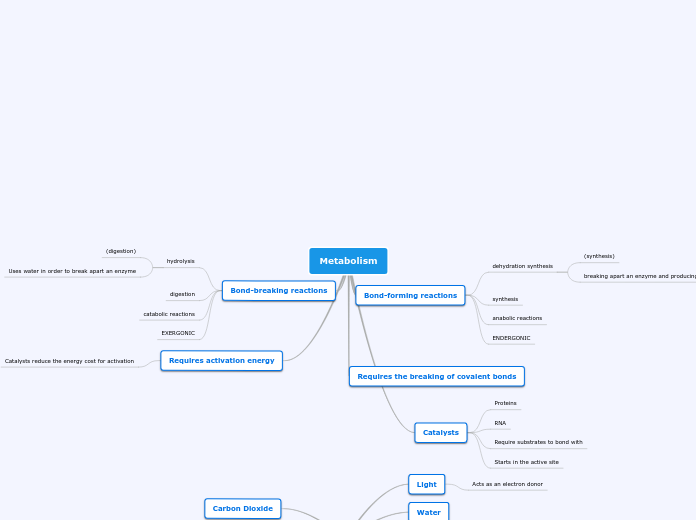
Metabolism
Bond-forming reactions
dehydration synthesis
(synthesis)
breaking apart an enzyme and producing water
synthesis
anabolic reactions
ENDERGONIC
Requires the breaking of covalent bonds
Catalysts
Proteins
RNA
Require substrates to bond with
Starts in the active site
Bond-breaking reactions
hydrolysis
(digestion)
Uses water in order to break apart an enzyme
digestion
catabolic reactions
EXERGONIC
Requires activation energy
Catalysts reduce the energy cost for activation
Photosynthesis
Light
Acts as an electron donor
Water
Light Dependant
Photosystem 2
Photosystem 1
Creates NADPH
Creates ATP synthase enzyme
Carbon Dioxide
Uses oxidation to lose electrons, reduction to gain them
Light Independant
Calvin Cycle
Cellular Respiration
1. Glycolosis
Starts in the Cytosol
Nets 2 ATP
Changes Glucose to Pyruvate
Produces NADH
2. Krebs Cycle
Nets 2 ATP
Uses NADH and FADH2
Electron Transport Chain
Includes Oxidative Phosphorylation
Nets 34 ATP
Uses a Hydrogen Gradient
Plant Structure
Stroma
Grana
Cytosol
Thylakoid
Chlorophyll
ETC
ATP Synthase
H+ Gradient
Chloroplasts
Transform light energy into ATP
Generates O2
Cannot absorb green as well
Passes electron to electron acceptor