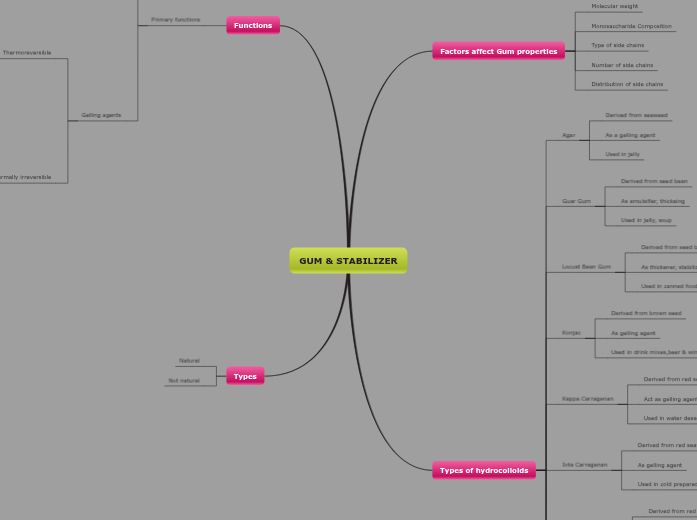
GUM & STABILIZER
Functions
Primary functions
Thickening agent
Xanthan Gum
Carboxymethylcellulose
Methyl Cellulose & hydroxypropyl cellulose
Galactomannans
Gelling agents
Thermoreversible
Gelatin
Agar
Kappa Carragenan
Iota Carragenan
Low Methoxyl Pectin
Gellan Gum
HPMC
Xathan gum and locus gum or konjac
Thermally irreversible
Alginate
HM pectin
Konjac mannan
Locust bean gum
Factors affect Gum properties
Molecular weight
Monosaccharide Composition
Type of side chains
Number of side chains
Distribution of side chains
Types of hydrocolloids
Agar
Derived from seaweed
As a gelling agent
Used in jelly
Guar Gum
Derived from seed bean
As emulsifier, thickeing
Used in jelly, soup
Locust Bean Gum
Derived from seed bean
As thickener, stabilizer
Used in canned food, soup & sauces
Konjac
Derived from brown seed
As gelling agent
Used in drink mixes,beer & wines
Kappa Carragenan
Derived from red seaweed
Act as gelling agent
Used in water dessert gel, canned & processsed meat
Iota Carragenan
Derived from red seaweed
As gelling agent
Used in cold prepared custard, beverages
Lambda Carragenan
Derived from red seaweed
Act as thickener, do not gel
Used in syrups, fruit drinks
High Methoxyl Pectin
Derived from citrus peel
Act as gelling agents
Used in jam, jelly
Gelatin
Derived from animal's protein
Act as gelling agent,thickener,stabiliser
Used in dairy products, confectionary & baked good
CMC
Derived from Sodium salt
Act as thickener, stabilising agent
Used in soups, cakes
Xanthan Gum
Derived from bacteria
As thickener, suspending agent & stabiliser
Used in sauce & ice cream
Types
Natural
Not natural