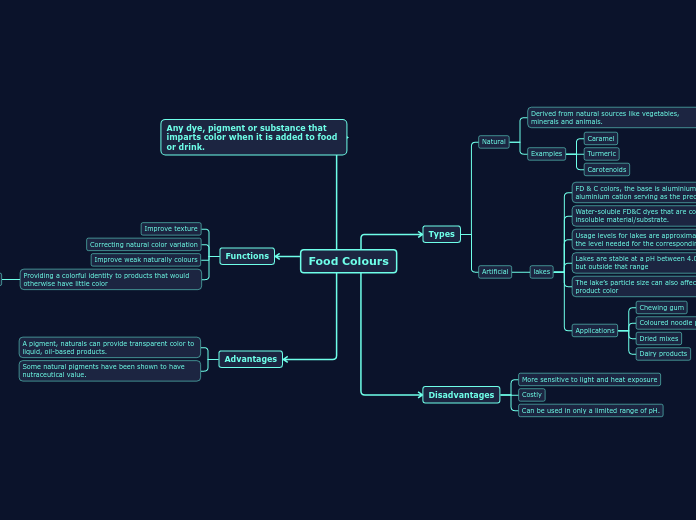
Food Colours
Types
Natural
Derived from natural sources like vegetables, minerals and animals.
Examples
Caramel
Turmeric
Carotenoids
Artificial
lakes
FD & C colors, the base is aluminium hydroxide, with aluminium cation serving as the precipitant
Water-soluble FD&C dyes that are combined with an insoluble material/substrate.
Usage levels for lakes are approximately ten times the level needed for the corresponding FD&C dye.
Lakes are stable at a pH between 4.0 to 8.0,
but outside that range
The lake’s particle size can also affect the finished product color
Applications
Chewing gum
Coloured noodle product
Dried mixes
Dairy products
Disadvantages
More sensitive to light and heat exposure
Costly
Can be used in only a limited range of pH.
Any dye, pigment or substance that imparts color when it is added to food or drink.
Functions
Improve texture
Correcting natural color variation
Improve weak naturally colours
Providing a colorful identity to products that would otherwise have little color
Eg. Gelatin
Advantages
A pigment, naturals can provide transparent color to liquid, oil-based products.
Some natural pigments have been shown to have nutraceutical value.