Bodily Systems
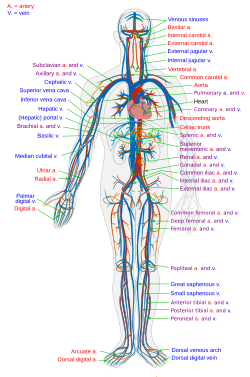
Circulatory System/Cardiovascular System
To circulate
Nutrients
Oxygen
Carbon dioxide
Blood cells
In fighting diesease
Plasma
Blood cells
Whole blood
Suspension
Proteins
Body
55%
Blood volume
Red blood cells
Oxygen
Body
Cyctoplasm
hemoglobin
red colour
White blood cells
Multipotent cells
Nuclei
Neutrophil
Eosinophil
Basophil
Lymphocyte
Monocyte
~7% of a persons body weight
Platelets
Clumping where injury exists
Blodd clots
Cell nucleus
Hemostasis
Lymphatic system
Lymph
Recycled excess blood plasma
interstitial fluid
The heart
Left ventricle
Right ventricle
Left atria
Right atria
The sinoatrial node
Blood vessels
The lymph
Lymph vessels
Systematic circulation
Oxygenated blood
Rest of the body
macrocirculation
microcirculation
Pulmonary circulation
deoxygenated blood
Right ventricles
Oxygenated blood
Left atrium
Ventricle of the heart
High blood pressure
Extreme pressure exerted when blood is pumped
Weight loss procedures
Reduction of sodium intake
Venous thromboembolism
Blood clotting within veins
Stroke
Anticoagulants
Blood clots
Myocardial infarction
A blockade within blood vessels leading to the heart
Bypass surgery
New passage-ways for blood
Stent procedures
Arteries
Medications
Anticoagulant
Digestive System
Cephalic Phase
Gastric Phase
2/3
Gastric Secretions
Gastric Secretions
Acetylcholine
Histamine
Gastrin
The stomach
Intestinal Phase
Stretching of the duodenum
Gastric Function
Vagal Nerve
Chyme
Gastric Secretions
The Gastrointestinal Tract
The Mouth
Salivy
Food
The Esophogus
Mucous Membranes
The throat
Stomach
Food and Fluids
Gravity
Muscle Contractions
The Stomach
The Small Intestine
Three Main regions
Duodenum
23 Centimeters in Length
Head of the Pancreas
Brunners glands
Alkaline Secretions
Jejunum
Midsection
2.5 Meters long
Villi
Ileum
3.0 Meters long
Vitamin B12
The Large Intestine
The Large Intestine
Salts and Water
Materials
Ileocecal Valve
The Liver
Solid Organ
Bile
The Pancreas
Solid Organ
Enzymes
Issues
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Stomach Acid
Esophagus
Common
Gallstones
Hard deposits
Gallbladder
An excess of waste
Bile
An excess of cholesteral
Abdomen Pain
Increasing fiber intake
Refined Carbohydrates
Celiac Diesease
Gluten
Immune system
Villi
Diarrhea
Blotation
Vomiting
Seizures
Depression
Initiating a gluten free diet
Sensory receptors are stimulated
Endocrine System
Chemical based messaging system
Feedback loops
Hromones
Internal glands
Endocrine glands
The thyroid gland
triiodothyronine
thyroxine
calcitonin
The adrenal glands
Adrenaline
Vascular
Ducts
Hormones
The Pineal gland
Melatonin
The pituitary gland
Physiological Processes
The pancreas
Ovaries
Hormones
eicosanoids
Signaling molecules
steroids
Biologically active compounds
amino acid
Organic compounds
the hypothalamus
testes
Androgens
The parathyroid gland
parathyroid hormone
Low blood calcium

Organs with secondary endocrine functions
Bone
Kidneys
The liver
The heart
The gonads
Endocrine glands
Ducts
Vascular
Intercellular Vacuoles
Diabetes
high blood pressure
diabetic ketoacidosis
Stroke
Type 1 Diabetes
Insulin
Dietary changes
Type 2 Diabetes
