par Danielle Brown Il y a 2 années
174
Behaviorism, Cognitivism, Constructivism: Comparing Critical Features From an Instructional Design Perspective
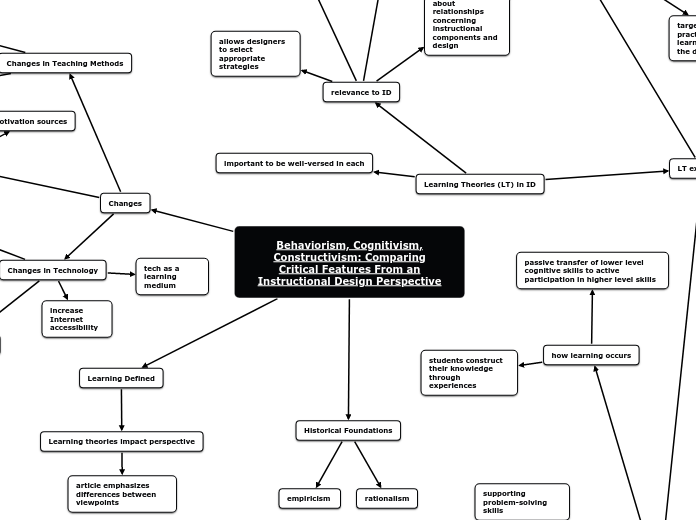
par Danielle Brown Il y a 2 années
174

Plus de détails
authentic and multiple opportunities for practice
instructor helps student to construct their own knowledge
assessment focused on transfer of skills
supporting problem-solving skills
variance in presentation of content
learner interaction with information
identification of context
best suited for advance knowledge acquistion
how transfer occurs
participation in authentic activities within meaningful contexts
focus on being able to use learning authentically
less concerned with memorization
environment-learner interactions
continual evolution
students construct their knowledge through experiences
passive transfer of lower level cognitive skills to active participation in higher level skills
build upon student prior knowledge and assimulating new and old information
basic assumptions
sequencing information
pre-requisite information
hierarchical analyses
active learning
stress efficient processing strategies
techniques
standardization
simplification
best for reasoning, problem-solving, information-processing
building upon prior knowledge
learner must believe that the knowledge is useful for it to transfer
instructors/designers responsible for assisting learners to relate and organize prior knowledge to new knowledge
utilization of techniques such as analogies, hierarchical relationships, and matrices, and other advanced graphic organizers
the thoughts, beliefs, attitudes, and values of a learner
how learners code, transform, rehearse, store and retrieve information
practice with corrective feedback
environmental conditions influence learning
learners as active participants
discrete changes between states of knowledge
structure of instruction
target simulus plus practice leads to learners manifesting the desired response
shared assumptions
use of cues, shaping and practice to ensure a strong stimulus response association
use of reinforcement
informative feedback
tangible rewards
sequencing of instructional presentation
pre-assessment
producing observable and measurable outcomes in students
results
best for lower level skills
difficult to acquire higher level skills
transfer occurs through
generalization
role of memory
memory not emphasized
factors that influence learning
environmental conditions
the arrangement of stimuli and consequences within the environment
how learning occurs
equates learning with changes in either the form frequency of observable performance
problem-solving
collaboration
"conversation" driving learning