood out to leave the heart
Rib Cage
(How does the rib cage help me breathe? | Functions of Muscles, 2021)
(Shaughnessy, J, 2021 20)
assists in breathing
Shows inhaling vs exhaling
(The respiratory system, 2019)
by using a pair of muscles between each rib
external intercostals
helps when breathing out (expiration)
internal intercostals
helps when breathing in (inspiration)
keeps the heart, major blood vessels and lungs protected by its cage, protects from physical damage
Diaphragm
slim layer of muscle at the bottom of the ribcage
Diaphragm breathing gif
(Gfycat, 2013)
it moves up and down when changing the volume of the lungs
when air is exhaled
rib cage contracts and drops downward causing the diaphragm to move up
this causes the lung volume to decrease
when air is inhaled
rib cage expands and moves upward causing the diaphragm to move down
this causes the lung volume to increase
Alveoli (Air sac)
made up of:
two differents jobs ^
(Shaughnessy, J, 2021 17)
(Hecht, 2018)
carbon dioxide diffuses to alveoli
These two are done during the process of exhaling and inhaling
0xygen and carbon dioxide being exchanged
Capilaries
blood vessels in the walls of alveoli
perfusion
pumping blood through your lungs
oxygen diffuses into blood
Lungs
this area contains the heart, trachea, esophagus
(Anatomy of the Lung | SEER Training, 2022)
sound protection
gif breathing in & out
(Pumping, Beating Heart, Breathing Lungs And Organ Animations | Lunges, Animation, Giphy, 2022)
of course allows us to breathe
inahing or allowing oxygen into our bodies and removing or exhaling carbon dioxide
exchange is called respiration
Bronchiole tubes
(Bronchioles and alveoli in the lungs, 2020)
Bronichole
(Inflamed bronchial tubes in asthma | NorthShore, 2021)
airway narrowed by a lung disease asthma
vs
airway shown when healthy
deliver tiny air sacs called alveoli
oxygen and carbon dioxide are being exchanged
air passages inside the lungs branch off the bronchi
to the alveolar sac
Homeostasis
example
Gas exchange
(CK-12 Foundation, 2022)
(Gas Exchange | Boundless Anatomy and Physiology, 2013)
gas exchange in alveoli in the lungs
helps maintain acid-base balance or pH levels in the body
blood passes through tiny capillaries in the alveolar sacs
allowing carbon dioxide and oxygen to go in and out of the body
this is done by changing pressure gradients
Bronchi
2 main bronchi
One in your right lung
Travels to the right lung
divides into smaller bronchi to enter the 3 lobes and is shorter
(Bronchial Tubes Structure, Functions, & Location | Bronchus Anatomy, 2017)
One in your left lung
Travels to the left lung
divides into smaller bronchi to enter the 2 lobes and is smaller
Bronchioles detailed picture
(Bronchioles Illustration, 2010)
Cartilage
keeps the bronchi from collapsing when inhaling and exhaling
lined with mucous membranes
this layer is a barrier to inhaled pathogens
which help prevent infections
passageways which connect your windpipe(trachea) to your lungs
waste gases (carbon dioxide) is eliminated from the body
body's tissue receives oxygen
Trachea
(the, 2018)
Cartilage rings
allowing the trachea to close somewhat where food can pass down to the esophagus
keeps it rigid so it doesn't collapse when breathing
Cartilage ring shown in the trachea
(The, 2016)
one part of airway system
carry waste gases such as carbon dioxide out of your lungs
which carry oxygen-rich air to lungs
Lined with cilla
cilla moves foreign particles up & out to be swallowed
Trachea detailed diagram
main job
inhaled air to the lungs
exhaled air out of the body
4 layers of trachea
adventitia
musculo cartilaginous
submucosa
Layers of the trachea wall
(Tracheal Wall Composition and Structure - Anatomy of the Tracheal Tube or Windpipe, 2017)
mucosa
As the trachea passes down air it warms and moistens it while being passed down to lungs
Larynx
(Suárez-Quintanilla et al., 2021)
contains vocal cords
when they vibrate
it produces human speech or sound
hollow tube which allows air pass from your throat to your trachea then lungs.
