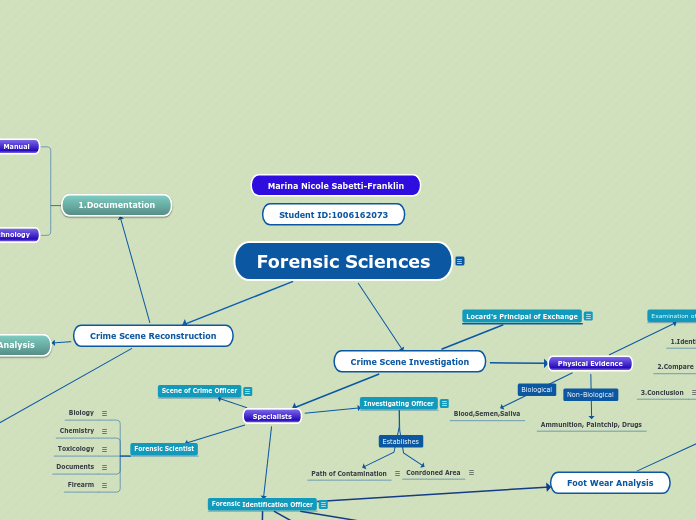
Forensic Sciences
Crime Scene Investigation
Physical Evidence
Ammunition, Paintchip, Drugs
Blood,Semen,Saliva
Examination of Evidence
1.Identify
2.Compare
3.Conclusion
Locard's Principal of Exchange
Specialists
Investigating Officer
Path of Contamination
Conrdoned Area
Scene of Crime Officer
Forensic Identification Officer
Forensic Scientist
Biology
Chemistry
Toxicology
Documents
Firearm
Foot Wear Analysis
Impression
2D
Locations
Route to Scene
Points/attempted points of Entry
Disturbed areas
Point of Exit
Mud, Blood, Paint
Dust Foot Print, Finger Print
Finding
1.Examine Floor
2.Darken Room
3.Use Oblique Lighting
4. Mark Location
Photography
Use Tape
Recovery
Fingerprint Powder and Lifting Tape
Electrostatic Lifter and Mylar Film
Gelatin Lifter
3D
Locations
Snow
Slush
Mud
Dirt
Sand
Photography
1.Set up Tripod
2.Place Scale
3.Use Oblique Lighting
4.Apply Contrast
Casting
Sulphur
Dental Stone
Identification
Footwear #
Officer's Initials/Badge
Date of Cast
Occurrence # /adress
Blood Stain Pattern Analysis
Classification
Exceptions
Dilution
Insect Interferance
Drying Over Time
Decomposition Over Time
Blood Clotting
Voids
Types
Passive
Drip Stain
Drip Trail
Drip Pattern
Splash Pattern
Pool Pattern
Flow Pattern
Saturation Pattern
Transfer
Simple Contact
Swipe
Wipe
Spatter
Projected
Cast-Off
Sessation Cast-Off
Expirated
Patterning due to Fire Arms
Impact Pattern
Blood
Composition
Plasma
Erythrocytes
Buffy Coat
Properties
Surface Tension
Viscosity
4x more than blood
Visualization/Enhancment
Chemicals
Hungarian Red
Amido Black
Leuco Crystal Violet
Simple Transfer
Alginate Lift
Point of Origin
Locating
1.Look for Directionality
2.Look for Area of Convergence
3.Calculate Angle of Impact
Visualization Meathods
String Meathod
Computer Modeling
Shooting Scene Examination
Fingerprint Analysis
Fingerprint
Identification
Impression Mark
Fingerprint Composition
Four Premises of Friction Ridges
1.Develop prior to birth
2.Never change unless scarring, disease, or death
3.Unique to every person
4.Vary within limits, allowing for classification
Anatomy of Friction Ridges
Also known as 'Volar'
Found on all primates
Allows for traction
Characterisitics
No sebaceous glands
More sweat glands per sq in
No hair
Minimal pigmentation
Many nerve endings
Structure
Made up of ridge units
Each unit has a sweat gland and pore
Units fuse together during fetal growth
Layers
Dermis
Epidermis
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Lucidum
Stratum Granulosum
Stratum Spinosum
Stratum Basal
Dermal Papillae
Identification
ACE-V
Analysis
Comparison
Evaluation
Verification
Conclusion
Exclusion
Inconclusive
Level Of Detail
Level 1 (Overall Flow)
Orientation
Pattern Types
Arch
Loop
Whorl
Focal Points
Core
Delta
Level 2 (Minutiae)
Ridge Unit
Short Ridge
Ridge Ending
Bifurcation
Enclosure
Level 3
Pores
End Shapes+Angles
Edge Shapes
Width
Examination
Matrix
Eccrine Sweat
Sebaceous Sweat
Foreign Materials
Substrate
Porous
Chemical
1,2 Indandione
1,8 Diazafluren-9-One
Ninhydrin
Powders
Grey
Fluorescent Magnetic
Nano Flourescent
Non-Porous
Cyanoacrtlate (Glue Fuming)
Basic Yellow
Blue Light
Rhodamine 6G
Trace Laser
Adrox
UV Light
Semiporous
Tape
Sticky Side Powder
Tape Glo
Further Visualization Methods
Vacum Metal Deposition Chamber
Gel Scan
Photo Editing
Infrared Photography
Recover Lift
Crime Scene Reconstruction
1.Documentation
Manual
Tape Measures
Strings
Sketches
3D Technology
3D Microscope
Structured Light Scanner
Laser Scanner
Time of Flight Meathod
Phase Shift Meathod
Drones
Video/Photogrammetry
3.Visualization
2D Plan Drawings
3D Rendering
Virtual Tours
Interactive 3D Models
3D Print
Virtual Reality
2Analysis
Blood Stain
Laser Scanner and Area of Origin Analysis
Shooting Scene
Laser Scanner and Bullet Trajectories
Suspect Height
Laser Scanner and CCTV Camera Technology
Cast-Off Stains
Motion Capture Suit and Laser Scanner
Forensic Facial Approximation
Facial Land Marks
Skin
Super glabell
Glabella
Nasion
Nasale
Nasospinale
(etc...)
Eyes
Medial Canthal Tendon
Superior Torssal Plate
Maylar/Witnall's Tubricle
Anterior-posterior Placement
Lips
Labial Commissar
Vermillion Boarder
Transitional Zone
Kelly and Kelly
Nose
Pro nasally
Nasal aperature
Anterior nasal spine
Width
Methods
Combination/Manchester
American
Digital
Target Audience
Casual
May know individual in passing
Primed
Seeking missing person ex.family
Identification
Positive Comparison
DNA
Radiological
Orthidontal
Fingerprint
Possible Comparison
1.Create a likness of individual
2.Present Likeness to Public
3.Generate new Leads
4.Establish Positive ID
Inconclusive Data
Hair Colour
Eye Colour
Hair Style
Skin Blemishes