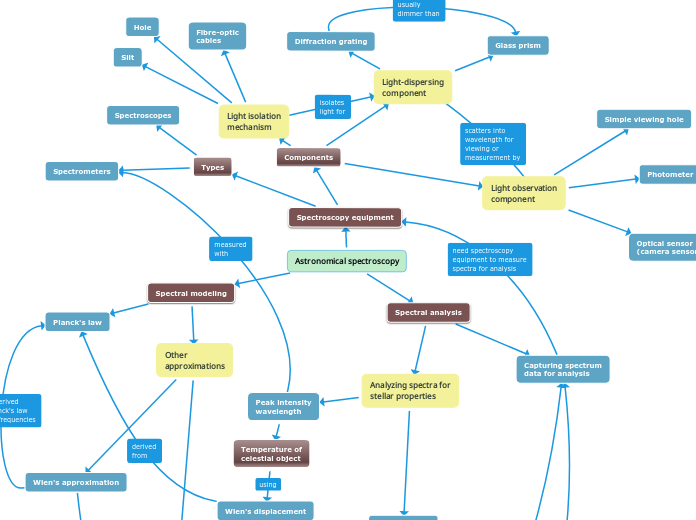
Astronomical spectroscopy
Spectral modeling
Other
approximations
Wien's approximation
Rayleigh-Jean's law
Ultraviolet catastrophe
Planck's law
Spectral analysis
Capturing spectrum
data for analysis
Analyzing spectra for
stellar properties
Spectral lines
Composition of
stellar atmospheres
Doppler shift using
spectral line offsets
Peak intensity
wavelength
Temperature of
celestial object
Wien's displacement
Spectroscopy equipment
Types
Spectroscopes
Spectrometers
Components
Light-dispersing
component
Diffraction grating
Glass prism
Light isolation
mechanism
Slit
Hole
Fibre-optic
cables
Light observation
component
Simple viewing hole
Photometer
Optical sensor
(camera sensor)