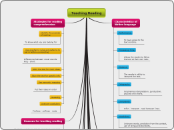
Teaching Reading
Characteristics of
Writen language
Performance
To have acces to the
text anytime.
Processing Time
Allows the reader to follow
the text at their own rate.
Distance
The reader's ability to
interpret the text.
Ortography
Graphemes interpretation, punctuation,
pictures and charts.
Complexity
Infer - interpret - read between lines.
Vocabulary
Unknown words, prediction from the context,
use of bilingual dictionaries.
Formality
Rethorical and organizational patterns.
Types of Classroom Reading Performance
Oral
Good for beginning and intermediate levels
- Pronunciation check
- Students' participation
Silent
Intensive
Linguistic and semantic details of the text.
(Grammatical forms)
Extensive
General understandig: Skimming - Skannig
Reading Levels
Use of authentic texts depending on the students' level
Whether texts are designed for intensive or extensive reading.
Reading Skills
Skanning
Skimming
Reading for detailed comprenhension
Looking for detailed information or
examples of language use.
Button-Up view of reading
Decoding a series of writen symbols - the reader matches the graphemes with the phonemes he/she already knows.
Print - Every letter discriminated - Phonemes and graphemes mathed - Blending - Pronunciation - Meaning
Button-Down view of reading
(Psycholinguistic)
- The reader is the heart of the reading process
- Emphasises the reconstruction of meaning
- Readers' expectations about the text
- Hypoteses formation
A link between knowlegde of linguistic forms adn knowledge about the world.
Often distinguishes between begining and fluent readers.
Strategies for reading
comprenhension
Identify the purpose
of reading
To know what you are looking for
Use graphemic rules and patterns to
aid in botton-up decoding
Differences between vowel sounds
long - short.
Skim the text for main ideas
Skan the text for specific info
Use semantic mapping
Put their ideas in order
Guessing
Analyze vocabulary
Prefixes - suffixes - roots
Reasons for teaching reading
Students want to be able to read texts in English
It is useful for language acqusition
Improves vocabulary and spelling
Encouragement to focus on vocabulary, grammar or punctuation
Kinds of reading
Extensive
- Away from the classroom
- Read for pleasure
Intensive
- Construction of reading texts
- Includes study activities
Details of meaning, uses of grammar
and vocabulary.
Reading Principles
To read as often and as much as possible
To be engaged and to enjoy reading
To respond to the content of a text - To explore feelings about it
To predict from the book cover, title (Clues)
To explore reading texts to the full
Principles for designing reading techniques
Not to forget the importance of specific instructions
Use motivating techniques
Autenticity and readability texts balance
Development of reading strategies
Include bottom-up and top-down techniques
Follow the sequence sQ3R
Survey: Skim the text
Question: Readers'
Read: Read the text to look for the previous questions answers.
Recite: Go through the silent proces of the text - oral and written way.
Review: Incorporate new knowledge to long-term associations.