CNS
Brain
Lobes
frontal
Structures
Precentral gyrus
Primary motor cortex
Brocas area (left side)
speech production
Brocas aphasia
Functions
Executive function
motor movement
impulse control
Parietal
Structures
Post central gyrus
Primary somatosensory cortex
Wernickes extends into inferior paietal
Lateral ventricles
Where CSF is made
CSF made from choroid plexus
Flow of CSF through the brain:
1. Lat ventricles
2. Interventricular foramina
3. 3rd ventricle
4. Cerebral aquaduct
4th ventricle
5. Spine
6. Back to blood
Functions
Spatial information or proprioception
Somatosensory info: Pain, touch, pressure, temperature, vibration
Subtopic
Temporal
Structures
Wernickes area(left side)
Speech comprehension
Sylvian(lateral) fissure
Heschells gyrus
Primary auditory cortex
Auditory association area
Functions
memory
Auditory processing
Language comprehension
Occipital
Structures
Parieto occipital sulcus
Secondary visual cortex
Primary visual cortex
Cuneus
Lingual gyrus
Calcarine fissure (medial occipital lobe)
*seperates cuneus and lingual gyrus
Functions
Visual perception
Spatial reasoning
eye movements
Insula
Structures
Gustatory cortex
Functions
Taste
Emotional processing
risk reward
Sensorimotor processing
Embryonic Development
Stages
Pre embryonic
Conception to day 14
embryonic disk forms(ectoderm, endoderm)
mesoderm forms toward end of stage
Embryonic
day 15 to week 8
Endoderm develops into
Gut, liver, pancreas, respiratory system
Ectoderm develops into
sensory organs
nervous system
Epidermis
Mesoderm develops into
Muscles, skeleton, excretory and circulatory systems
Stage 2 development
Sclerotomes
Bones
myotomes
Muscles
Dermatomes
Skin
Formation of neural tube occurs
If it DOES NOT close
Spina bifida
Tube -->CNS
Crest--> PNS
Fetal
End of week 8 to conception
Myelination takes place