Weight changes
Thyroid diesease
Immune system
Biological processes
Organism
Diesease
Pathogens
Innate immune system
Preconfigured responses
groups of situations and stimuli
All animals
Microbes are identified
pattern recognition receptors
White blood cells
Structure
Cell lineage
No immunological memory
nearly all forms of life
An immediate response
Adaptive immune system
Tailored responses
Stimuli
Molecules it has previously seen
Exposure that leads to immunological memory
jawed vertebrates
A lagged response
Chemical barrier
Chemical substances
Defense
Subtopic
Allergies
Abnormal sensitivity to what are normal antigens
Medication
Immunotherapy
Purified allergen extracts
AIDS
White blood cells
antiretroviral therapy
Cure

Muscular System
Skeletal muscles
Striated muscle
myocytes
myofibrils
sarcomeres
Actins
myosin
Coordinated contractions
639
Bones
Tendons
of cells
Tension
Smooth muscles
non-striated muscle
Single unit
Smooth muscles
multiunit smooth muscle
Hollow organs
Cardiac muscles
Muscle fibers
Involuntary movement
The sinus node
Electrical stimulation
action potential
Calcium
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Blood
Body
Blood
Autonomous muscles
The cardiac muscle
Involuntarily
cerebral palsy
loss of motor function
brain damage
Injections of onabotulinumtoxinA
diazepam
Relax muscles
Polymyositis
Weakness in muscle
Corticosteroids
Relieves symptoms
Physical therapy
Muscle cramps
Involuntary contraptions of certain muscles

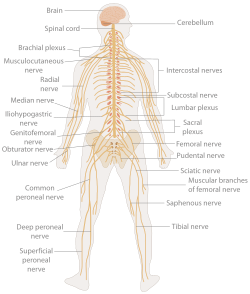
Nervous System
Central Nervous System
The brain
Cerebrum
Voluntary actions
The spinal cord
Signals
Brain and Peripheral Nerves
Peripheral Nervous System
Nerves
Somatic nervous system
Mediate voluntary movements
Autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic part
Cases of emergencies
Energy
Parasympathetic part
Organisms are in a state of rest
Enteric nervous sytem
gastrointestinal system
Endocrine System
Neurons
electrochemical waves
Axons
Neurotransmitters
Synapses
multicellular organisms
Hormones
internal Ciculation
Seizures
Bursts of abnormal signals
Regular signals
Anti-Epileptic Drugs
Ketogenic Diets
Surgery, removing parts of the brain that cause seizures
Loss of coordination
Cerebellum
Physical Therapy
Decrease in cognitive abilities
Abnormal clumps of beta-amyloid protein
Lewy bodies
microscopic clumps
protein
Parkinson's disease, dementia
strokes
Reduced blood flow
Decreasing alcohol consuption
practicing proper hygiene and maintaining a proper sleep schedule
Renal System
Kidneys
Blood
From a process of blood filtration
Glomerulus
Small blood vessels
Nephrons
Structional unit
waste
Dorsal body wall
Renal arteries
the removal of toxins
Ureters
Tubes
Smooth muscle fibers
Urine
Bladder
20-30 Centimeters in length
urothelial cells
The pelvis
renal arteries
common iliac arteries
internal iliac arteries
Peristalsis
The bladder
Fundus
Body
Apex
Neck
Openings
vesical arteries
vesical veins
superior vesical artery
internal iliac arteries
inferior vesical artery
The urethra
The urinary bladder
Urinary meatus
Expels urine received from the bladder
Waste
Blood volume
Blood pressure
Electrolytes
Blood ph
Nephritis