Larynx broken down
(Larynx Anatomy: Image Details - NCI Visuals Online, 2012)
Chronic Bronchitis
affects smokers the most
people with this disease tend to get more lung infections
(Chronic Bronchitis, 2013)
affects carbon dioxide and oxygen exchange
reduces the flow of carbon dioxide a waste gas leaving out body and oxygen coming inside of our body
due to the muscles swelling and becoming tighter
long term inflammation of the bronchi
Asthma
(Using a Peak Flow Meter to Manage Asthma | AAFA.org, 2020)
muscles around the airway become tightened
chest pain
shortness of breathe
Medical device that is used to monitor
Peak flow meters
can measure narrowing hours
before you even have any symptoms
Peak flow meter being demonstrated
(Health, 2020)
measures how air moves out of your lungs
very difficult for air to move in and out of the lungs
the airways are inflamed which is just another word for swollen which produces lots of thick mucus
(shaughnessy, J 2021 Mechanism of Breathing (9,11)
internal respiration
the air pressure in your lungs increase
this is because the air rushes out of your lungs
between capillaries and cells
where the blood delivers oxygen to the cells and receives carbon dioxide from cells
The diaphragm moves up which allows it to rest
ribs move down and in
Labeled diagram displaying internal vs external respiration
(Aldona Griškevičienė, 2020)
external respiration
the air pressure in your lungs decrease
which pulls air into lungs
oxygen moves from lungs to RBC (red blood cells)
red blood cells release oxygen into the alveoli
between alveoli and blood
The diaphragm moves down as it contracts
the muscles between the ribs contract which pulls the ribs up and out
Throat (Pharynx)
Used for food, liquids and to breathe air
pushes food into the esophagus so that it is not breathed in
Body immune defences found in the throat
adenoids
Adenoids & Adenoidectomies
(Adenoids and Adenoidectomies (for Kids) - Nemours KidsHealth, 2019)
traps harmful viruses or bacteria we breathe in
it can also block all of the airflow through the nasal passages
mass of lymphoid tissue; near the back of the nose
tonsils
filter bacteria and viruses to make sure nothing harmful goes in our lungs
located near the throat
Back of your mouth
(Bradford, 2018)
parts of the throat
Auditory (eustachian) tubes
2 tubes connected ears to the throat
Laryngopharynx
Bottom part of the throat near the voicebox
Lets air pass to to get to the lungs
Helps food and fluid get to the esophagus
Labelled diagram of the throat
Oropharynx
Middle part of the throat connected to the mouth
allowing air, fluid and food to pass through
Nasopharynx
Top part of the throat connected to the throat helps let air in
Air from the nasal cavity, larynx and trachea is collected
Nose
nasal septum divides the nose into 2 sides; left & right
made up of cartilage and bone
the front of the nose is made up of
Upper and lower lateral cartilages
cartilage
Overview of what the nose is made up of
(The Nasal Skeleton - Bones - Cartilage - Fractures - TeachMeAnatomy, 2013)
Passages
lined around with muscles membrane and cilia (tiny hairs)
which help to clean and filter the air
Nasal Cavity
regulates flow of air, behind the nose, lined with muscle membrane and cilia
(The Nasal Cavity - Structure - Vasculature - Innervation - TeachMeAnatomy, 2012)
Detailed diagram of the nasal cavity
(UFO Themes, 2018)
Filters and heats air
Mucus moistens
Removes minute airborne particles
Normal villi vs Celiac disease
(Celiac Disease - Symptoms, Testing & Treatment | BeyondCeliac.org, 2021)
can also cause inflammation in other parts of your body
bloating
diarrhea
vomiting
stops your body from taking nutrients that comes from foods
cause by the indigestive of gluten
effects the small intestine
which doesn't allow nutrients to be absorbed
(Irritable bowel syndrome - Symptoms and causes, 2021)
IBS labelled diagram
(https://www.facebook.com/MayoClinicHealthSystem, 2022)
can be controlled by a good diet
symptoms
bloating, cramping, gas
feeling depressed
effects the large intestine
Lower part of the large intestine where stool is stored until it can be pushed out of your anus
(Digestive System: Function, Organs & Anatomy, 2021)
First part of the large intestine, receives any undigested food material from the small intestine
(Pancreas Anatomy Illustration, 2015)
inside the abdomen, behind the stomach, creates pancreatic juices called enzymes.