Brain development
prosencephalon(forebrain)
Telencephalon
Cerebral hemispheres, cerbral cortex, basal ganglia
Lateral ventricles
Diencephalon
thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus, retina
third ventricle
Mesencephalon(midbrain)
Mid brain (brain stem)
cerebral aquaduct
Rhombencephalon(hind brain)
Metencephalon
cerebellum , pons
fourth ventricle
Myelencephalon
Medulla oblongata
fourth ventricle
Protection
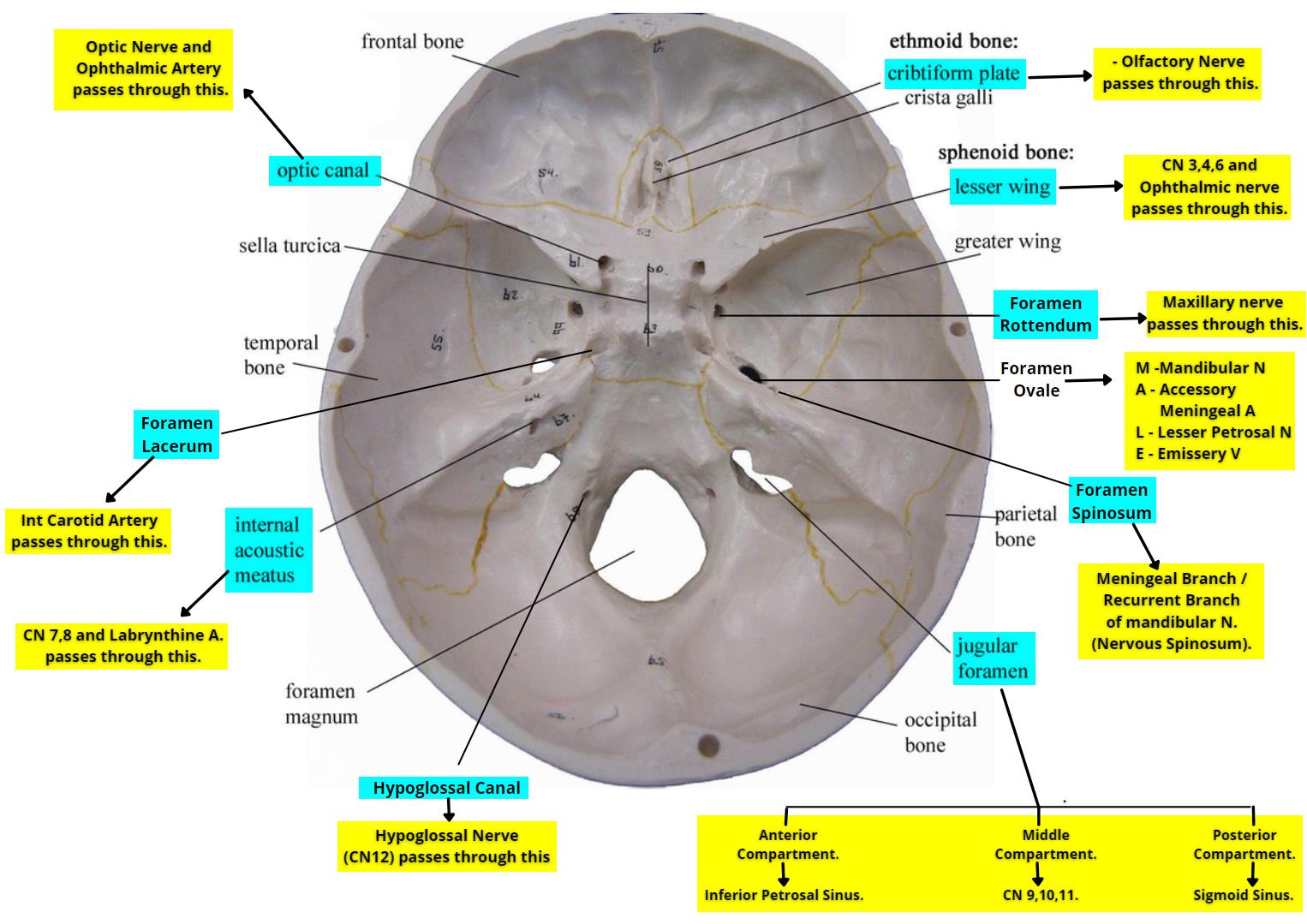
Skull
Viscerocranium
Maxilla, mandible, zygomatic bones, lacrimal bones, nasal conchae
Neurocranium
Ethmoid, frontal, occipital, parietal, sphenoid, temporal
Fossa
Anterior fossa
CN 1, CN2
Middle fossa
superior orbital fissure
Houses CN 3,4,V1, 6
Rotundum
CN v2
Spinosum
CNV3
Posterior fossa
Internal acoustic meatus
Houses CN 7,8
Jugular foramen
Houses CN 9,10,11
Blood supply
main arteries supplying the brain
Vertebral arteries
Internal carotid artery
Anterior circulation(4)
ACA, ICA,ACOMM,MCA
Posterior circulation(7)
PCOMM, PCA, Basilar, SCA, AICA, PICA, vertebral
Circle of willis(6)
ACA, ICA, MCA, ACOMM, PCA, PCOMM
ACA feeds
Medial frontal and parietal lobes, part of the basal ganglia
MCA feeds
Basal ganglia, lateral inferior frontal, parietal, inferior temporal)
PCA feeds
Medial inferior temporal and occipital lobe, thalamus and hypothalamus
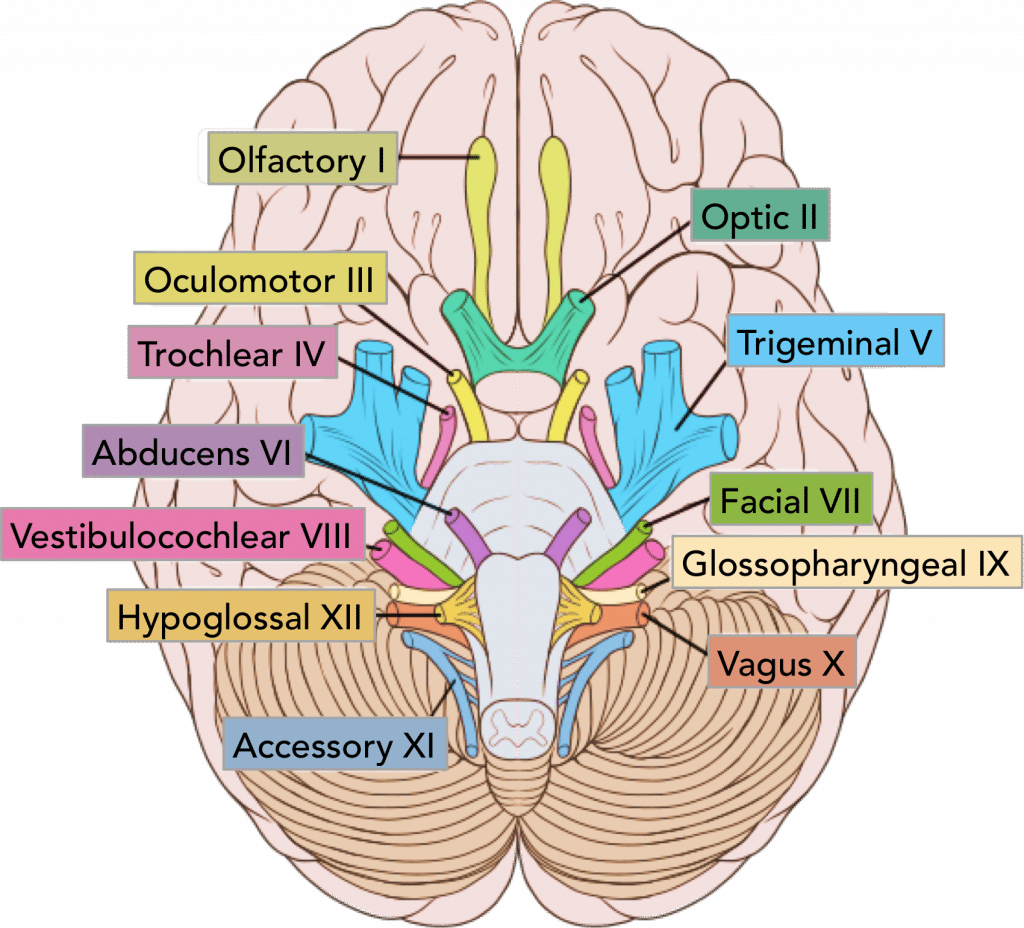
Cranial nerves
Oh
Olfactory(Sensory)
F: Smell
Fo: Olfactory foramina
Connects to reticular formation, and amygdala
once
Optic(sensory)
Supplies: Photoreceptors
F: Vision, light reflex
Fo: optic canal
Pathway
eye --> Nerve --> Optic chiasm--> Optic tract--> Lateral geniculate body
one
Oculomotor(Motor)
Supplies: eye muscles
Involved with: Tecto spinal tract
F: Controls pupil size
FO: Superior orbital fissure
takes
Trochlear(motor)
