HISTOLOGÍA ANIMAL
Global warming is the ongoing rise of the average temperature of the Earth's climate system which has various negative effects.
Tejido Conjuntivo
Overpopulation creates an increased demand for energy as well as having negative effects on our environment and ecosystems.
D. T. SANGUÍNEO
b.- ELEMENTOS FORMES
Plaquetas
Participa en la coagulación sanguínea y cicatrización de las heridas
Glóbulos blancos
Defensa: contra los agentes extraños
Glóbulos rojos
Respiratoria: Transporte de gases
a.- PLASMA
Interviene en la coagulación sanguínea, mediante el fibrinógeno
C.2.- T. Óseo
Que es : Soporte de tejidos blandos.
- Protección de órganos vitales
Concepto : Sus células son los osteocitos, osteoblastos y osteoclastos
C.1.- T. Cartilaginoso
Que es : Sus células son los condrocitos y los condroblastos
Concepto : Es el esqueleto de sostén de los embriones
B.- T. ADIPOSO
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish from a body of water at a rate that the species cannot replenish, resulting in those species becoming underpopulated in that area.
This will lead to a Marine Ecosystem imbalance with time.
Que es: Sus células son los adipocitos y los adipoblastos
Función : Almacén de combustibles ricos en calorías
A.- T. FIBROSO
Water is essential for agricultural production and food security. It is the lifeblood of ecosystems, including forests, lakes, and wetlands.
Overpopulation affects our water and this has negative outcomes.
Que es : La matriz está formada por abundantes fibras de colágeno
Función : Nutrición y mantenimiento de los órganos
Over-cultivation is the practice of excessive farming on a piece of land to the point of degradation of the soil as well as the land itself.
Secretan un material intercelular llamado matriz
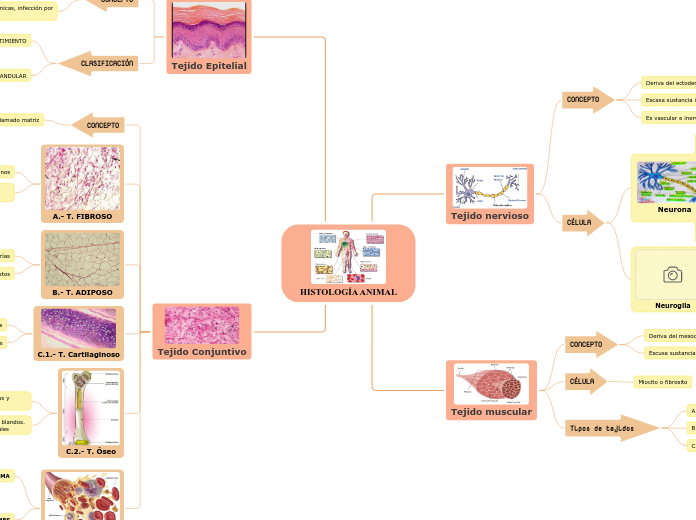
Tejido Epitelial
Climate change is likely to both increase electricity demand for cooling in the summer and decrease electricity, natural gas, heating oil, and wood demand for heating in the winter.
CLASIFICACIÓN
How will climate change affect the production of clean energy?
e.g.: solar, wind, water
B.- EPITELIO GLANDULAR
Endocrina
Glándulas que secretan su producto al torrente sanguíneo
Glándula Exocrina
Glándulas que llevan su producto al exterior (glándulas mamarias, sudoríparas, sebáceos)
A.- DE REVESTIMIENTO
Tapizan, revisten, recubren órganos huecos, cavidades o superficies externas del cuerpo
New infrastructure investments may be necessary to meet increased energy demand.
e.g.: nuclear power plants
Función : Protección: contra lesiones mecánicas, infección por
microorganismos,
Fuerte adhesión entre células.
son avasculares
Tejido muscular
Healthy ecosystems and rich biodiversity are fundamental to life on our planet.
Even small changes in average temperatures can have a significant effect upon ecosystems.
Tipos de tejidos
The inter-connected nature of ecosystems means that the loss of species can have knock-on effects upon a range of ecosystem functions.
e.g. bees go extinct
C. Estriado liso :
B . estirado cardíaco : Rodea el corazón , es involuntario
A . estirado o esquelético :Rodea a los huesos
Climate change will affect mountain and lowland ecosystems, the diversity of wildlife, and the distribution of freshwater.
e.g.: forest fires
Miocito o fibrosito
Climate change is affecting the habitats of several species, which must either adapt or migrate to areas with more favorable conditions.
e.g.: natural habitat disappearing
Escusa sustancia intercelular
Deriva del mesodermo
Tejido nervioso
Climate change is supported by scientific evidence.
CÉLULA
Write down the consequences caused by the melting of the ice-caps and how it will affect our lives and the environment in the future.
e.g.: decreasing of polar bear habitat
Neuroglia
Microglía :tejido nervioso con capacidad fagocitaria y de soporte
Oligodentrocito : envuelve y protege los tejidos nerviosos del cerebro
Astrocito : soporte y nutrición
Neurona
Write down the consequences caused by this issue and how it will affect our lives and the environment in the future.
e.g.: flooding, rainfall increase
transporta , conduce y genera el impulso nerviosos
CONCEPTO
Write down the consequences caused by this issue and how it will affect our lives and the environment in the future.
e.g.: decreasing of land surface
Es vascular e inervado
Escasa sustancia intercelular
Deriva del ectodermo