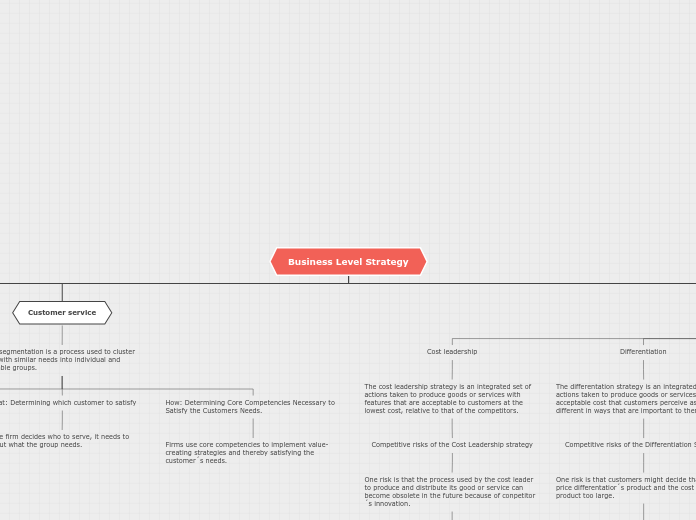
Business Level Strategy
Business strategy
Customer service and the importance it has on business strategies
Effectively managing relationships with custumers
The firm’s relationships with its customers are
strengthened when it delivers superior value to
them.
Reach, Richness and Affilation
Reach, this part is concerned with the firms ability to connect and acces the customer or client. The other dimension that is richness is concerned with the depth and detail of the two way flow of information between the firm and the customer.
Affiliation
Affiliation is the third dimension we see is concerned in facilitating useful interactions with customers.
Richness
The other dimension that is richness is concerned with the depth and detail of the two way flow of information between the firm and the customer.
Customer service
Market segmentation is a process used to cluster people with similar needs into individual and identifiable groups.
Who: Determining the customers to serve
The customers must be divided in groups using market segmentation
What: Determining which customer to satisfy
After the firm decides who to serve, it needs to figure out what the group needs.
How: Determining Core Competencies Necessary to Satisfy the Customers Needs.
Firms use core competencies to implement value-creating strategies and thereby satisfying the customer´s needs.
Business Strategies and the types
Cost leadership
The cost leadership strategy is an integrated set of actions taken to produce goods or services with features that are acceptable to customers at the lowest cost, relative to that of the competitors.
Competitive risks of the Cost Leadership strategy
One risk is that the process used by the cost leader to produce and distribute its good or service can become obsolete in the future because of conpetitor´s innovation.
A second risk is that too much focus by the cost leader on cost reductions may
occur at the expense of trying to understand customers’ perception of competitives levels of differentiation.
The third risk is imitation
Differentiation
The differentation strategy is an integrated set of actions taken to produce goods or services at an acceptable cost that customers perceive as being different in ways that are important to them.
Competitive risks of the Differentiation Strategy
One risk is that customers might decide that the price differentatior´s product and the cost leader´s product too large.
Another risk of the differentiation strategy is that a firm’s means of differentiation may cease to provide value for which customers are willing to pay.
A third risk of differentiation is that experience can narrow customer´s perception value of a product´s differentiated features.
Focused Cost Leadership
The focus strategy is an integrated set of actions taken to produce goods or services that serve the needs of a particular competitive segment.
Focused Differentation
The focus strategy is an integrated set of actions taken to produce goods or services that serve the needs of a particular competitive segment.
Competitive risks of the Differentiation Strategy
The first risk is that a competitors may be able to focus on a more narrowly defined competitive segment and outfocus the focuser.
A second risk is that a company competing on a wide-base industry may decide that the market segment served by the focus strategy firm is attractive and worthy of a competitive persuit.
The third risk is that the needs of the customer within a narrow competitive segment become more similar to those of industry wide customers as a whole.
Integrated cost differentiation/cost leadership
The objective of using this strategy is to efficiently produce products with some differentiated attributes. Efficient production is the source of keeping costs low while some differentiation is the source of unique value.
Competitive risks of the Differentiation/Cost Leadership Strategy
Firms that fail to perform the primary and support activities in an optimum manner become stuck in the middle meaning that the firm´s structure is not low enough to allow it to attractively price its products and that its products are not sufficiently differentiated to create value for the target customer.
Firms can also become stuck in the middle when they fail to successfully implement either the cost leadership or the differentiation strategy.
Purpose of a Business Strategy
The purpose of creating a business strategy is to create differences between the firm´s position and those of its competitors.