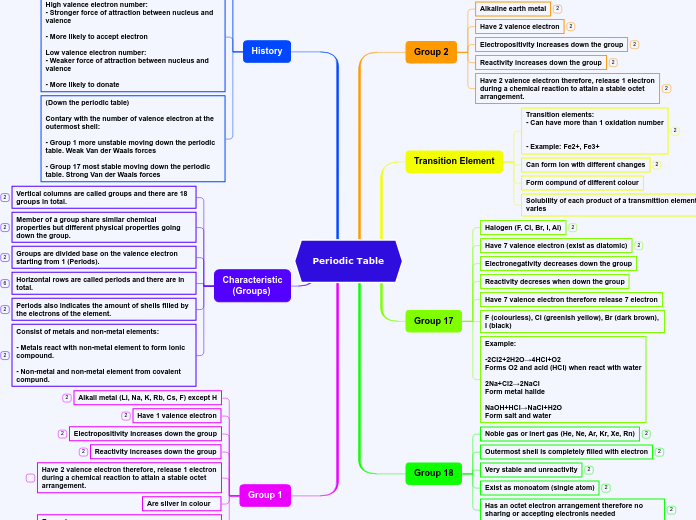
Periodic Table
Group 2
Alkaline earth metal
Have 2 valence electron
Electropositivity increases down the group
Reactivity increases down the group
Have 2 valence electron therefore, release 1 electron during a chemical reaction to attain a stable octet arrangement.
Transition Element
Transition elements:
- Can have more than 1 oxidation number
- Example: Fe2+, Fe3+
Can form ion with different changes
Form compund of different colour
Solubility of each product of a transmittion element varies
Group 17
Halogen (F, Cl, Br, I, Al)
Have 7 valence electron (exist as diatomic)
Electronegativity decreases down the group
Reactivity decreses when down the group
Have 7 valence electron therefore release 7 electron
F (colourless), Cl (greenish yellow), Br (dark brown), I (black)
Example:
-2Cl2+2H2O→4HCl+O2
Forms O2 and acid (HCl) when react with water
2Na+Cl2→2NaCl
Form metal halide
NaOH+HCl→NaCl+H2O
Form salt and water
Group 18
Noble gas or inert gas (He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn)
Outermost shell is completely filled with electron
Very stable and unreactivity
Exist as monoatom (single atom)
Has an octet electron arrangement therefore no sharing or accepting electronis needed
History
Dimtri Mendelev arranged the elements in the order of incresing atomic mass.
The current periodic table is arranged in order of incresing proton number in relation to the electron arrangement.
(Across the periodic table)
High valence electron number:
- Stronger force of attraction between nucleus and valence
- More likely to accept electron
Low valence electron number:
- Weaker force of attraction between nucleus and valence
- More likely to donate
(Down the periodic table)
Contary with the number of valence electron at the outermost shell:
- Group 1 more unstable moving down the periodic table. Weak Van der Waals forces
- Group 17 most stable moving down the periodic table. Strong Van der Waals forces
Characteristic
(Groups)
Vertical columns are called groups and there are 18 groups in total.
Member of a group share similar chemical properties but different physical properties going down the group.
Groups are divided base on the valence electron starting from 1 (Periods).
Horizontal rows are called periods and there are in total.
Periods also indicates the amount of shells filled by the electrons of the element.
Consist of metals and non-metal elements:
- Metals react with non-metal element to form ionic compound.
- Non-metal and non-metal element from covalent compund.
Group 1
Alkali metal (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, F) except H
Have 1 valence electron
Electropositivity increases down the group
Reactivity increases down the group
Have 2 valence electron therefore, release 1 electron during a chemical reaction to attain a stable octet arrangement.
Are silver in colour e
Example:
H20+2Na→2NaOH+H2
From hydrogen and base(NaOH) when react with water
O2+4Na→2Na2O
Form metal oxide when react with O2
2Na+Cl2→2NaCl
Form metal halide when react with halogen