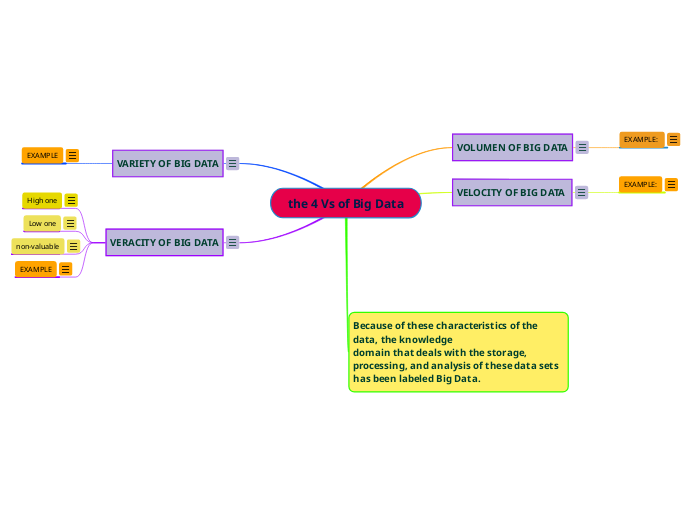
the 4 Vs of Big Data
VOLUMEN OF BIG DATA
EXAMPLE:
VELOCITY OF BIG DATA
EXAMPLE:
Because of these characteristics of the data, the knowledge
domain that deals with the storage, processing, and analysis of these data sets has been labeled Big Data.
VARIETY OF BIG DATA
EXAMPLE
VERACITY OF BIG DATA
High one
Low one
non-valuable
EXAMPLE