Only one that starts in dorsal view
Supplies: Superior oblique
F: Eye movement
FO: Superior orbital fissure
the
Trigeminal (Both sensory and motor)
Supplies: Muscles of mastication amongst others
F: Sensation of pain, Blink reflex(corneal)
V1 Fo: Sup orbital fissure
V2: Fo: Foramen rotundum
V3 Fo: Foramen ovale
V1: Opthalamic
V2: maxillary
V3: Mandibular
anatomy
Abducens(motor)
Supplies: Lateral rectus
F: Eye movement
Fo: Superior orbital fissure
If CN6 affected: Esotropia
final
Facial(Both sensory and motor)
Supplies: Muscles of facial expression, anterior 2/3rds tongue
F: Muscles of facial expression, taste, sensation of touch, pain, temperature *Helps with corneal reflex
Fo: Internal auditory meatus
very
Vesitibulocochlear(sensory)
Supplies: Vestibulobranch(Some fibers reach cerebellum though inf cerebellar peduncle) ; cochlear branch
Involved with: Lateral and medial vestibulospinal tracts
F: posture, static and dynamic balance *mostly sensory
FO: IAM
good
Glossopharyngeal(both sensory and motor)
Supplies:
F: lift pharyn and larynx, taste posterior tongue, blood pressure
FO: Jugualr foramen
vacations
Vagus(both sensory and motor)
Supplies: Pharynx, larynx, thoracic and abdominal viscera, epiglottis, aortic arch
F: Main parasympathetic nerve; supplies 75% of organs
Fo: Jugular foramen
are
Accessory(motor)
Supplies: SCM, trapezius, pharynx , soft palate mm
F: Flexion of neck, contralateral head rot, elevates and retracts scap
FO: Jug foramen
Heavenly
Hypoglossal(motor)
Supplies: Extrinsic and intrisic muscles of the tongue
F: Swallow, speak, move stuff in mouth
FO: Hypoglossal canal
Basal ganglia
Most important blood supply of the basal ganglia: Lenticulostriate arteries(small vessels off the MCA)
4 channels
Motor channel
Direct path
Structures involved
Striatum, GPI, SNR, thalamus
