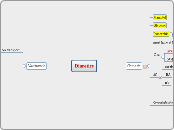
Diuretics
Osmotic
Mannitol
Glycerol
Isosorbide
greatest effect on the eye
used mostly prior to ocular surgery
must have at least SOME urine production
Uses:
pre-surgery, can reduce intracranial and intraocular pressure
prophylaxis for acute renal failure
AE:
cerebral edema
HA
n/v
Contraindications:
Anuria
Peripheral edema
Heart failure
Dehydration
Natriuretic
(loop) high-ceiling diuretics
drug of choice
furosemide
AE:
hypokalemia
ototoxicity
hyperaldosteronism
hyperglycemia
hypertriglyceridemia
GI disturbances
worsens gout
if diabetic pt...
bumetanide
potency differs from furosemide
ethacrynic acid
no sulfonamide group!
torsemide
2x bioavailability as furosemide
longer t1/2 permits qd dosing
direct inhibition of Na transport
thiazides
cholorthizide & hydrocholrothiazide
ineffective when GFR < 30ml/min (low renal fxn)
chlorthalidolone
AE
hyperglycemia
increased serum lipoproteins, TG, LDL
hypersensitivity reactions
drug interactions
K-sparing diuretics
site 2 diuretics
Li
glucocorticoids
hypokalemia increases digitalis toxicity!!!
if pt has high cholesterol or diabetes...
metolazone & indapamide
better AE profile
exception to thiazide rule!: effective in renal failure when combined with a loop diuretic
don't alter lipids
don't cause hyperglycemia
K-sparing
disruption of electrical gradients
amiloride
unmetabolized (excreted uncharged by the kidney!)
triamterene
shorter t1/2
some hepatic metabolism
competition with aldosterone
spironolactone
AE:
hyperkalemia
elevated aldosterone level (in those w/ HF)
anti-androgenic effects/hypoandrogenism
gynecomastia
impotence
menstrual irregularities
contraindications
pts w/ diabetes
pts w/ impaired renal function
if pt. hypertensive or post-MI
epleronone
AE:
hyperkalemia
carbonic anhydrase inhib
acetazolamide
AE:
metabolic acidosis
hypokalemia
drugs which alter renal hemodynamics
dopamine
caffeine