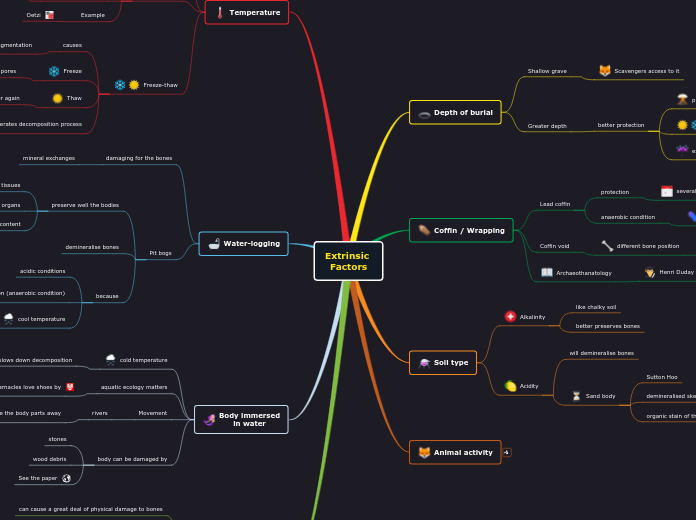
Extrinsic
Factors
Depth of burial
Shallow grave
Scavengers access to it
Greater depth
better protection
physical disturbances
extremes in temperature
extent rainwater
Coffin / Wrapping
Lead coffin
protection
several hundred years
anaerobic condition
inhibit bacterial action
Coffin void
different bone position
indication of burial practice
Archaeothanatology
Henri Duday
Université de Bordeaux
Soil type
Alkalinity
like chalky soil
better preserves bones
Acidity
will demineralise bones
Sand body
Sutton Hoo
demineralised skeletton
organic stain of the body
outlined print
Animal activity
Temperature
Warmth
accelerates
decomposition
particularly if humid
Example
Tsunami
Very cold
preserves bodies well
inhibit microbes
decomposing soft tissues
Example
Oetzi
Freeze-thaw
causes
bone fragmentation
Freeze
water extends within pores
Thaw
ice melt into water again
Accelerates decomposition process
Water-logging
damaging for the bones
mineral exchanges
Pit bogs
preserve well the bodies
soft tissues
internal organs
stomach content
demineralise bones
because
acidic conditions
no oxygen (anaerobic condition)
cool temperature
Body immersed
in water
cold temperature
slows down decomposition
aquatic ecology matters
barnacles love shoes by
Dr Paola Magni
Movement
rivers
move the body parts away
body can be damaged by
stones
wood debris
See the paper
Plant activity
can cause a great deal of physical damage to bones
Roots cause
etch
stain
Fungi
can penetrate the bone
causing
damage
stains