Striatum releases GABA to inhibit GPI and SNR, so no GABA is released to the thalamus , movement is stimulated
Cortex
Striatum(GABA inside)
GABA
GPI and SNR
GPI and SNR
NO GABA
Thalamus
Glutamate
To stimulate motor cortex
Indirect pathway
Structures involved
Striatum, GPE, Subthalamus nucleus, GPI, SNR, thalamus
Subthalamus nucleus releases glutamate which stimulates GPI and SNR, these release GABA to the thalamus and movement is inhibited
Cortex
Striatum
GPE
GABA
Subthalamic nucleus
Glutamate
GPI and SNR
GABA
Thalamus
thalamus inhibited
Breaks movement
Oculomotor channel
Conttrols eye movement, saccadic eye movement
Prefrontal channel
Cognitive processes of frontal lobe and behavior control
Limbic channel
Regulation of emotions
Cerebellum
Anatomy
connection with brainstem by cerebella peduncles
Superior cerebellar peduncle: Connects with midbrain
Middle cerebellar peduncle: Connects with pons
Inferior cerebellar peduncle: Connects with medulla
External feuatures
Two cerebellar hemispheres right and left
control extremities
Median vermis
Controls trunk
Peduncles
Extremities and trunk
Anterior lobe
regulation of muscle tone, coordination of skilled voluntary movement
Posterior lobe
Planning of voluntary activity
Flocculo nodular lobe
Maintenance of balance, control of eye movements
Inner white matter: Arbor vitae
Cells
Purkinje cells
Largest in brain essential to output tracts
Granule cells
Smaller ; use glutamate as MT and are excitatory
Nuclei
Dentate nucleus
Fine control of voluntary mvoements
Emboliform nucleus
Regulates precision of limb movements
Fastigal
Estimate movement of the body through space
Glubose
Balance, posture, and orientation
Input tracts
Cuneocerebellar tracts (Carry info from upper limbs and upper trunk)
