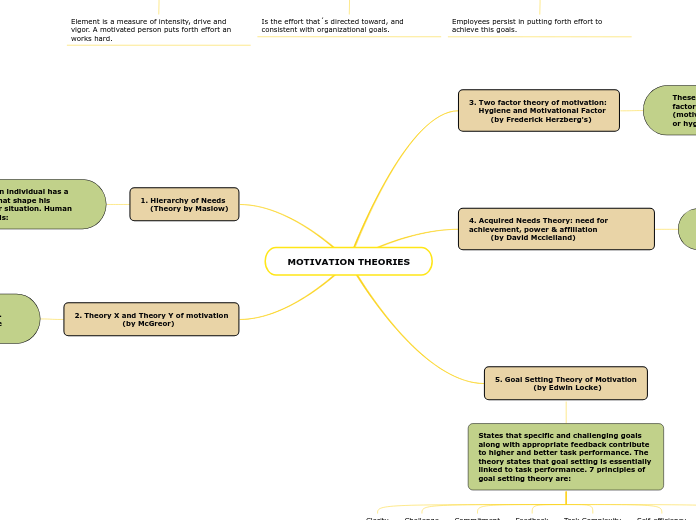
MOTIVATION THEORIES
3. Two factor theory of motivation:
Hygiene and Motivational Factor
(by Frederick Herzberg's)
These theory is based on two types of factors. These factors are satisfiers (motivational) and dissatisfy (maintenance or hygiene)
Motivators
Satisfaction
No Satisfaction
Hygiene Factors
No Dissatisfaction
Dissatisfaction
4. Acquired Needs Theory: need for achievement, power & affiliation
(by David Mcclelland)
These theory studies individuals' needs and classifies them into three motivating drivers need for achievement, power or affiliation.
Need for Achievement (nAch)
Which is the drive to succeed and excel in relation to a set of standards.
Need for Power (nPow)
Which is the need to make others behave in a way that they would no have behaved otherwise.
Need for Affiliation (nAff)
Which is the desire for friendly and close interpersonal relationships.
5. Goal Setting Theory of Motivation
(by Edwin Locke)
States that specific and challenging goals along with appropriate feedback contribute to higher and better task performance. The theory states that goal setting is essentially linked to task performance. 7 principles of goal setting theory are:
Clarity
Challenge
Commitment
Feedback
Task Complexity
Self-efficiency
Goal Commitment
1. Hierarchy of Needs
(Theory by Maslow)
This theory shows that an individual has a hierarchy of five needs that shape his reaction to any particular situation. Human has a hierarchy of 5 needs:
Physiological
Safety Needs
Social
Esteem
Self-actualization
2. Theory X and Theory Y of motivation
(by McGreor)
Douglas McGregor expressed his views of human nature in two sets of assumptions. These two theories represent the extreme ranges of assumptions.
Theory X Stands for the set of traditional beliefs held.
Theory Y Stands for the set of beliefs based on researchers in behavioral science which are concerned with modern social views on the man at work.
MOTIVATION
Refers to the process by which a person's efforts are energized, directed, and sustained toward attaining a goal.
Elements
Energy
Element is a measure of intensity, drive and vigor. A motivated person puts forth effort an works hard.
Direction
Is the effort that´s directed toward, and consistent with organizational goals.
Persistence
Employees persist in putting forth effort to achieve this goals.