Lipase
breaks down triglycerides into glycerol and fat free acids, fat digesition
Trypsin Enzymes
Helps us digest proteins
Breaks down sugars, fats and starches
mostly produced in the pancreas, stomach and small intestine
Eliminating cholesterol, hormones, drugs, bilirubin
Bilirubin
produced when old red blood cells break down, yellowish orange substance found in bile formed in the liver
Stores vitamins, minerals and glycogen
produces bile
Gallbladder
Sac located under the liver
digestive juice to breakdown the fat in foods
Synthesis of plasma proteins
ex: albumin
Blood passes through the liver as it leaves the stomach and intestines which then the liver processes this blood and breaks down, creates nutrients and metabolizes drugs into different types of forms that are easy for the rest of the body to use
Liver + Main function
(The Digestive Process: The Liver and its Many Functions, 2022)
Large Intestine
From the undigested food water gets absorbed and forms a waste material
(Small & Large Intestine | SEER Training, 2022)
Detailed large intestine
(NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms, 2021)
Small Intestine
(The Digestive Process: What Does the Small Intestine Do? | University Hospitals, 2021)
villi
protrusions
cell that lines the surface of your body
Cells that line up the small intestine
increases the surface area to help the absorption in digested food by thicker cells that line up
Ileum
3rd and final section of digestion in the small intestine where absorption of bile acids, fluid and vitamin B-12 take place
Microvilli
helps the absorption of non-digested food along with water molecules
epithelial cells
lining the intestine to increase the surface area
Jejunum
2nd phase to further help digest food that comes from the stomach. Specifically absorbs nutrients and water which can be used up by the body
Duodenum
1st phase to complete digestion, where the food from the stomach is mixed with enzymes from the pancreases which help break down the food
Pancreases
Make pancreatic juice (enzymes) which help break down sugars, fats and starches
nutrients aka vitamins, protein, fats, carbohydrates and water are absorbed from food in this organ so they can be used up by the body
an organ that holds the digestive juices of food while being varied with stomach enzymes.
The acid in your stomach varies from 1.5 to 2.5 of a pH level which is highly acidic but is required for the chemical breakdown of the food. Once broken down the food is passed to your small intestine. Chemical and mechanical digestion is shown in the stomach. (Stomach: Anatomy, Function, Diagram, Parts Of, Structure, 2022)
Pepsin enzyme
breaks down the proteins in the food during digestion
Stomach enzymes again help the process to break down foods
tube that carries food and liquid from you mouth to the stomach
The muscles in your esophagus help bring food down to your stomach to digest.
(Slide show: See how your digestive system works, 2020)
Lower esophageal sphincter
muscle of ring which forms a valve near the lowest end of the esophagus where it joins the stomach
The lower esophageal sphincter also known as the (LES) also remains closed expect only when swallowing and allowing food to pass down from the esophagus to the stomach. The reason being the LES closes is because it prevents the stomach acid from returning back up the esophagus which leads to heart burns along with a major disease GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease)
(Lower esophageal sphincter (LES), 2019)
Peristalsis is a series of wave like movements the muscles of the esophagus does to help push the food to the stomach
wave-like movements
(Peristalsis image, 2022)
The digestion of the food begins with the mouth as food enters and chewing helps break the food into smaller pieces
Food begins the digestion process in the mouth as our teeth help us chew food into smaller pieces along with saliva digesting starches and fats with the help of enzymes. The tongue then helps to move the chewed up pieces of food into the esophagus by swallowing. (Ch. 1 Introduction - Biology 2e | OpenStax, 2018)
Salivary glands then make saliva which helps food move more easily through.
