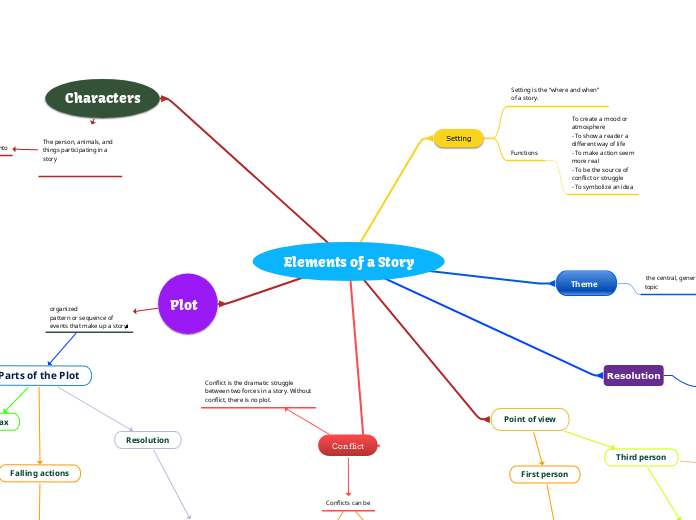
Elements of a Story
Setting
Functions
To create a mood or
atmosphere
- To show a reader a
different way of life
- To make action seem
more real
- To be the source of
conflict or struggle
- To symbolize an idea
Theme
the central, general message, the main idea, the controlling
topic
Resolution
The conclusion; all loose
ends are tied up.
Point of view
First person
Third person
outside narrator is telling the story;
uses the pronouns “he”, “she”, “they”
Types
Third-Person Limited
The narrator knows the
thoughts and feelings
on only ONE character
in a story.
Third-Person Omniscient
The narrator knows the
thoughts and feeling of
ALL the characters in a
story.
Characters
divides into
Protagonist
Antagonist
this person may not be “bad” or
“evil”, but he/she opposes the protagonist in a
significant way
Plot
Parts of the Plot
Exposition
introduction; characters, setting and
conflict are introduced
Rising actions
events that occur as result of
central conflict
Climax
highest point of interest or suspense of a
story
Falling actions
tension eases; events show the
results of how the main character begins to resolve
the conflict
Resolution
loose ends are tied up; the conflict is
solved
Conflict
Conflict is the dramatic struggle
between two forces in a story. Without
conflict, there is no plot.
Conflicts can be
External
outside force may be
person, group, animal, nature, or a
nonhuman obstacle
Internal
takes place in a
character’s mind