par LUISJOSE BILBAOGODOY Il y a 4 années
321
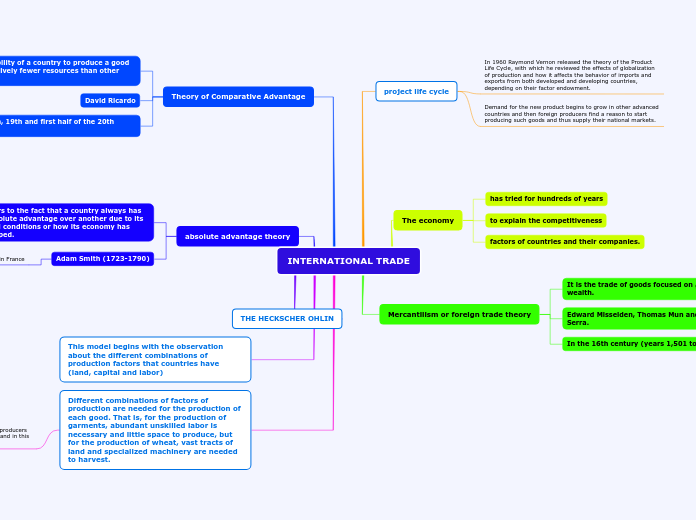
INTERNATIONAL TRADE
par LUISJOSE BILBAOGODOY Il y a 4 années
321

Plus de détails
In linguistics, syntax is the set of rules, principles, and processes that govern the structure of sentences in a given language, usually including word order.
A compound sentence is a sentence that has at least two independent clauses joined by a comma, semicolon or conjunction. An independent clause is a clause that has a subject and verb and forms a complete thought.
Create your own compound sentences, using the coordinators above.
When independent clauses are joined with coordinators (also called coordinating conjunctions), commas and semicolons, they do more than just join the clauses. They add meaning and flow to your writing.
A complex sentence is a sentence that contains an independent clause and one or more dependent clauses.
An independent clause can stand alone as a sentence, but a dependent clause even though it has a subject and a verb cannot stand alone.
The subject clause is a dependent clause that acts as a subject.
A predicative clause may be introduced by conjunctions - that, whether, whether... or, as, as if, as though, because, lest, the way - or connectives.
The latter may be conjunctive pronouns - who, whoever, what, whatever, which - or conjunctive adverbs - where, wherever, when, whenever, how, why.
The object clause is a phrase on which a verb performs an action. It falls at the end of a sentence, and is governed by a verb or a preposition.
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim is the driver.
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim drives the car.
Traditional grammar defines the object in a sentence as the entity that is acted upon by the subject.
The predicate of a sentence is the part that modifies the subject in some way. Because the subject is the person, place, or thing that a sentence is about, the predicate must contain a verb explaining what the subject does and can also include a modifier.
The subject of a sentence is the person, place, thing, or idea that is doing or being something. You can find the subject of a sentence if you can find the verb.
Ask the question, 'Who or what 'verbs' or 'verbed'?' and the answer to that question is the subject.