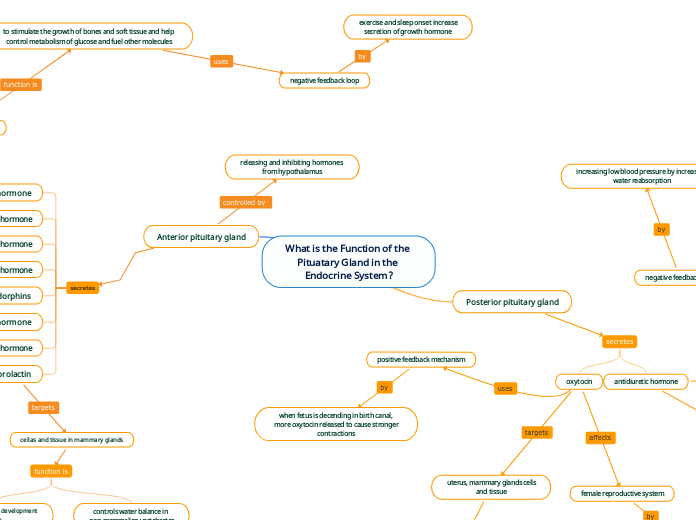
What is the Function of the
Pituatary Gland in the Endocrine System?
Posterior pituitary gland
secretes
oxytocin
uterus, mammary glands cells
and tissue
to promote uterine contractions and
milk release from breasts
positive feedback mechanism
when fetus is decending in birth canal,
more oxytocin released to cause stronger
contractions
female reproductive system
stimulate contractions
at the end of pregnancy
antidiuretic hormone
kidney cells and tissues
to increase blood volume and pressure
by increasing water reabsorption in kidneys
negative feedback loop
increasing low blood pressure by increasing
water reabsorption
excretory system
directly affecting kidneys
Anterior pituitary gland
secretes
growth hormone
bone and soft tissue cells
to stimulate the growth of bones and soft tissue and help control metabolism of glucose and fuel other molecules
negative feedback loop
exercise and sleep onset increase
secretion of growth hormone
thyroid stimulating hormone
thyroid gland cells and tissues
to stimulate the secretion of
thyroid hormones and the growth
of thyroid gland
negative feedback system
stopping secretion as concentration
of thyroid hormone in blood increases
follicle-stimulating hormone
ovaries in females,
testes in males
to stimulate egg growth and development and
secretion of sex hormones in females, in males it
stimulates sperm production
negative feedback loop
in females, hormone secretion
decreases at end of menstrual cycle
being regulated by testosterone
in males
melanocyte-stimulating hormone
melanocytes in skin and
some vertebrae's
to promote darkening of skin
endorphins
pain pathways in nervous
system
to inhibit perception of
pain
negative feedback system
pain stimulates the production of
endorphins
luteinizing hormone
ovaries in females,
testes in males
to regulate ovulation in females
and secretion of sex hormones
in males
reproductive system of female and males
regulation of ovulation controls
menstrual cycle of females
male sex hormones directly impacts puberty, development of secondary sex characteristics, and spermatogenesis
adrenocorticotropic hormone
cells and tissue in the
adrenal cortex
to stimulate secretion of glucocorticoids
by the adrenal cortex
prolactin
cellas and tissue in mammary glands
function is
to stimulate breast development
and milk production
positive feedback system
secreting more prolactin to create more
lactation when infant is suckling
controls water balance in
non-mammalian vertebrates
excretory system
expelling or conserving water in kidneys
when necessary
releasing and inhibiting hormones
from hypothalamus