par mariana macias Il y a 5 années
376
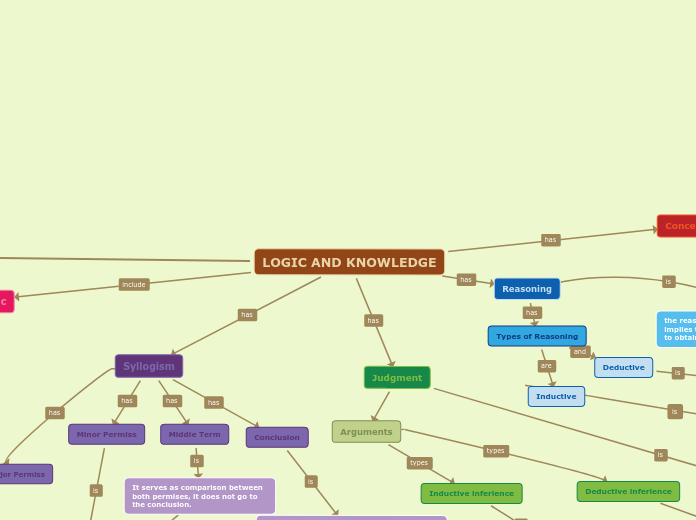
LOGIC AND KNOWLEDGE
par mariana macias Il y a 5 années
376

Plus de détails
It is the complexity of its structure, since it is directly related to our intellectual capacity and the complexity of our thinking.
Thought can be defined as all that mental process that occurs due to intellect and rationality.
Consists of formulation of the law of general conclusion based on the observation
We start from various observations made about the same fact or object, so that the conclusion is a statement that can be generalized to all cases that share the properties observed so far.
Logic principles
It tell us that by having two statements that contradict each other.
Principle of sufficent reason
Principle of excluded middle
To decide that a permiss is tru or false.
Principle of non-contradiction
It is impossible to affirm that a proposition is true and false as the same time and uder the same time circumstances.
Principle of identity
The word and statement of our inferiences must have the same unique meaning.
Leads to unecessary conclusions; part of the facts and absolute security.
Where is the predicate of the conclusion or Major Term (P).
Fallacies
Appeal to force
Use of force -physical or verbal- to impose a vision or opinion.
Appeal to emotions
Seeks to expose an idea that moves the feeling.
Appeal to ignorance
When it is intended to offer the ignorance of something as an explanition to evade responsability.
Appeal to authority
When an idea or argument is not analyzed but is taken for garanted as correct or valid.
Petition of principle
In making an argument, one of the permises is again and again established a conclusion.
False generalization
Consists in generalizing from very few observed cases.
Appeal to popularity
When we support our arguments in poplular opinions.
Attack to the person
Any condition of the person who issues an opinion.