par Donna C Il y a 12 années
328
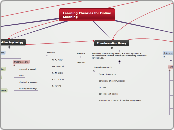
Learning Theories for Online Learning
par Donna C Il y a 12 années
328

Plus de détails
Interactions
Learner-context
Learner-support
Learner-expert
Learner-instructor
Learner-learner
Learner-content
Learner-interface
Meaningful assignments
Reflect & internalize
Learner controls process
Collaborative & cooperative
construct knowledge
Active process
situation encountered during learning process
self-image of learner
process
conditions of communication
frame of reference
existing knowledge
depth of processing
effort
processing capacity
Apply to real situations
Metacognition
Learner adjusts learning strategy
Motivate
Keller's ARCS Model
Satisfaction
Confidence
Relevance
Attention
extrinsic
intrinsic
Modes of presentation
verbal
visual
textual
Cognitive styles
Learning styles
Concrete experience
Use sensation to promote perception and attention
Retirieve existing info & construct memory link
Chunk to prevent overload
Apply, analyze, synthesize, evaluate, & contextualize
Accommodate cognitive styles
Field independent
Field dependent
Accommodate learning styles
Processing
Active experimentation
Abstract conceptualization
Perceiving
Reflective observation
Concrete expereince
Learners should be told explicit outcomes
Learners must be tested
Learning materials must be sequenced
Learners must receive feedback
Subtopic