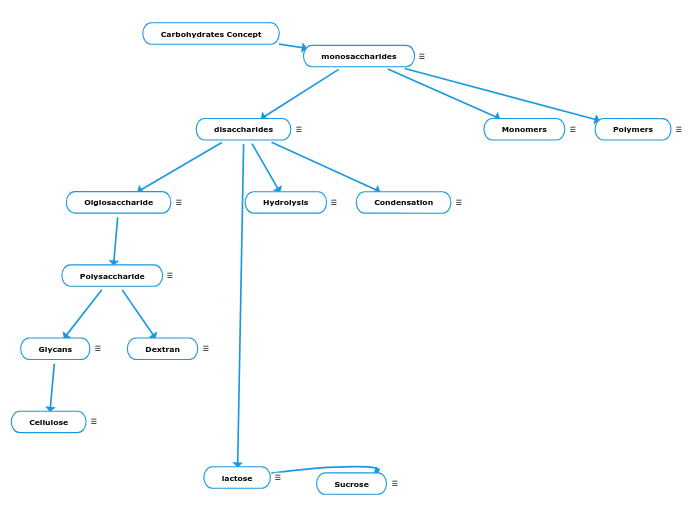
Carbohydrates Concept
monosaccharides
Monosaccharides are the smallest units that make up a carbohydrate (considered to be the building blocks). Monosaccharides are simple sugars that can be built up to become polysaccharides, olgisaccharides and disaccharides.Saccharide means sugar.A few examples of a monosaccharide:glucosefructoseribose
disaccharides
Disaccharides are made of two monosaccharides, commonly called a double sugar. These form due to a glycosidic linkage/bond , a covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate molecule (monosaccharide) with another carbohydrate molecule (in this case. glycosidic linkages can also be a different grouping attached to the carbohydrates).Examples of a disaccharide include:lactosesucrosemaltose
Olgiosaccharide
Olgiosaccharides are short chains of less than 20 monosaccharides. A large number of oligosaccharides have been prepared by partially breaking down more complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides). Most of the natural olgiosaccharides are plants.Fun Fact: Olgiosaccharides help plants induce a response to plants that can save them from disease.
Polysaccharide
A polysaccharide is a chain of more than 20 monosaccharides.Most carbohydrates in nature are polysaccharides (Glycans) examples are: potatoescornunripe fruitPolysaccharides can be both homo-polysaccharides and hetero-polysaccharides. Homo-polys can only contain the same type of monosaccharides (ex. only glucose chains).Hetero-polysaccharides can have more than one type of monosacchardies. (ex: a long chain of lactose)Polysaccharides can be unbranched or branched. Polysaccharides are used like storage forms of monosaccharides in plants.
Glycans
Glycans are carbohydrate-based polymers made by all living organisms. Glycans are found mostly in nature.
Cellulose
Cellulose is an example of a glycan. Cellulose is a structural component in plants that make up plants cell walls and cellulose is an unbranched homo-polysaccharides consisting of thousands of glucose molecules in cellulose, glucose molecules have a beta configuration and will therefore bond with the beta bond glucose molecules.
Dextran
Dextran is a structural component in bacteria and yeast.It's a polysaccharide that is derrived from the condensation of glucose. They are glucose polymers.
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis is a double decomposition. Happens when water is added to an alpha 1,2, 4. Reverse reaction is condesation.
Condensation
Condensation is the process where 2 monosaccharides link together. (This is also in relation to olgiosaccharides and polysaccharides). Reverse reaction is hydrolysis.
lactose
Lactose is made of galatocose and glucose.Lactose and sucrose are related because they are structural isomers have the same formula yet have a different structure.
Sucrose
Sucrose is naturally occuring in plants.
Monomers
Monomers are parts that make up the substance. Monomers are like tiny building blocks.
Polymers
Polymers are called macromolecules. Polymers are natural or synthetic substances composed of very large molecules.