The glomerulus
Hepatitis
HIV
Antibiotics
Medication
Kidney Stones
Deposits of calcium within kidneys
Pain killers
Parathyroid gland surgery
Hyperparathyroidism
Bladder cancer
Bladder cells uncontrollably grow into a tumor
transurethral resection of bladder tumour
The tumor within the bladder, through access from the Urethra
cystectomy
All or part of the bladder
urinary diversion
A new pathway for urine to leave the body

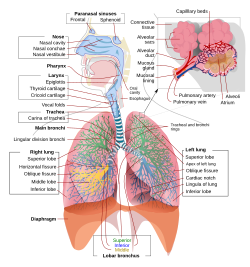
Respiratory System
Respiratory tract
Lower respiratory tract
Lower Larynx
Breathing
Sound and Pitch
Trachea
cartilaginous tube
Larynx
Air
Two primary Bronchi
Bronchi
Lungs
right main bronchus
left main bronchus
Bronchioles
bronchial airways
Alveoli
lung parenchyma
Gas exchange occurs
Lung aveoli
Acini
alveolar ducts
respiratory bronchioles
alveolar sacs
"Respiratory tree"
Upper respiratory tract
Nose
Air
Nasal cavitie
two cavities
nasal septum
Continuations of the nostrils
Respiratory segment
Olfactory segment
Nasal passage
Air
Sinuses
maxillary sinuses
The eyes
Frontal sinuses
ethmoidal sinuses
sphenoidal sinuses
Pharynx
Food
The nasopharynx
The pharynx
The base of the skull
respiratory epithelium
Auditory tube
oropharynx
anteriorly
Mouth
palatine tonsi
Lateral wall
tonsil
tonsillar fossa
tonsillar pillars
epiglottis
Aspiration
Food
laryngopharynx
Pathway Divergences
Respiratory pathway
Digestive Pathway
pyriform sinus
postcricoid area
posterior pharyngeal wall
Passageway
Food, air
stratified squamous epithelium
pharyngeal plexus
Vocalization
Upper Larynx
Pneumonia
Bacteria
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Viruses
Antibiotics
Resting
Asthma
Sticky secretions
STeroids
bronchodilator inhalers
prescription of corticosteroids
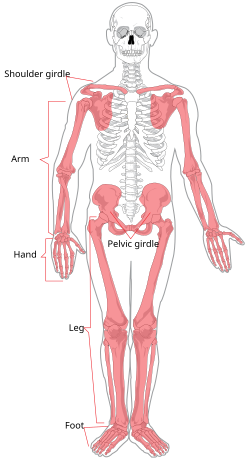
Skeletal System
Individual or joined bones
Ligaments
Bone
Bone
Nucleas
Tendons
Muscle
Bone
Muscles
Cartilage
Support
Move
White blood cells
Redblood cells
Osteoblasts
osteocytes
Hard tissue
cortical bone
ancellous bone
Exoskeleton
External
Soft tissues and organs of the body
Endoskeletan
Internal support structure
mesodermal
Hydroskeletan
Semi-rigid structure
Liquid
Cytoskeletan
Cells
Cellular motion
Organs
Osteoporosis
Reduced minearal bone density
bisphosphonates
Paget’s Disease
Abnormally large ormisshapen bones
Calcium supplements
Vitamin D supplements
Integumentary System
Hair
Nails
Skin
1-5-2.0m^2
The epidermis
An initial barrier
External Environment
Basement membrane
Melanocytes
Nerve endings
stratified squamous epithelial cells
Stratum Corneum
stratum granulosum
stratum spinosum
stratum basale
stem cells in the basal layer that develop into the corneum
keratinocyte
The dermis
The Papillary
The reticular layers
Connective tissue
Vessels
Glands
Follicles
hair roots
Sensory nerve endings
Muscular Tissue
The hypodermis
fat
Bodily temperature
Insulator
exocrine glands
Skin cancer
Abnormal cells
The body
basal-cell skin cancer
squamous-cell skin cancer
melanoma
ultraviolet Radiaton
Radiation therapy
Chemotherapy
Immunotherapy
Photodynamic therapy
Vitiligo
Lack of melanin within skin cells
Inflammation controlling drugs
Psoralen and Light therapy
Skin grafting
Vitamin D