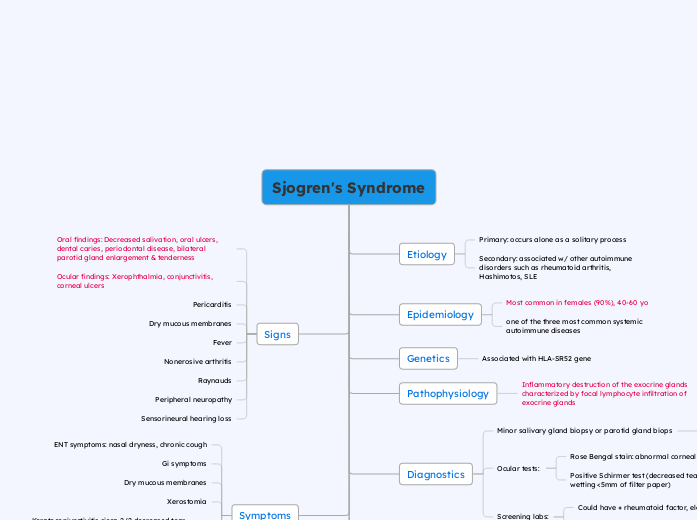
Sjogren's Syndrome
Etiology
Primary: occurs alone as a solitary process
Secondary: associated w/ other autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, Hashimotos, SLE
Epidemiology
Most common in females (90%), 40-60 yo
one of the three most common systemic autoimmune diseases
Genetics
Associated with HLA-SR52 gene
Pathophysiology
Inflammatory destruction of the exocrine glands characterized by focal lymphocyte infiltration of exocrine glands
Aggregation of lymphocytes, primarily CD4+ T-cells and memory cells
Diagnostics
Minor salivary gland biopsy or parotid gland biops
Findings of gland fibrosis & lymphocytic infiltration confirm diagnosis
Ocular tests:
Rose Bengal stain: abnormal corneal epithelium
Positive Schirmer test (decreased tear production - wetting <5mm of filter paper)
Screening labs:
Could have + rheumatoid factor, elevated ESR
ANA: Anti SSA/Ro, Anti SSB/La
Signs
Oral findings: Decreased salivation, oral ulcers, dental caries, periodontal disease, bilateral parotid gland enlargement & tenderness
Ocular findings: Xerophthalmia, conjunctivitis, corneal ulcers
Pericarditis
Dry mucous membranes
Fever
Nonerosive arthritis
Raynauds
Peripheral neuropathy
Sensorineural hearing loss
Symptoms
ENT symptoms: nasal dryness, chronic cough
Gi symptoms
Dry mucous membranes
Xerostomia
Keratoconjunctivitis sicca 2/2 decreased tear production
Dyspareunia 2/2 decr vaginal secretions
Constitutional symptoms:
fatigue, weakness, sleep disturbances, anxiety, depression
generalized pain, arthralgias
Treatment
Artificial tears
Artificial saliva, fluoride
Pilocarpine or Cevimeline (cholinergics aka muscarinic antagonists)
SE: diaphoresis, flushing, bradycardia, diarrhea, N/V, incontinence, blurred vision (2/2 pupil constriction), bronchoconstriction
Cevimeline has less of an effect on cardiac & lung tissue
MOA: increases lacrimation and salivation
Health Promotions
Increased fluid intake
Chew sugar-free gum
Vitamin D supplementation to decrease risk of neuropathy & lymphoma