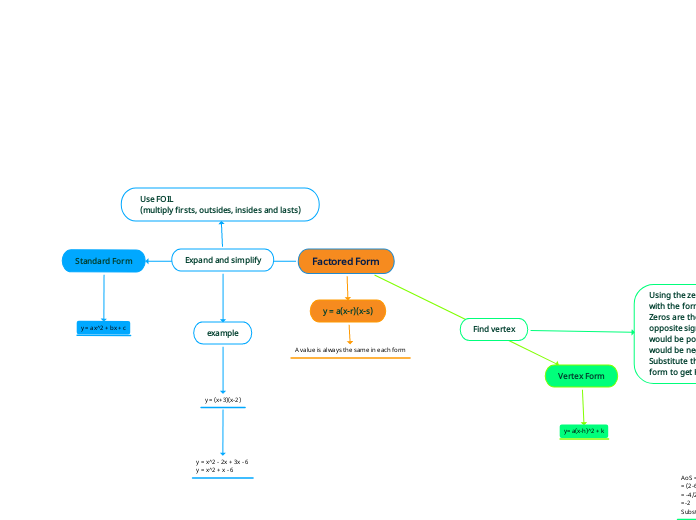
Expand and simplify
example
y = (x+3)(x-2)
y = x^2 - 2x + 3x - 6
y = x^2 + x - 6
Use FOIL
(multiply firsts, outsides, insides and lasts)
Find vertex
Using the zeros, find AoS (x-value of vertex) with the formula: (r+s)/2
Zeros are the value of r and s but the opposite signs (if r was negative, the zero would be positive, if r was positive the zero would be negative. Same applies to value s)
Substitute the AoS (for value x) in factored form to get K (y-value of vertex)
When you have the vertex and are writing the vertex form. The x-value (AoS) will be the opposite sign (if it is -, in the equation it will be +. If it is +, in the equation it will be -). The y-value stays the same. h = x-value of vertex and k = y-value of vertex
Example
y = (x-2)(x+6)
AoS = (r+s)/2
= (2-6)/2
= -4/2
=-2
Substitute -2 into factored form to get K
Y = 1(-2-2)(2+6)
Y = 1(-4)(8)
Y = -16
Vertex: (-2,-16)
y = (x+2)^2 - 16
Factored Form
Vertex Form
y= a(x-h)^2 + k
Standard Form
y = ax^2 + bx + c
y = a(x-r)(x-s)
A value is always the same in each form