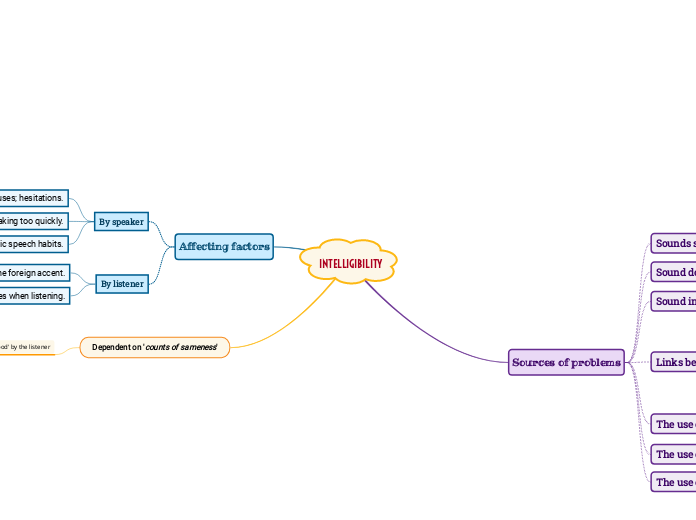
INTELLIGIBILITY
Affecting factors
By speaker
> Lack of confidence about pronunciation; pauses; hesitations.
> Speaking too quickly.
> Idiosyncratic speech habits.
By listener
> Familiarity with the foreign accent.
> Ability to use contextual clues when listening.
Sources of problems
Sounds substitutions
Substituting one sound for another.
'My friend is sick' ≠ 'My friend is thick'. 'sick' and 'think' pronounced as /s/
Sound deletions
Leaving out a sound.
'hold' → final consonant 'd' deleted → sounds like 'hole'
Sound insertions
Adding sounds.
'speak' → short vowel added at the beggining → 'a-speak'
Links between words
Word boundaries are negotiated by
Linking sounds
Inserting /w/ or /j/ to link words: 'go in' → 'go win' 'the aim...' → 'the yame'
A sound mierger
Final consonant merges with the first consonant 'nice shoe' → 'ny shoe'
A composite sound
'this year' → using consonant /ʃ/ between words → 'the shear'
The use of stress
Not stressing one syllable more than another. Stressing the wrong syllable.
'written' → 'retain' 'comfortable' → 'come for a table'
The use of rhythm
There must be an alternation of stressed and unstressed syllables.
The use of intonation
Using pitch variation to send information, like expressing intentions.
No variation in pitch → impression that the speaker is bored or uninterested.
Dependent on 'counts of sameness'
'being understood' by the listener