Dorsal spinocerebellar tract (Carry info from lower limb and lower trunk)
Output tracts
Rostral spinocerebellar: Pain and temp from the upper extremities
Ventral spinocerebellar: Pain and temp coming from the lower extremities
Blood supply
PICA, AICA, SCA
Communication
Ascending(sensory) tracts
DCML
Function: Sensory info of fine touch,vibration and proprioception to post central gyrus
2 fibers
FG: T6 and below
FC: T6 and up
Originates in dorsal horn of SC
Terminates in post central gyrus
Decussation: At medulla
1st order: From effector to medulla
2nd Order: Medulla to VPL in thalamus
3rd order: VPL to post central gyrus
ALS Spinothalamic
F: Pain, temperature, crude touch
Decussation: Spinal cord
Descending (motor) tracts
Lateral corticospinal
Voluntary movement for the whole body
Starts in cortex and decussates in medulla
Supplies entire cord
Anterior Corticospinal
Voluntary movement for the upper extremity and trunk
Starts in cortex and bifurcates in the spinal cord
Ends at T10
Lateral vestibulospinal
Balance
Starts in the pons and supplies entire cord
Medial vestibuospinal
Controls head and neck
Originates at medulla and bifurcates at medulla
Ends at T1
Reticulospinal
2 tracts
Medullary
Pontine
Starts in superior colliculus in mid brain
Supplies the entire cord
Posture and gait
Tectospinal
Head and eye coordination
Starts in superior colliculus in mid brain
Ends at T1
Decussates: midbrain
Rubrospinal
Fine coordination
Starts in red nucleus in midbrain
ends T1
Decussates at midbrain
Neuron
Synapse
Electrical
Only in the CNS, gap junctions
Chemical
Most common, USe of neurotransmitters
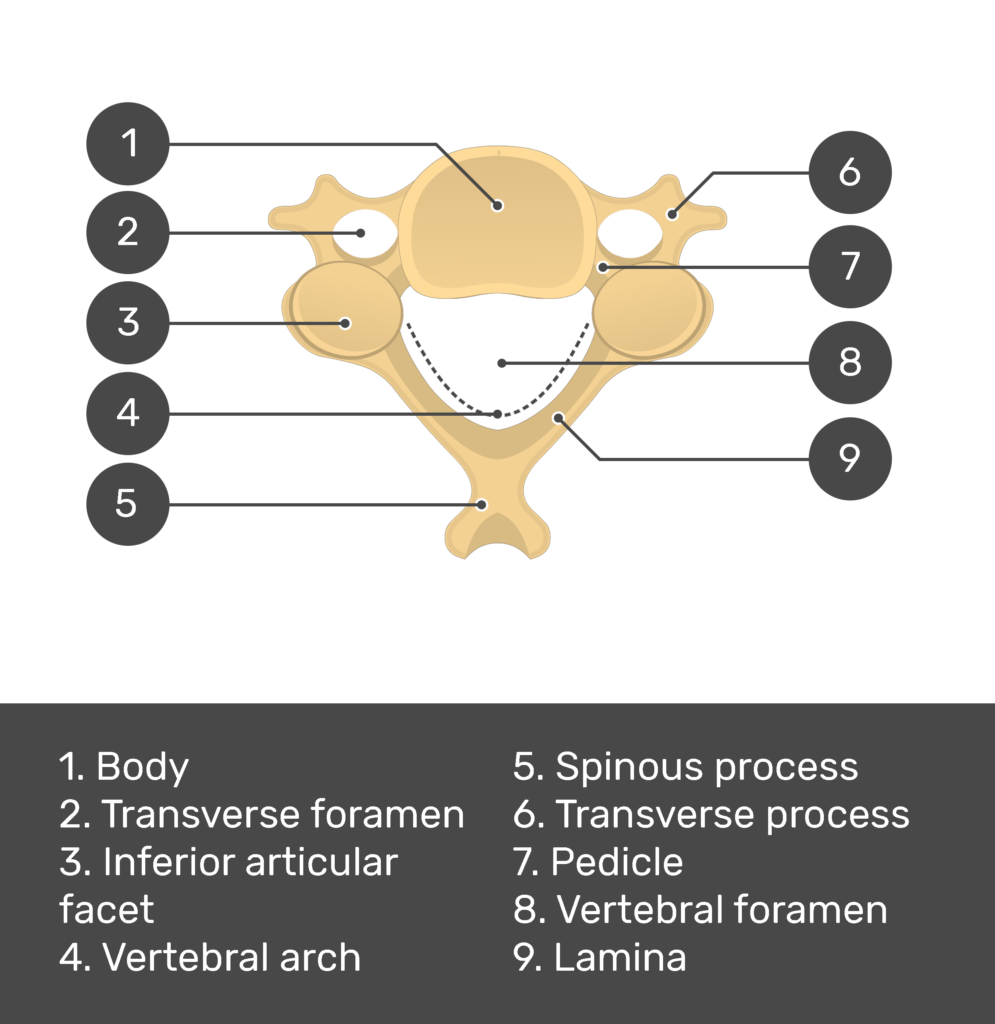
Spine
Regions
Cervical
Vertebrae
7 total
C3-C7 considered typical
Distinguishing features: Foramina in transverse processes in which vertebral arteries go through and bifid spinous process