The saliva also helps breaks down the starches in your food because it contains enzyme
Amylase enzyme
helps digest food
Digestive enzymes are proteins in saliva that can turn nutrients into substances by quick chemical reactions that is easier for our digestive system to absorb
(Enzymes: What Are Enzymes, Pancreas, Digestion & Liver Function, 2022)
Mouth in detail
Mouth diagram shown in detail (pay attention to the glands)
(What is the oesophagus? | The gullet, 2020)
High in mineral foods to keep you healthy
Nuts
Vegetables
Milk
Fish/Meat
Foods that contain minerals
(Vitamins and Minerals For Your Body, 2019)
2 types
trace minerals
Small amounts are needed
iodine
copper
zinc
iron
macrominerals
These are much more needed and needed to consume more than trace minerals
potassium
sodium
magnesium
phosphorus
calcium
help you healthy and are used for different jobs throughout the body
making enzymes and hormones
heart and brain working properly
muscles and bones strong
proactive foods
Basic structure
(Carpi, 2003)
oxygen
hydrogen
carbon
help provide the materials needed to build cell membranes
provide energy to the body by the help of cells
keep us healthy, protect us from diseases
Types of vitamins
B (thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, biotin, B6, B12, and folate)
energy levels
overall maintaining good health and well being
K
supports to make protein
needed for blood clotting
helps wounds heal faster
D
maintaining/building healthy bones
c
antioxidant
helps protect cells against the effect radicals, repair of body tissues
A
important nutrient towards vision, growth, cell division, reproduction and lastly immunity
(What are proteins and what do they do?: MedlinePlus Genetics, 2021)
Aid in muscle movements
ex: contraction
contracting across joints causes muscle movements
extend from the muscle fiber through connected tissues to pull on bones
causes skeletal movements
Diagram displaying how your body consumes the protein when eaten
When protein is consumed our body breaks it down into amino acids which supply us with energy, build muscles and make antibodies to help us fight immunity from diseases
(Proteins: building blocks of the body | Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., 2022)
To speed up chemical reaction in the cells they act like catlysts
Transport ions into the cell membrane
Fights against diseases and infections
Made up of thousands of amino acids
20 types of amino acids that are combined to make a protein
Examples of proteins
(Van, 2018)
Antibodies
recognizes bacteria, viruses and infections
Enzymes
ex: amylase
digestion
Hemoglobin
makes red blood cells
4 protein chains
2 beta chains
2 alpha chains
Collagen
made up of amino-acids
Bones and teeth are made by adding mineral crystals to collagen
(PDB101: Molecule of the Month: Collagen, 2022)
molecular cables which strengthen the tendons
Insulin
protein made up of 2 chains
B chain- 30 amino acids
A chain- 21 amino acids
Build tissues, muscles
Repairing body tissues
Storage and expresses the genetic information and growth of the organism
Nucleic acids are polynucleotides (chain like molecules)
Consists of 3 structures
process is known as biosynthesis which involves the protein chain like molecules from individual amino acids in specific series/order.
Amino acids- molecules that are merged together to form proteins
3 main amino acids
(Kubala, 2018)
(Shaughnessy, J, 2021 13,2)
Amino Acid
(Mitra, 2021)
Molecules that are merged together to form proteins
3 main amino acids
Valine
Isoleucine
Leucine
Examples
Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
Takes part in protein synthesis and comes in many different molecular forms
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
Translates the information a cell needs to make protein in a code for the body to understand
Stores energy reserves for later, provides materials in order to build cell membrane, signalling molecules within the body and cushion vital organs
(Shaughnessy, J, 2021 2)
Ex: Fatty foods
Avocado
Butter
Cheese
Nuts/Seeds
Fatty meats and fish
Lipids in fat foods
(1.4.3: Introduction to Lipid Structure, 2018)