Chapter 3 #2
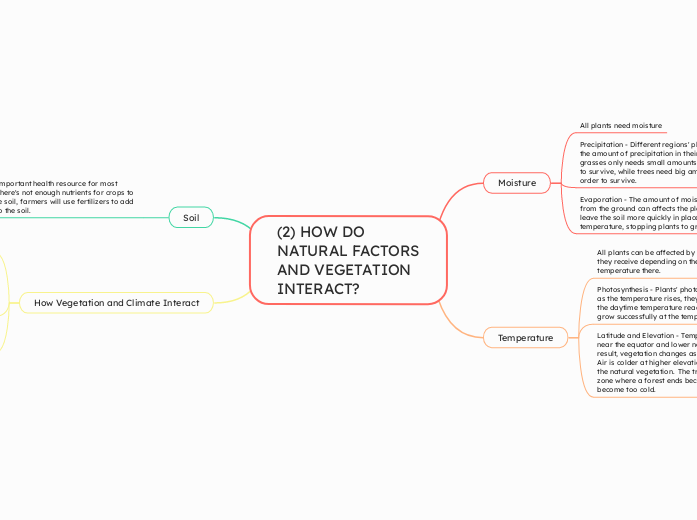
Moisture
All plants need moisture
Precipitation - Different regions' plants change to the amount of precipitation in their region, just like grasses only needs small amounts of precipitation to survive, while trees need big amount of water in order to survive.
Evaporation - The amount of moisture that dry up from the ground can affects the plants. Moisture leave the soil more quickly in places with high temperature, stopping plants to grow smoothly.
Temperature
All plants can be affected by the amount of heat they receive depending on their location/ temperature there.
Photosynthesis - Plants' photosynthesis increases as the temperature rises, they stop growing until the daytime temperature reaches 6°C. Plants can grow successfully at the temperature 20°C.
Latitude and Elevation - Temperatures are higher near the equator and lower near the poles. As a result, vegetation changes as the latitude changes. Air is colder at higher elevations and this affects the natural vegetation. The treeline is the transition zone where a forest ends because the climate has become too cold.
Soil
Soil is an important health resource for most plants. If there's not enough nutrients for crops to grow in the soil, farmers will use fertilizers to add nutrients to the soil.
How Vegetation and Climate Interact
Natural vegetation and climate affect each other.
Plants take mid-latitude rain from grassland for photosynthesis. When they have some leftovers for the air, they return it back. As they grow, the amount of the moisture they need will increase, returning less to the air, making the overall climate of that area drier over time.
Overall, the Sahara Desert was created over time by the connection between the climate, the natural vegetation, and the soil.