Atlas(C1)
Nodding head yes
Axis(C2)
Dens process
Shaking head no
Craniocervical ligaments (C1 and C2)
Alar ligament: secondary stabilization for transverse ligament
Apical Ligament
Transverse ligaments: Supports posterior dens and prevents anterior translation of of atlas on axis
Cruciate ligament:
Superior longitudinal band
Transverse lig
Inferior longitudinal band
Nerves
8 nerves
Joints
Facet
45 degrees
antlantooccipital
Atlantoaxial
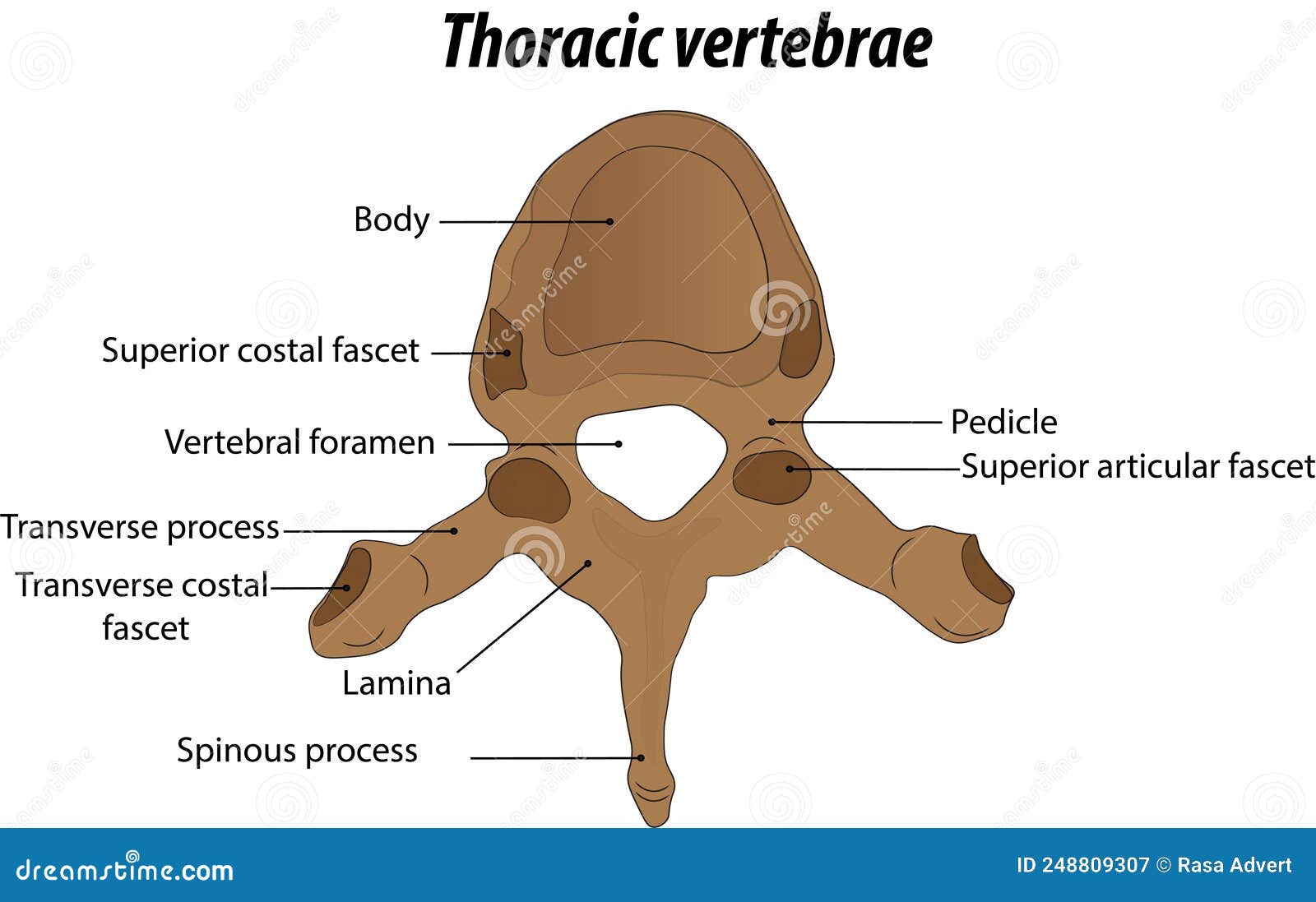
Thoracic
Vertebrae
12 total
Unique
Demifacets on transverse process: two on each side
Facet orientation
60 degrees
Ligaments running the entire length of vertebral column
Posterior longitudinal ligamnent
Anterior longitudinal ligament
Supraspinous ligament
Other ligaments
Superior and inferior costotransverse ligaments
Rib attachment sites
Head of rib
Demifacet of vertebral body
Tubercle of rib
Demifacet of transverse process
Lumbar
Vertebrae
5
Facet orientation
90 degrees
Sacral
Vertebrae
5
Coccygeal
Vertebrae
3-5
Functions
Weight bearing
Protection of CNS and Viscera
Force attenuation
Allows and guides movement
Sites for muscular attachment
Provides upright posture
Muscles
Extrinsic
Extrinsic superficial
Trapezius
Lats
Rhomboid major
Rhomboid minor
levator scapulae
Intermediate extrinsic
Serratus posterior superior
Serratus posterior inferior
Function for both: Respiration and proprioception
Intrinsic
Superficial
Splenius capitus
Splenius cervicus
attach to transverse process
Erector spinae
Iliocostalis
Longissimus
Spinalis
Transversospinalis
Semispinalis
Multifidus
Rotatores
Deep segmental
Interspinalis
Levator costarum
Intertransversarii

Circle of willis

3 branches of trigeminal nerve supplies
Floating topic

Floating topic
Floating topic

Regions of the spine
Cervical Spine
Thoracic vertebrae